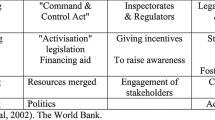
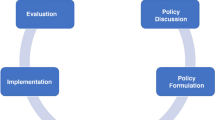
Abstract
In this work, I make seven remarks on two topics viz, (1) Corruption control paradigm and (2) Implementation issues that are closely related with the new corruption control campaign. The arguments are about relationship between corruption and growth, conceptualising corruption, corruption measurements, empirical relationship between corruption and other indicators of governance, continuing corruption control dilemma in developing countries, lack of demand from the powerful for controlling corruption and the need for looking beyond corruption merely as problem. By bringing-out the inadequacies of current corruption control approach both on conceptual and empirical aspects, this study argues in favour of a rethinking by making corruption control efforts comprehensive and beneficial to the developing world.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Organisation for Economic Development and Cooperation.
United Nations Convention Against Corruption.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crimes.
Shows the coverage of all aspects of the variable.
Shows correlation among indicators of the same variable.
Shows correlation with the initially valid indicator.
Shows predictability of the future outcome of a variable.
References
Aghion P, Alesina A, Trebby F (2004) The endogenous political institutions. Q J Econ 119:195–220
Aidt T, Dutta J (2008) Policy compromises: corruption and regulation in a democracy. Econ Politics 20(3):335–60
Alam MS (1995) A theory of limits on corruption and some applications. Kyklos 48(3):419–435
Amundsen I (1997) Political corruption: introduction to the issues. Chr. Michelson Institute, Bergen, Norway
Andvig, Amundsen & Søreide, (2000). Research on corruption. s.l.:Michelsen Institute (CMI) & Norwegian Institute of International Affairs (NUPI).
Angeles L, Neanidis K (2010) Colonialism, elite formation and corruption. University of Glasgow, Glasgow
Arndt C, Oman C (2006) Uses and abuses of governance indicators. OECD Development centre, Paris
Arriola LR (2009) Patronage and political stability in Africa. Comp Polit Stud 42(10):1339–1362
Bedirhanoglu P (2007) The neo-liberal discourse on corruption as a means of consent building: reflections from post-crisis Turkey. World Q 28(7):1239–1254
Bhargava V (2005) The cancer of corruption, s.l.: World Bank
Blackburn K (2006) The incidence and persistence of corruption in economic development. J Econ Dyn Control 30:2247–2267
Brooks, Walsh, D, Lewish C, Kim (2013) Defining corruption. Springer nature.
Brubaker R (1998) Ethnic and nationalist violence. Ann Rev Sociol 24:423–452
Bustikova L, Corduneanu-Huci C (2009) The correlates of clientelism: economic development and historical state capacity. American Political Science Association, Toronto
Chimezie C (2016) The role of good governance and development administration in national development. Int J Dev Manag Rev 11(3):176–186
Donchev D, Ujhelyi G (2007) Do corruption indices measure corruption? Economics Deparment, Harvard University, London
Duncan N (2006) The non-perception based measurement of corruption: a review of issues and methods from a policy perspective. Ashgate Publishing, London
Edgrado B (1995) Judicial reforms in Latin America: the obstacles ahead. Lat Am Aff 3:8–13
Egger P, Winner H (2005) Evidence on corruption as an incentive for foreign direct investment. Eurp J polit Econ 21:932–952
Enste D (2017) Causes and consequences of corruption – an overview of empirical results. Institut der deutschen Wirtschaft Köln, Konrad-Adenauer-Ufer
Francisco & Javier, (2007) Assessing corruption: an analytical review of corruption measurement and its problems-perception, error and utility. Edmund A. Walsh School of Foreign Service, Georgetown University, Georgetown
Gephart M (2009) Contextualizing conceptions of corruption: challenges for the international anti-corruption campaign. German Institute of Global and Area study, Hamburg
Hicken A (2011) Clientalism. Ann Rev Polit Sci 20(2):289–310
Johnston M (2005) Syndromes of corruption: wealth, power, and democracy, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Jong-Sung Y, Khagram s, (2005). A comparative study of inequality and corruption. American Sociological Review, 136–157.
Kaufman D (1999) Aggregating governance indicators. World Bank, Washington
Khan MH (1998) Patron-client networks and the economic effects of corruption in Asia. Eur J Dev Res 10(1):15–39
Khan M (2006) Governance and anti-corruption reforms in developing countries: policies, evidence and ways forward. United Nations Publications, New York
Klitgaard (2004). Leadership under systemic corruption, s.l.: cgu.edu.
