Abstract
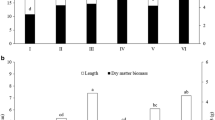
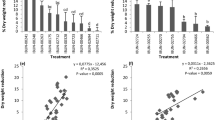
This study selected plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) combined with silicon (Si) able to alleviate biotic and abiotic stresses. The PGPRs were Serratia sp. (BRM 32113, BRM 32114, BRM 63521, BRM 63523, and BRM 63522), Bacillus sp. (BRM 32110 and BRM 32109), Pseudomonas nitroreducens (BRM 32112) and Burkholderia cepacia (BRM 32111). E1 and E2 assays detected indoleacetic acid (IAA) production and ACC deaminase activity. In E3 and E4 assays, PGPRs isolates combined with monosilicic acid (0.5 g L−1) were tested for resistance to osmotic potential induced by PEG-6000 in the concentrations of 79.8 g L−1 (-0.1 MPa); 121.1 g L−1 (-0.2 MPa); 180.2 g L−1 (-0.4 MPa); 264.2 g L−1 (-0.8 MPa); 298.1 g L−1 (-1.0 MPa) and 328.9 g L−1 (-1.2 MPa). In E5, rice seed, treated with BRM 32110, BRM 32111 and BRM 63523 were cultivated in culture medium containing different concentrations of PEG-6000 and Si (0.5 g L−1) in a completely randomized design, with six replications. In E6, BRM 32110, BRM 32111 and BRM 63523 was tested for antagonist efficiency to Magnaporthe oryzae, under osmotic pressure. In E7, rice seeds were sown in plastic trays containing 3 kg of soil fertilized with calcium and magnesium silicate (2 ton ha−1), in a greenhouse. Treatments T1 (control), T2 (Si fertilized soil), T3 (BRM 32111), and T4 (T2 + T3) were submitted to water deficit, followed by challenge spray inoculation with M. oryzae (3 × 105con.mL−1), at 25 days after sowing. The treatments were evaluated for photosynthetic rate (A, μmol CO2 m‒2 s‒1), transpiration rate (E, mmol H2O m‒2 s‒1), stomatal conductance (gs, mol H2O m‒2 s‒1), internal carbon (Ci, μmol mol‒1), and leaf blast severity. BRM 32110, BRM 32111 and BRM 63523 were resistant to osmotic stress (E3 and E4) and were identified as IAA and ACC deaminase producers (E1 and E2). Rice plants treated with BRM 32110, BRM 32111 and BRM 63523 and in the presence of monosilicic acid, showed an increase of 71.34, 110.27 and 126.56% in the total root length and 60.75, 127.60 and 180.82% in the total root surface area, respectively (E5). The rhizobacteria BRM 32110, BRM 32111 and BRM 63523 reduced 78.36, 60.89 and 39.37% of M. oryzae mycelial growth (E6), respectively. In (E7), rice plants treated with BRM 32111 and Si showed higher rates of A, E, gs and Ci with an increase of up to 56.25%, 58.63%, 71.33% and 37.4% under water deficit conditions, in addition to 62.8% of leaf blast suppression. Therefore, we prove that rhizobacteria and silicon, in combination, are efficient to mitigate the water deficit and suppress the severity of leaf blast in the tropical region, thus constituting an alternative to compose sustainable rice management.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahemad M, Kibret M (2013) Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Current perspective. Journal of King Saud University - Science 26:1–20
Alori ET, Dare MO, Babalola OO (2017) Microbial inoculants for soil quality and plant health. In: Sustainable agriculture reviews. Springer, Switzerland, pp 281–307
Arshad M, Shaharoona B, Mahmood T (2008) Inoculation with Pseudomonas spp. containing ACC-desaminase partially eliminates the effects of drought stress on growth, yield, and ripening pea (Pisum sativum L.) Pedosphere 18:611–620
Back ÁJ, Just MC (2018) Consumo de água em lavouras de arroz irrigadas em sistema coletivo. Revista Tecnologia e Ambiente 24:133–145
Bao Y, Aggarwal P, Robbins NE, Sturrock CJ, Thompson MC, Tan HQ, Tham C, Duan L, Rodrigues PL, Vernoux T, Mooney SJ, Bennett MJ, Dinneny JR (2014) Plant roots use a patterning mechanism to position lateral root branches toward available water. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111:9319–9324
Bauer P, Elbaum R, Weiss IM (2011) Calcium and silicon mineralization in land plants: transport, structure and function. Plant Science 180:746–756
Bélanger RR, Bowen PA, Ehret DL, Menzies JG (1995) Soluble silicon - its role in crop and disease management of greenhouse crops. Plant Disease 79:329–336
