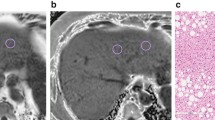
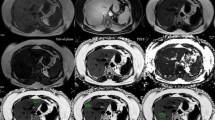
Abstract
Purpose
1H Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is currently considered to be the standard for MR-based fat quantification without the need of histopathologic correlation. The purpose of this prospective study was to examine whether T2*-iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least squares estimation (T2*-IDEAL) technique accurately predicts different hepatic steatosis grades.
Methods
Hepatic fat fraction was quantified by 1H MRS and T2*-IDEAL methods. Geometric homogeneity, intraobserver reliability, and interobserver agreement were examined for T2*-IDEAL method. The relationship between fat fraction measured by T2*I-DEAL (FFIDEAL) and that measured by 1H MRS (FFMRS) was examined by linear regression analysis. Based on 1H MRS, accumulated hepatic steatosis grade including HSF5, HSF15, HSF30, and HSF60, representing hepatic steatosis with fat fraction no less than 5%, 15%, 30%, and 60%, respectively, were calculated. Body mass index and FFIDEAL were used to predict the accumulated hepatic steatosis grade, respectively.
Results
FFMRS and FFIDEAL were 16.36% ± 12.96 and 15.57% ± 11.13, respectively. Linear regression analysis showed that the FFIDEAL was significantly and positively associated with FFMRS (y = 0.8226x + 2.1068, R2 = 0.9181, p < 0.001). The percentage error of FFIDEAL was − 5.2% ± 22.2% for HSF5. FFIDEAL and BMI predicted hepatic steatosis grade HSF5, HSF15, and HSF30 with an AUC of 0.988, 0.967, and 0.996 (all p = 0.0001) for FFIDEAL and 0.742, 0.836, and 0.883 (all p < 0.01) for BMI, respectively.
Conclusion
T2*-IDEAL method accurately predicts the accumulated hepatic steatosis grades with high intraobserver reliability, interobserver agreement, and geometric homogeneity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szczepaniak, L. S., Nurenberg, P., Leonard, D., Browning, J. D., Reingold, J. S., Grundy, S., Hobbs, H. H., & Dobbins, R. L. (2005). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content: Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. American journal of physiology Endocrinology and metabolism, 288(2), E462–E468. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00064.2004.
Cairns, S. R., & Peters, T. J. (1983). Biochemical analysis of hepatic lipid in alcoholic and diabetic and control subjects. Clinical science (London England: 1979), 65(6), 645–652. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs0650645.
Idilman, I. S., Aniktar, H., Idilman, R., Kabacam, G., Savas, B., Elhan, A., Celik, A., Bahar, K., & Karcaaltincaba, M. (2013). Hepatic steatosis: Quantification by proton density fat fraction with MR imaging versus liver biopsy. Radiology, 267(3), 767–775. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13121360.
Chalasani, N., Younossi, Z., Lavine, J. E., Diehl, A. M., Brunt, E. M., Cusi, K., Charlton, M., & Sanyal, A. J. (2012). The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the american Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology (Baltimore Md), 55(6), 2005–2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.25762.
MMustapic, S., Ziga, S., Matic, V., Bokun, T., Radic, B., Lucijanic, M., Marusic, S., Babic, Z., Grgurevic, I. S., Ziga, S., Matic, V., Bokun, T., Radic, B., Lucijanic, M., Marusic, S., Babic, Z., & Grgurevic, I. (2018). Ultrasound grade of liver steatosis is independently associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2018, 8490242. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8490242
Paige, J. S., Bernstein, G. S., Heba, E., Costa, E. A. C., Fereirra, M., Wolfson, T., Gamst, A. C., Valasek, M. A., Lin, G. Y., Han, A., Erdman, J. W., Jr., O’Brien, W. D., Jr., Andre, M. P., Loomba, R., & Sirlin, C. B. (2017). A pilot comparative study of quantitative Ultrasound, Conventional Ultrasound, and MRI for Predicting Histology-Determined steatosis Grade in adult nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. AJR American journal of roentgenology, 208(5), W168–W177. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.16.16726
Hernaez, R., Lazo, M., Bonekamp, S., Kamel, I., Brancati, F. L., Guallar, E., & Clark, J. M. (2011). Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: A meta-analysis. Hepatology (Baltimore Md), 54(3), 1082–1090. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24452.