Kohli (2009). Power, patronage and clientalism: limits of political governance in India
Kpundeh S (2004) Building state capacity in Africa, 1st edn. World Bank Publications, Washington
Kube I (2017) The importance of social norms in defining corruption. In: Schwickerath AK (ed) How to conceptualize corruption? Interdisciplinary Corruption Research Forum, Paris
Lambsdorff JG (2007) The institutional economics of corruption and reform: theory, evidence and policy. Cambridge University Press, London
Marquette H, Peiffer C (2015) Collective action and systemic corruption. University of Warsaw, Warsaw
Mauro P (1995) Corruption and economic growth. Q J Econ 110:681–712
Meon P, Weil L (2010) Is corruption an efficient grease? World Dev 48:244–259
Miller WL (1998) How citizens cope with post communist officials: evidence from focus group discussions in Ukraine and the Czech Republic. Polit. Stud 45(3):597–625
Naidoo V (2013) The politics of anti-corruption enforcement in South Africa. J Contemp Afr Stud 31(4):523–542
Nicholls C (2011) Corruption and misuse of public office. Oxford University Press, London
Peiffer C, Alvarez L (2014) Who will be the “principald principals”? the determinants of active opposition to corruption. Developmental Leadership Programme, University of Birmingham
Persson A, Rothstein B, Teorell J (2010) The failure of anti-corruption Policies- a throertical mischaracterization of the problem. Department of Political Science, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Persson A, Rothstein B, Teorell J (2013) Why anti-corruption reforms fail?. Systemic corruption as a collective action problem. Governance 26(3):449
Pertiwi K (2017) Contextualizing corruption: a cross-disciplinary approach to studying corruption in organizations. Administrative sciences, pp 1–19
Perumal K (2019) State capacity, drivers of corruption and anti-corruption interventions: contextualizing corruption in Indian context- a rational choice approach. Int J Dev Res 9(11):323–330
Rodriguez-Sanchez JI (2018) Measuring corruption in Mexico. Baker III Institute for Public Policy of Rice University, Mexico
Rohwer A (2009) Measuring corruption: a comparision between the Transparency International’s corruption perception index and World Bank’s global governance index. Ifo Institute for Economic Research, Munich
Rose-Ackerman S, Palifka BJ (2016) Corruption and government: causes, consequences, and reform. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rose-Ankerman, (1997). Corruption and development. International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, New York
Schwickerath A, Düsseldorf, (2017) Conceptualizing corruption in fragile states. In: Schwickerath AK (ed) How to conceptualize corruption? Interdisciplinary Corruption Research Forum, Paris, pp 29–33
Seleim A, Bontis N (2009). The relationship between culture and corruption: a cross-national study. J Intell Cap :165–182
Semenova E (2018) The global encyclopedia of informality, 2nd edn. Freie Universität, Berlin
Shukhova A, Yulil N (2017) Measurement of validity of corruption indices. Higher School of Economics, National Research University, Mannheim
Svensson J (2005) Eight questions about corruption. J Econ Perspect 5(19):19–42
Tanzi V, Davoodi H (1998) Corruption, public investment and growth. In: Ihori T (ed) The welfare state, public investment and growth. Springer, Tokyo, pp 41–60
Transparency International, 2013. Retrieved from https://www.transparency.org/
Trantidis A, Tsagkroni V (2017) Clientalism and corruption: institutional adaptation of state capture strategies in view of resource scarcity in Greece. Br J Polit Int Relat 19(2):263–281
UNDP (2015) User’s guide to measuring corrupn and anti-corruption, 1st edn. United Nations, New York
UNODC (2004) UN anti-corruption toolkit, 3rd edn. Uniter Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, Vienna
Vannucci A (2015) Three paradigms for the analysis of corruption. Labour Laws Issues 1(2):3–31
Walton G, Jones A (2017) The geographies of collective action, principal agent theory and potential corruption in Paupa New Guinea. Development Policy Centre, Crawford School of Public Policy, Australian National University
Weingast BR (2008) Why developing countries resist the rule of law. Department of Political Science, Stanford University, California
Wigwe C (2016) Corruption as economic barrier to development in third world countries. Harcourt J Business Law 2(1):324–336
World Bank, 2019. worldbank.org. [Online] Available at: http://info.worldbank.org/governance/wgi/Home/Reports
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I do not have any conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Perumal, K. Rethinking global anti-corruption campaign. J. Soc. Econ. Dev. 25, 365–379 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40847-023-00237-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40847-023-00237-0