Berni RF, Prabhu AS (2003) Eficiência relativa de fontes de silício no controle de brusone nas folhas em arroz. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira 38:195–201
Bernier J, Atlin GN, Kumar A, Spaner D (2008) Breeding upland rice for drought resistance. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 88:927–939
Bremer E, Reinhard Krämer R (2019) Responses of Microorganisms to Osmotic Stress. Annual Review of Microbiology 73:313–334
Bhom W (1979) Methods of studyng root systems. Springer-Verlag, New York
Blankenagel S, Yang Z, Avramova V, Schon CC, Grill E (2018) Generating plants with improved water use efficiency. Agronomy 8:194
Bozkurt TO, Schornack S, Banfield MJ, Kamoun S (2012) Oomycetes, effectors, and all that jazz. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 15:483–492
Cai T, Cai W, Zhang J, Zheng H, Tsou AM, Xiao L, Zhong Z, Zhu J (2009) Host legume-exuded antimetabolites optimize the symbiotic rhizosphere. Molecular Microbiology 73:507–517
Calbo MER, Moraes JA (2000) Efeitos da deficiência de água em plantas de Euterpe oleracea (açaí). Revista Brasileira De Botânica 23:225–230
Campos H, Cooper M, Habben JE, Edmeades GO, Schussler JR (2004) Improving drought tolerance in maize: a view from industry. Field Crops Research 90:19–34
Cardoso EJBN, Andreote FD (2016) Microbiologia do solo, 2nd edn. ESALQ, Piracicaba
Chen D, Wang S, Yin L, Deng X (2018) How does silicon mediate plant water uptake and loss under water deficiency? Frontiers in Plant Science 9:281
Chérif M, Menzies JG, Benhamou N, Bélanger RR (1992) Studies of silicon distribution in wounded and Pythium ultimum infected cucumber plants. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 41:371–385
Cooke J, Leishman MR (2016) Consistent alleviation of abiotic stress with silicon addition: a meta-analysis. Functional Ecology 30:1340–1357
Cortês ACAS, Sousa TP, Cortes MVC, Rodrigues FA, Silva GB, Filippi MCC (2015) Enzyme-Induced Defense Response in the Suppression of Rice Leaf Blast (Magnaporthe oryzae) By Silicon Fertilization and Bioagents. International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences 3:22–32
Costa NB, Faria DR, Mendonça SM, de Moraes MG, Coelho GRC, de Filippi MCC, Boshale R, de Castro AP, Lanna AC (2023) Silicon and bioagents pretreatments synergistically improve upland rice performance during water stress. Plant Stress 7:100142
Crusciol CA, Soratto RP, Castro GS, Costa CH, Neto JF (2013) Aplicação foliar de ácido silícico estabilizado na soja, feijão e amendoim. Revista Ciência Agronômica 44:404
Cruz MFA, Rodrigues FA, Polanco LR, Curvêlo CRS, Nascimento KJT, Moreira MA, Barros EG (2013) Inducers of resistence and silicone on the activity of defense enzymes in the soybean-Phakopsora pachyrhizi interation. Bragantia 72:162–172
Cui Y, Tian Z, Zhang X, Abid M, Han H, Jiang D, Cao W, Dai T (2015) Effect of water deficit during vegetative growth periods on post-anthesis photosynthetic capacity and grain yield in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 37:1–10
Datnofft L, Elmer W, Huber D (2007) Mineral nutrition and plant disease. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN
Dennis C, Webster J (1971) Antagonistic properties of species groups of Trichoderma III. Hyphal interactions. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 57:363–369
Debona D, Rodrigues FA, Datnoff LE (2017) Silicon’s role in abiotic and biotic plant stresses. Annual Review Phytopathology 55:85–107
Detmann KC, Araújo WL, Martins SCV, Sanglard LMVP, Reis JV, Detmann E, Rodrigues FA, Nunes-Nesi A, Fernie AR, Damatta FM (2012) Silicon nutrition increases grain yield, which, in turn, exerts a feed-forward stimulation of photosynthetic rates via enhanced mesophyll conductance and alters primary metabolism in rice. New Phytologist 196:752–762
Ehmann A (1977) The van urk – salkowski reagenta sensitive and specific chromogenic reagente for silica gel thin-layer chromatographic detection and identification of indolederivates. Journal of Chromatography 132:267–276
