Abstract
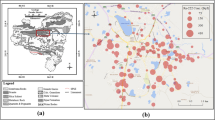
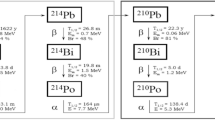
Due to many cancer cases and deaths in a population of 80,000 in Hashimiya, mid-Iraq, a radiologic and hydrogeologic study was carried out. 222Rn, among many pollutants, was encountered in concentrations exceeding the allowable limit of 100 Bq L−1 according to the WHO, during continuous groundwater pumping for > 3 hours from unconfined Quaternary aquifer deposits at many locations. Investigations used 20 wells and the Alpha GUAR PQ2000 PRO, Alpha PUMP and Aqua KIT device for 140 groundwater sample tests, revealing that radon concentrations reached 113 Bq L−1. Geologically, Hashimiya consists of Quaternary deposits of unconsolidated fine-grained sediments of the flood plains of the Euphrates River and are mainly of layers of clay, silt, sand and gypsum. It was found that piezometric and groundwater velocities of ∼ 1 cm day−1 and ∼ 0.3 cm day−1, respectively, are low enough to cause the immediate local creation of 222Rn beneath the rocks and soil and to produce concentrations that increase preceding pumping, rather than 222Rn being carried from a distance. It was found that the annual dosages reached 0.28 mSv year −1 with residence times of 12 day−1. A mathematical model was used to simulate the groundwater scheme and recirculation to remediate 222Rn contamination using the property of radon release during exposure to air. The results indicated that the recirculation process reduced radon concentrations from > 100 Bq L−1 to range of 1.06–1.21 Bq L−1 at the Kids and Sareaa streams. The number of pumping and injection wells needed per annum for conducting the recirculation process for the selected contaminated sector are 216 and 112, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abojassim AA (2013) Radon concentration measurement for drinking water in Kufa City/Iraq using Active Detecting Method. Kufa Unv. Library, V.26
Ahmad N, Jaafar MS, Alsaffar MS (2015) Study of radon concentration and toxic elements in drinking and irrigated water and its implications in Sungai Petani, Kedah, Malaysia. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 8:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.04.003
Ali A, Maria R, Ailreza B, Mario D (2012) Indoor radon measurement and effective dose assessment of 150 apartments in Mashhad, Iran. J Environ Monit Assess 184:1085–1088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2022-x
Althoyaib SS, El-Taher A (2015) Natural radioactivity measurements in groundwater from Al-Jawa, Saudi Arabia. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 304:547–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3874-7
Attiyah KHH, Kadhim IH (2013) Measurement and study of radioactive radon gas concentrations in a selected samples of Hilla River/Iraq. J Nat Sci Res 3:117–124
Beven K, Binley A (1992) The future of distributed models: model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol Process J 6:279–298. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.3360060305
Carrera J, Neuman SP (1986) Estimation of aquifer parameters under transient and steady state conditions: 1. Maximum likelihood method incorporating prior information. J Water Resour Res 22:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR022i002p00199
Daniel MB (2014) 222Rn, 220Rn and other dissolved gases in mineral waters of southeast Brazil. J Environ Radiol 132:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.01.005
Dixon KL (1989) Radon in groundwater supplies. WWJOA9 43:44–49
Drost W, Klotz D, Koch A, Moster H, Neumaier F, Rauert W (1968) Point dilution methods of investigating groundwater flow by means of radioisotopes. J Water Resour Res 4:125–146. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR004i001p00125
Duggal V, Sharma S, Mehra R (2017) Radon levels in drinking water of Fatehabad district of Haryana, India. J Appl Radiat Isot 123:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.02.028
Ellins KK, Roman-Mas A, Lee R (1990) Using 222Rn to examine groundwater\surface discharge interaction in Rio Grand. J Hydro 115:319–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(90)90212-G
European Commission (2001) Official Journal of the European Communities, L 147, 31.5.2001, 1–40
Faraji HH (1990) The use aerial photographs and satellite data in the study of the tectonic for alluvial plain in Iraq of the area lies between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. MSc. Letter, Coll. of Sci., Unv. of Baghdad
Ghose D, Paul D, Sastri RC (2003) Radon as tracer for hilium exploration in geothermal area. J Water Resour Res 36:375–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4487(03)00154-9
Hammood HA, Al-Khalifa IJ (2011) Radon concentration in Dhi-Qar governorate in Iraq. J Basrah Res 37:5
Hohener P, Surbeck H (2004) Radon-222 as a tracer for nonaqueous phase liquid in the vadose zone: experiment and analytical method. Vad Zone J 3:1276–1285. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2004.1276
Jobbágya V, Altzitzogloua T, Malo P, Tanner V, Hult M (2017) A brief overview on radon measurements in drinking water. J Environ Radiol 173:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.09.019
Jubouri HK (2003) Hydrogeological map, of Karbala. Ministry of industry and minerals, Geosurvey, p 32
Kaliprasad CS, Narayana Y (2018) Distribution of natural radionuclides and radon concentration in the riverine environs of Cauvery, South India. J Water Health 16:476–486. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2018.242