Alpern, M. B., Lawson, T. L., Foley, W. D., Perlman, S. J., Reif, L. J., Arevalos, E., & Rimm, A. A. (1986). Focal hepatic masses and fatty infiltration detected by enhanced dynamic CT. Radiology, 158(1), 45–49. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.158.1.3940396.
Hamer, O. W., Aguirre, D. A., Casola, G., Lavine, J. E., Woenckhaus, M., & Sirlin, C. B. (2006). Fatty liver: Imaging patterns and pitfalls. Radiographics: a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America Inc, 26(6), 1637–1653. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.266065004.
Boyce, C. J., Pickhardt, P. J., Kim, D. H., Taylor, A. J., Winter, T. C., Bruce, R. J., Lindstrom, M. J., & Hinshaw, J. L. (2010). Hepatic steatosis (fatty liver disease) in asymptomatic adults identified by unenhanced low-dose CT. AJR American journal of roentgenology, 194(3), 623–628. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.09.2590.
Dixon, W. T. (1984). Simple proton spectroscopic imaging. Radiology, 153(1), 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.153.1.6089263.
Fowler, K. J., Saad, N. E., & Linehan, D. (2015). Imaging approach to hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and metastatic colorectal cancer. Surgical oncology clinics of North America, 24(1), 19–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soc.2014.09.002.
Goceri, E., Shah, Z. K., Layman, R., Jiang, X., & Gurcan, M. N. (2016). Quantification of liver fat: A comprehensive review. Computers in biology and medicine, 71, 174–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.02.013.
Bohte, A. E., van Werven, J. R., Bipat, S., & Stoker, J. (2011). The diagnostic accuracy of US, CT, MRI and 1H-MRS for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis compared with liver biopsy: A meta-analysis. European radiology, 21(1), 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1905-5.
Reeder, S. B., Pineda, A. R., Wen, Z., Shimakawa, A., Yu, H., Brittain, J. H., Gold, G. E., Beaulieu, C. H., & Pelc, N. J. (2005). Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL): Application with fast spin-echo imaging. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 54(3), 636–644. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20624.
Liu, C. Y., McKenzie, C. A., Yu, H., Brittain, J. H., & Reeder, S. B. (2007). Fat quantification with IDEAL gradient echo imaging: Correction of bias from T(1) and noise. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 58(2), 354–364. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.21301.
Yu, H., McKenzie, C. A., Shimakawa, A., Vu, A. T., Brau, A. C., Beatty, P. J., Pineda, A. R., Brittain, J. H., & Reeder, S. B. (2007). Multiecho reconstruction for simultaneous water-fat decomposition and T2* estimation. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI, 26(4), 1153–1161. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21090.
Yokoo, T., Serai, S. D., Pirasteh, A., Bashir, M. R., Hamilton, G., Hernando, D., Hu, H. H., Hetterich, H., Kühn, J. P., Kukuk, G. M., Loomba, R., Middleton, M. S., Obuchowski, N. A., Song, J. S., Tang, A., Wu, X., Reeder, S. B., & Sirlin, C. B. (2018). Linearity, Bias, and Precision of hepatic Proton Density Fat Fraction measurements by using MR Imaging: A Meta-analysis. Radiology, 286(2), 486–498. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017170550. & RSNA-QIBA PDFF Biomarker Committee
Haufe, W. M., Wolfson, T., Hooker, C. A., Hooker, J. C., Covarrubias, Y., Schlein, A. N., Hamilton, G., Middleton, M. S., Angeles, J. E., Hernando, D., Reeder, S. B., Schwimmer, J. B., & Sirlin, C. B. (2017). Accuracy of PDFF estimation by magnitude-based and complex-based MRI in children with MR spectroscopy as a reference. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI, 46(6), 1641–1647. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25699.