El-Shetehy M, Moradi A, Maceroni M, Reinhardt D, Petri-Fink A, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Mauch F, Schwab F (2020) Silica nanoparticles enhance disease resistance in Arabidopsis plants. Nature Nanotechnology 16:344–353
Enebe MC, Babalola OO (2018) The influence of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in plant tolerance to abiotic stress: a survival strategy. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 102:7821–7835
Etesami H, Jeong BR (2018) Silicon (Si): review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotoxicology Environmental Safety 147:881–896
FAO - Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2016) FAO Rice Market Monitor: FAO. https://www.fao.org/markets-and-trade/commodities/rice/en/. Accessed 08 Jan 2022
Fauteux F, Rémus-Borel W, Menzies JG, Bélanger RR (2015) Silicon and plant disease resistance against pathogenic fungi. Federation European Microbiology Societies 249:1–6
Fawe A, Abou-Zaid M, Menzies J, Bélanger R (1998) Silicon-mediated accumulation of flavonoid phytoalexins in cucumber. Phytopathology 88:396–401
Fernandez J, Orth K (2018) Rise of a cereal killer: the biology of Magnaporthe oryzae biotrophic growth. Trends in Microbiology 26:582–597
Ferreira LM, de Oliveira CM, Arruda LN, Braga RP, Tavares OCH, de Souza SR, Fernandes MS, Santos LA (2020) Characteristics of the root system in two Brazilian upland rice varieties which exhibit contrasting behavior towards drought tolerance. Semina: Ciências Agrárias 41:421–434
Filippi MCC, Silva GB, Silva-Lobo V, Côrtes MVCB, Moraes AJG, Prabhu AS (2011) Leaf blast (Magnaporthe oryzae) suppression and growth promotion by rhizobacteria on aerobic rice in Brazil. Biological Control 58:160–166
Filippi MCC, Silva GB, Prabhu AS (2007) Indução de resistência à brusone em folhas de arroz por isolados avirulentos de Magnaporthe oryzae. Fitopatologia Brasileira 32:387–392
Flexas J, Carriquí M, Nadal M (2018) Gas exchange and hydraulics during drought in crops: who drives whom? Journal of Experimental Botany 69:3791–3795
Fortunato AA, Rodrigues FA, Datnoff LE (2015) Silicon control of soil-borne and seed-borne diseases. Silicon and Plant Diseases. Springer International Publishing Cham pp. 53–66
Ghanmi D, McNally DJ, Benhamou N, Menzies JG, Bélanger RR (2004) Powdery mildew of Arabidopsis thaliana: a pathosystem for exploring the role of silicon in plant–microbe interactions. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 64:189–199
Glick BR (1995) The enhancement of plant growth by free-living bacteria. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 41:109–117
Gomes CF, Marchetti ME, Novelino JO, Mauad M, Alovisi AMT (2011) Disponibilidade de silício para a cultura do arroz, em função de fontes, tempo de incubação e classes de solo. Pesquisa Agropecuária Tropical 41:531–538
Gunes A, Pilbeam DJ, Inal A, Coban S (2008) Influence of silicon on sunflower cultivars under drought stress, in growth, antioxidant mechanisms, and lipid peroxidation. Journal Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 39:1532–2416
Habib A, Javed N, Sahi ST, Waheed M (2012) Detection of seed borne mycoflora of different coarse and fine rice varieties and their management through seed treatments. Pakistan Journal of Phytopathology 24:133–136
Han YK, Wen JH, Peng ZP, Zhang DY, Hou ML (2018) Effects of silicon amendment on the occurrence of rice insect pests and diseases in a field test. Journal of Integrative Agriculture 17:2172–2181
Hawerroth C, Araujo L, Bermúdez-Cardona MB, Silveira PR, Wordell Filho JA, Rodrigues FA (2018) Silicon-mediated maize resistance to macrospora leaf spot. Tropical Plant Pathology 44:192–196
Heinemann AB, Sentelhas PC (2011) Environmental group identification for upland rice production in central Brazil. Science in Agriculture 68:540–547
Heinemann AB, Barrios-Perez C, Ramirez-Villegas J, Arango-Londono D, Bonilla-Findji O, Medeiros JC, Jarvis A (2015) Variation and impact of drought-stress patterns across upland rice target population of environments in Brazil. Journal of Experimental Botany 66:3625–3638