Keramati H, Ghorbani R, Amin YA, Khaneghah M, Conti GO, Ferrante M, Ghaderpoori M, Taghavi M, Baninameh Z, Bay A, Golaki M, Moradij B (2018) Radon 222 in drinking water resources of Iran: a systematic review, meta-analysis and probabilistic risk assessment (Monte Carlo simulation). J Food Chem Toxicol 115:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.03.042
Kreyszig E (1972) Advance engineering mathematics, 3rd edn. Wiley, Congress library, USA
Krishan G, Rao MS, Kumar CP, Semwal P (2015) Radon concentration in groundwater of east coast of West Bengal, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:2221–2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1096
Kumar A, Kaur M, Sharma S, Mehra R (2016) A study of radon concentration in drinking water samples of Amritsar city of Punjab (India). Radiat Prot Environ J 39:13–19. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-0464.185155
Kumar A, Narang S, Mehra R (2017) Assessment of radon concentration and heavy metal contamination in groundwater samples from some areas of Fazilka district, Punjab, India. Indoor Built Environ J 26:295–297. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X15591639
Kumar A, Sharma S, Mehra R, Kanwar P, Mishra R, Kaur I (2018) Assessment of radon concentration and heavy metal contamination in groundwater of Udhampur district, Jammu & Kashmir, India. Environ Geochem Health J 40:815–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0027-2
Lee GM, Falcon NL (1952) The geographic history of the Mesopotamian plain. Geogr J 118:24–38
Loomis DP (1987) Radon-222 concentration and aquifer lithology in North Carolina. J Groundw Monit Remeditat 7:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.1987.tb01039.x
McNaboe LA, Robbins GA, Dietz ME (2017) Mobilization of radium and radon by deicing salt contamination of groundwater. J Water Air Soil Pollut 228:94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3227-y
Messier KP, Serre ML (2017) Lung and stomach cancer associations with groundwater radon in North Carolina, USA. Int J Epid 46:676–685. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyw128
Nagataki S, Takamura N (2016) Radioactive doses—predicted and actua—and likely health effects. J Clinic Oncol 28:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2015.12.028
Najah ML (2018) Applicability of Horton model and recharge evaluation in irrigated arid Mesopotamian soils of Hashimiya, Iraq. Arab J Geosci 11:610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3986-4
Parsons RM (1957) Groundwater resources of Iraq. Mesopotamia plain, development board ministry of Iraq, pp 5–21
Prickett TA, Lonngquist CG (1971) Selected digital computer techniques for groundwater resource evaluation. Ill State Water Surv Bull 55:62
Schubert M, Brueggemann L, Knoeller K, Schirmer M (2011) Using radon as environmental tracer for estimating groundwater flow velocity in single well test. J Water Resour Res 47(1–8):W03512. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010WR009572
Sharma S, Duggal V, Kumar A, Mehra R (2017) Assessment of radiation dose from exposure to radon in drinking water from Western Haryana, India. Int J Environ Res 11:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s4174
Shivakumara BC, Chandrashekara MS, KavithaL E, Paramesh L (2014) Studies on 226Ra and 222Rn concentration in drinking water of Mandya region, Karnataka State, India. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2014.08.005
Siddiki AA (1978) Subsurface geology of Southern Iraq. In: 10th Arabic Petroleum Congress, Tripoli, Libya, p 47
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Jacob N, Selvam S, Johnsonbabu G, Anandhan P (2016) Radon levels in groundwater in the Tuticorin district of Tamil Nadu, South India. J Radiol N Chem 307:1165–1173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4312-1
Sissakian V, Ibrahim F, Al-Ali N (2000) Geologic map of Iraq, 3rd edn. Geo-survey, Baghdad, p 13
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1991) Management control plan. National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP)
World Health Organization WHO (2008) World health report
World Health Organization WHO (2009) World health statistics
Yoneda M, Inoue Y, Takine N (1991) Location of groundwater seepage points into a river by measurement of 222Rn concentration in water using activated charcoal passive collectors. J Hydrol 124:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(91)90021-9
Zhang Y, Li H, Xiao K, Xuejing Wang X, Lu X, Zhang M, An A, Qu W, Wan L, Zheng C, Wang X, Jiang X (2017) Improving estimation of submarine groundwater discharge using radium and radon tracers: application in Jiaozhou Bay, China. JGR Oceans 122:8263–8277. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JC013237
Zhuo W, Lida T, Yang X (2001) Occurrence of 222Rn, 226Ra, 228Ra and U in groundwater in Fujian province, China. J Environ Radiol 53:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0265-931X(00)00108-9
Funding
This study was funded by Al Furat Al-Awsat University (Grant number 5213720446462215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al Maimuri, N.M.L. Radon (222Rn) occurrence in quaternary deposits, annual dosage, and groundwater recirculation in Hashimiya, Iraq. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 6, 11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00364-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00364-0