Kim, H. J., Cho, H. J., Kim, B., You, M. W., Lee, J. H., Huh, J., & Kim, J. K. (2019). Accuracy and precision of proton density fat fraction measurement across field strengths and scan intervals: A phantom and human study. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI, 50(1), 305–314. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26575.
Weiss, K. L., Richards, C. R., Sun, D., & Weiss, J. L. (2009). Subminute fat-water-separated dual-echo automated spine survey iterative scan technique. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology, 30(10), 1840–1846. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1619.
Takasu, M., Tani, C., Sakoda, Y., Ishikawa, M., Tanitame, K., Date, S., Akiyama, Y., Sakai, A., Asaoku, H., Kajima, T., & Awai, K. (2012). Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL) imaging of multiple myeloma: Initial clinical efficiency results. European radiology, 22(5), 1114–1121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2351-8.
Chang, H. C., Juan, C. J., Chiu, H. C., Cheng, C. C., Chiu, S. C., Liu, Y. J., Chung, H. W., & Hsu, H. H. (2014). Effects of gender, age, and body mass index on fat contents and apparent diffusion coefficients in healthy parotid glands: An MRI evaluation. European radiology, 24(9), 2069–2076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3265-z.
Chang, H. C., Juan, C. J., Chiu, H. C., Liu, Y. J., Cheng, C. C., Chiu, S. C., Chen, C. Y., Huang, G. S., & Chung, H. W. (2013). Parotid fat contents in healthy subjects evaluated with iterative decomposition with echo asymmetry and least squares fat-water separation. Radiology, 267(3), 918–923. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12112599.
Su, G. Y., Wang, C. B., Hu, H., Liu, J., Ding, H. Y., Xu, X. Q., & Wu, F. Y. (2019). Effect of laterality, gender, age and body mass index on the fat fraction of salivary glands in healthy volunteers: Assessed using iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation method. Dento maxillo facial radiology, 48(3), 20180263. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20180263.
Campo, C. A., Hernando, D., Schubert, T., Bookwalter, C. A., Pay, A. J. V., & Reeder, S. B. (2017). Standardized Approach for ROI-Based measurements of Proton Density Fat Fraction and R2* in the liver. AJR American journal of roentgenology, 209(3), 592–603. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.17.17812.
Selzner, M., & Clavien, P. A. (2001). Fatty liver in liver transplantation and surgery. Seminars in liver disease, 21(1), 105–113. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-12933.
Lee, S. G. (2015). A complete treatment of adult living donor liver transplantation: A review of surgical technique and current challenges to expand indication of patients. American journal of transplantation: official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, 15(1), 17–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.12907.
Brunt, E. M., Janney, C. G., Di Bisceglie, A. M., Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A., & Bacon, B. R. (1999). Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. The American journal of gastroenterology, 94(9), 2467–2474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01377.x.
Tang, A., Tan, J., Sun, M., Hamilton, G., Bydder, M., Wolfson, T., Gamst, A. C., Middleton, M., Brunt, E. M., Loomba, R., Lavine, J. E., Schwimmer, J. B., & Sirlin, C. B. (2013). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: MR imaging of liver proton density fat fraction to assess hepatic steatosis. Radiology, 267(2), 422–431. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120896.
Linares, I., Hamar, M., Selzner, N., & Selzner, M. (2019). Steatosis in liver transplantation: Current Limitations and future strategies. Transplantation, 103(1), 78–90. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000002466.
Sanyal, A. J., Chalasani, N., Kowdley, K. V., McCullough, A., Diehl, A. M., Bass, N. M., Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A., Lavine, J. E., Tonascia, J., Unalp, A., Van Natta, M., Clark, J., Brunt, E. M., Kleiner, D. E., Hoofnagle, J. H., Robuck, P. R., NASH CRN. (2010). Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The New England Journal of Medicine, 362(18), 1675–1685. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0907929
Wildman-Tobriner, B., Middleton, M. M., Moylan, C. A., Rossi, S., Flores, O., Chang, Z. A., Abdelmalek, M. F., Sirlin, C. B., & Bashir, M. R. (2018). Association between magnetic resonance Imaging-Proton Density Fat Fraction and Liver Histology features in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology, 155(5), 1428–1435e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.018.