Heinemann AB, Ramirez-Villegas J, Nascente AS, Zeviani WM, Stone LF, Sentelhas PC (2017) Upland rice cultivar responses to row spacing and water stress across multiple environments. Experimental Agriculture 53:609–626
Hernandez-Apaolaza L (2014) Can silicon partially alleviate micronutrient deficiency in plants a review. Planta 240:447–458
Holub EB, Cooper A (2004) Matrix, reinvention in plants: how genetics is unveiling secrets of non-host disease resistance. Trends in Plant Science 9:211–214
Huang XF, Zhou D, Lapsansky ER, Reardon KF, Guo J, Andales MJ, Vivanco JM, Manter DK (2017) Mitsuaria sp. and Burkholderia sp. from Arabidopsis rhizosphere enhance drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana and maize (Zea mays L.). Plant and Soil 419:523–539
Jaleel CA, Manivannan P, Wahid A, Farooq M, Al-Juburi HJ, Sanda S, Yoshida K, Masayoshi K, Kawamura T, Munekage YN, Akashi K, Yokota A (2011) Responses of the photosynthetic electron transport system to excess light energy caused by water deficit in wild watermelon. Physiologia Plantarum 142:247–264
Jha A, Popat T (2021) Burkholderia cepacia BAM-12 isolated from mungbean field in Rajasthan augments plant growth in agricultural field soil of Gujarat, India. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences 11:e3222–e3222
Kavamura VN, Santos SN, Silva JL, Parma MM, Avila LA (2013) Screening of Brazilian cacti rhizobacetria for plant growth promotion under drought. Microbiological Research 168:183–191
Kikuta M, Yamamoto Y, Pasolon YB, Rembon FS, Miyazaki A, Makihara D (2016) How growth and yield of upland rice vary with topographic conditions: a case of slash-and-burn rice farming in South Konawe Regency, Southeast Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. Tropical Agriculture and Development 60:162–171
Kim YH, Khan AL, Waqas M, Lee IJ (2017) Silicon regulates antioxidant activities of crop plants under abiotic-induced oxidative stress: a review. Frontiers in Plant Science 8:510
Koevoets I, Venema JH, Elzenga JTM, Testerink C (2016) Roots withstanding their environment: exploiting root system architecture responses to abiotic stress to improve crop tolerance. Frontiers in Plant Science 7:1335
Kumar H, Ahmad S, Zacharia S, Kumar S, Ali A (2017) Impact of different fungicides combination against brown leaf spot (Drechslera oryzae) of rice under the invitro and in vivo. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 6:341–344
Liang Y, Sun W, Zhu Y-G, Christie P (2007) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: a review. Environmental Pollution 147:422–428
Lima DT, Sampaio MV, Albuquerque JB, Pereira HS, Geraldo W (2019) Silicon accumulation and its effect on agricultural traits and anthracnose incidence in lignocellulosic sorghum. Pesq Agropec Trop 49:e54201
Lynch J (1995) Root architecture and plant productivity. Plant Physiology 109:7–13
Lucon CMM, Akamatsu MA, Harakava R (2008) Promoção de crescimento e controle de tombamento de plântulas de pepino por rizobactérias. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira 43:691–697
Luz JMQ, Guimaraes STMR, Korndörfer GH (2006) Produção de alface em solução nutritiva com e sem silício. Horticultura Brasileira 4:295–300
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Zhang C, Freitas H (2016) Inoculation of Brassica oxyrrhina with plant growth promoting bacteria for the improvement of heavy metal phytoremediation under drought conditions. Journal of Hazardous Materials 320:36–44
Ma JF, Yamaji N (2015) A cooperative system of silicon transport in plants. Trends in Plant Science 20:435–442
Ma JF, Tamai K, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Konishi S, Katsuhara M, Ishiguro M, Murata Y, Yano M (2006) A silicon transporter in rice. Nature 440:688–691
Ma JF (2004) Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 50:11–18
Ma JF, Miyake Y, Takahashi E (2001) Silicon as a beneficial element for crop plants. In: Datnoff LE, Snyder GH, Korndörfer GH (eds) Silicon in agriculture. Elsevier Science, New York, NY, USA, pp 17–39
Marulanda A, Porcel R, Barea JM, Azco NR (2009) Drought tolerance and antioxidant activities in lavender plants colonized by native drought-tolerant or drought-sensitive Glomus species. Microbial Ecology 54:543–552
Niinemets Ü, Díaz-Espejo A, Flexas J, Galmés J, Warren CR (2009) Role of mesophyll diffusion conductance in constraining potential photosynthetic productivity in the field. Journal of Experimental Botany 60:2249–2270
Notteghem JL (1981) Cooperative experiment on horizontal resistance to rice blast. In: Blast and upland rice: report and recomendation from the meeting for international collaboration in upland rice improvement. Los Baños, IRRI, pp. 43–51
Nuernberger T, Lipka V (2005) Non-host resistance in plants: new insights into an old phenomenon. Molecular Plant Pathology 6:335–345
Ortiz N, Armada E, Duque E, Roldan A, Azcon R (2015) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and/or bacteria to enhancing plant drought tolerance under natural soil conditions: effectiveness of autochthonous or allochthonous strains. Journal Plant Physiol 174:87–96
Osakabe Y, Osakabe K, Shinozaki K, Tran LSP (2014) Response of plants to water stress. Frontiers in Plant Science 5:86
Prabhu AS, Filippi MCC (2006) Brusone em arroz: controle genético, progresso e perspectivas. Embrapa Arroz e Feijão, Santo Antônio de Goiás
Price AH, Cairns JE, Horton P, Jones HG, Griffiths H (2002) Linking drought-resistance mechanisms to drought avoidance in upland rice using a QTL approach: progress and new opportunities to integrate stomatal and mesophyll responses. Journal of Experimental Botany 53:989–1004
Puthiyottil P, Akkara Y (2021) Pre treatment with Bacillus subtilis mitigates drought induced photo-oxidative damages in okra by modulating antioxidant system and photochemical activity. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants 27:945–957
Ratnayake RMRNK, Daundasekera WAM, Ariyarathne HM, Ganehenege MYU (2016) Some biochemical defense responses enhanced by soluble silicon in bitter gourd-powdery mildew pathosystem Australasian Plant Pathology 45:425–433
Rodrigues FA, Dallagnol LJ, Duarte HSS, Datnoff LE (2015) Silicon control of foliar diseases in monocots and dicots. Silicon and Plant Diseases 17:67–108
Rodrigues FA, Mcnally DJ, Datnoff LE, Jones JB, Labbé C, Benhamou N, Menzies JG, Bélanger RR (2004) Silicon enhances the accumulation of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice: a potential mechanism for blast resistance. Phytopathology 94(2):177–183
Rodrigues FÁ, Benhamou N, Datnoff LE, Jones JB, Bélanger RR (2003) Ultrastructural and cytochemical aspects of silicon-mediated rice blast resistance. Phytopathology 93:535–546
Rosales MA, Ocampo E, Rodriguez-Valentin R, Olvera-Carrillo Y, Acosta-Gallegos J, Covarrubias AA (2012) Physiological analysis of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars uncovers characteristics related to terminal drought resistance. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 56:24–34
Saeidi M, Ardalani S, Jalali-Honarmand S, Ghobadi ME, Abdoli M (2015) Evaluation of drought stress at vegetative growth stage on the grain yield formation and some physiological traits as well as fluorescence parameters of different bread wheat cultivars. Acta Biologica Szegediensis 59:35–44
Samuels A, Glass A, Ehret D, Menzies J (1991) Distribution of silicon in cucumber leaves during infection by powdery mildew fungus (Sphaerotheca fuliginea). Canadian Journal of Botany 69:140–146
Santos RF, Carlesso R (1998) Déficit hídrico e os processos morfológico e fisiológico das plantas. Revista Brasileira De Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental 2:287–294
Shaner G, Finney RF (1977) The effects of nitrogen fertilization on the expression slow-mildewing in Knox wheat. Phytopathology 67:1051–1056
Shi CL, Park HB, Lee JS, Ryu S, Ryu CM (2010) Inhibition of primary roots and stimulation of lateral root development in Arabidopsis thaliana by the rhizobacterium Serratia marcescens 90–166 is through both auxin-dependent and -independent signaling pathways. Molecules and Cells 29:251–258
Shi Y, Zhang Y, Han W, Feng R, Hu Y, Guo J, Goung H (2016) Silicon enhances water stress tolerance by improving root hydraulic conductance in Solanum lycopersicum L. Frontiers in Plant Science 7:196