Décarie, P. O., Lepanto, L., Billiard, J. S., Olivié, D., Murphy-Lavallée, J., Kauffmann, C., & Tang, A. (2011). Fatty liver deposition and sparing: A pictorial review. Insights into imaging, 2(5), 533–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-011-0112-5.
Ratziu, V., Charlotte, F., Heurtier, A., Gombert, S., Giral, P., Bruckert, E., Grimaldi, A., Capron, F., Poynard, T., & LIDO Study Group. (2005). Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology, 128(7), 1898–1906. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.03.084.
Qayyum, A., Goh, J. S., Kakar, S., Yeh, B. M., Merriman, R. B., & Coakley, F. V. (2005). Accuracy of liver fat quantification at MR imaging: Comparison of out-of-phase gradient-echo and fat-saturated fast spin-echo techniques–initial experience. Radiology, 237(2), 507–511. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2372040539.
Hsu, H. W., Tsang, L. L., Yap, A., Huang, T. L., Chen, T. Y., Lin, T. S., Concejero, A. M., Ou, S. Y., Yu, C. Y., Chen, C. L., & Cheng, Y. F. (2011). Magnetic resonance cholangiography in living donor liver transplantation. Transplantation, 92(1), 94–99. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31821c1e33.
Hu, H. H., Kim, H. W., Nayak, K. S., & Goran, M. I. (2010). Comparison of fat-water MRI and single-voxel MRS in the assessment of hepatic and pancreatic fat fractions in humans. Obesity (Silver Spring Md), 18(4), 841–847. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2009.352.
Chen, C. L., Fan, S. T., Lee, S. G., Makuuchi, M., & Tanaka, K. (2003). Living-donor liver transplantation: 12 years of experience in Asia. Transplantation, 75(3 Suppl), S6–S11. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.TP.0000046533.93621.C7
McCormack, L., Dutkowski, P., El-Badry, A. M., & Clavien, P. A. (2011). Liver transplantation using fatty livers: Always feasible? Journal of hepatology, 54(5), 1055–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.004.
Luca, L., Westbrook, R., & Tsochatzis, E. A. (2015). Metabolic and cardiovascular complications in the liver transplant recipient. Annals of gastroenterology, 28(2), 183–192.
de Baere, T., Roche, A., Elias, D., Lasser, P., Lagrange, C., & Bousson, V. (1996). Preoperative portal vein embolization for extension of hepatectomy indications. Hepatology (Baltimore Md), 24(6), 1386–1391. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.1996.v24.pm0008938166.
Baba, Y., Hayashi, S., Nagasato, K., Higashi, M., Tosuji, N., Sonoda, S., & Yoshiura, T. (2018). Oxidative stress induced by portal vein embolization in fatty liver: Experimental study of a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model. Biomedical reports, 9(4), 357–363. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2018.1141.
Chiang, H. J., Chang, W. P., Chiang, H. W., Lazo, M. Z., Chen, T. Y., Ou, H. Y., Tsang, L. L., Huang, T. L., Chen, C. L., & Cheng, Y. F. (2016). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation Proceedings, 48(4), 1003–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.10.068
Peng, C. J., Yuan, D., Li, B., Wei, Y. G., Yan, L. N., Wen, T. F., Zhao, J. C., Yang, J. Y., Wang, W. T., & Xu, M. Q. (2009). Body mass index evaluating donor hepatic steatosis in living donor liver transplantation. Transplantation Proceedings, 41(9), 3556–3559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.06.235
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Yan-Chang Chen for his assistance in performing MRI experiments.
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design—C-HL and C-JJ; collection and assembly of data—C-HL, H-CC, W-CL, T-PL, and C-HJ; data analysis and interpretation—C-HL, C-JJ, H-CC, and Y-JL; manuscript writing—All authors; final approval of manuscript—All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the institutional review board of Tri-Service General Hospital (TSGHIRB 099-05-265).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CH., Chang, HC., Liu, YJ. et al. Accumulated Hepatic Steatosis Grades Predicted by T2*-IDEAL Fat Fraction. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 43, 706–714 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-023-00819-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-023-00819-7