Silva MA, Jifon JL, Santos CM, Jadoski CJ, Silva JAG (2013) Photosynthetic capacity and water use efficiency in sugarcane genotypes subject to water deficit during early growth phase. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 56:735–748
Sousa TP, Souza ACAD, Cortes MVB, Lanna AC, Pinheiro HA, Filippi MCC, Silva GB (2017) Bioagents and silicon promoting fast early upland rice growth. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 25:1–12
Souza ACA, Filippi MCC, Nascente AS, Prabhu AS, Alves E (2021) Silicon rates and beneficial microorganism on blast suppression and productivity of upland rice. Journal of Plant Science and Phytopathology 5:20–27
Staudinger C, Mehmeti-Tershani V, Gil-Quintana E, Gonzalez EM, Hofhans F, Bachmann G, Wienkoop S (2016) Evidence for a rhizobia-induced drought stress response strategy in Medicago truncatula. Journal Proteome 136:202–213
Stefan M, Munteanua N, Stoleru V, Mihasan M, Hritcu L (2013) Seed inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria enhances photosynthesis and yield of runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Scientia Horticulturae 151:22–29
Stone LF, Libardi PL, Reichardt K (1986) Produtividade do arroz e absorção de nitrogênio afetadas pelo veranico e pela adição de vermiculita ao solo. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, Brasília 21:117–125
Taiz L, Zeig E, Møller IM, Murphy A (2015) Plant physiology and development. Sinauer Associates, Oxford
Tang YW, Bonner J (1947) The enzymatic inactivation of indole-acetic, acid. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 13:11–25
Van Bockhaven J, Spichal L, Novak O, Strnad M, Asano T, Kikuchi S, Hofte M, De Vleesschauwer D (2015) Silicon induces resistance to the brown spot fungus Cochliobolus miyabeanus by preventing the pathogen from hijacking the rice ethylene pathway. New Phytology 206:761–773
Verma KK, Wu KC, Verma CL, Li DM, Malviya MK, Singh RK, Singh P, Chen GL, Song XP, Li YR (2020) Developing mathematical model for diurnal dynamics of photosynthesis in Saccharum officinarum responsive to different irrigation and silicon application. PeerJ 8:e10154
Vivancos C, Labbé JG, Menzies RR, Bélanger (2015) Silicon-mediated resistance of Arabidopsis against powdery mildew involves mechanisms other than the salicylic acid (SA)-dependent defence pathway. Molecular Plant Pathology 16(6):572–582
Zhang C, Wang L, Zhang W, Zhang F (2013) Do lignification and silicification of the cell wall precede silicon deposition in the silica cell of the rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaf epidermis? Plant and Soil 372:137–149
Yamaji N, Mitani N, Ma JF (2008) A transporter regulating silicion distribution in rice shoots. The Plant Cell 20:1381–1389
Wang Y, Wang Y (2018) Phytophthora sojae effectors orchestrate warfare with host immunity. Current Opinion in Microbiology 46:7–13
Wang M, Gao L, Dong S, Sun Y, Shen Q, Guo S (2017) Role of silicon on plant-pathogen interactions. Frontiers Plant Science 8:701
West PC, Gerber JS, Engstrom PM, Mueller ND, Brauman KA, Carlson KM, Cassidy ES, Johnston M, MacDonald GK, Ray DK, Siebert S (2014) Leverage points for improving global food security and the environment. Science 345:325–328
Acknowledgements
We thank the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) for granting the scholarship and to Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (Embrapa) for the financial support to the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Denner Robert Faria, Sillas Martins Mendonça e Maythsulene Inácio de Sousa Oliveira: research, writing-reviewing and editing. Anna Cristina Lanna: methodology and analyses and writing-review. Marta Cristina Corsi de Filippi: Advisor, analyses, writing-review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Faria, D.R., Mendonça, S.M., de Sousa Oliveira, M.I. et al. Rhizobacteria and silicon mitigate multiple stresses in upland rice. Trop. plant pathol. 48, 508–522 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-023-00593-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-023-00593-6