Abstract
Objective
To describe a platform for 4-channel parallel transmission (pTx) integrated on a 3 T MRI system; to demonstrate utility of the platform with a pTx method to reduce localized radiofrequency (RF) heating during MRI of a test object implanted with an electrically conductive wire; and to compare the pTx results with those from a standard birdcage (BC) head coil.
Methods
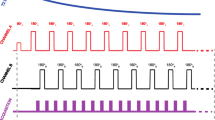
A 4-channel pTx system with independent amplitude and phase control was added to a Siemens Prisma MRI system. Turbo spin echo pTx MRI of a homogenous tissue-mimicking head phantom, including an implanted wire to simulate a deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrode, was performed in (a) circular-polarized “quadrature” transmission mode to demonstrate localized RF heating effects, and (b) an optimized RF shim “suppression” mode to counteract RF heating at the tip of the implanted wire. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and temperature results from the pTx experiment were compared with imaging using a Siemens BC head coil.
Results
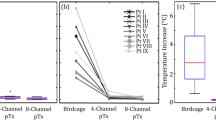
The pTx platform provided effective control of RF amplitude and phase to minimize localized RF heating at the wire tip. No temperature elevation was detected for pTx in suppression mode, whereas maximum increases of 6.9 °C and 2.7 °C were observed for pTx quadrature mode and imaging using the BC head coil, respectively.
Conclusion
The platform has been adapted to a Siemens MRI system without impacting the standard RF transmission pathway, while providing accurate RF signal modulation. Demonstration of the platform showed substantial reduction of localized RF heating in a simulated DBS implant without significant SNR loss.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunheim, S., Gratz, M., Johst, S., Bitz, A., Fiedler, T., Ladd, M., et al. (2018). Fast and accurate multi-channel B1 + mapping based on the TIAMO technique for 7T UHF body MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 79(5), 2652–2664.
Adriany, G., Van de Moortele, P. F., Ritter, J., Moeller, S., Auerbach, E. J., Akgün, C., et al. (2008). A geometrically adjustable 16-channel transmit/receive transmission line array for improved RF efficiency and parallel imaging performance at 7 Tesla. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 59(3), 590–597.
McElcheran, C. E., Yang, B., Anderson, K. J. T., Golenstani-Rad, L., & Graham, S. J. (2015). Investigation of parallel radiofrequency transmission for the reduction of heating in long conductive leads in 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS ONE, 10(8), e0134379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134379.
McElcheran, C. E., Yang, B., Anderson, K. J. T., Golestanirad, L., & Graham, S. J. (2017). Parallel radiofrequency transmission at 3 Tesla to improve safety in bilateral implanted wires in a heterogeneous model. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 78(6), 2406–2415.
Wei, P. S., Yang, B., McElcheran, C. E., Golestanirad, L. & Graham, S. J. (2018). Reducing radiofrequency-induced heating in realistic deep brain stimulation lead trajectories using parallel transmission: Proceedings of the 26 scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 638). Paris.
McElcheran, C., Golestanirad, L., Iacono, M., Yang, B., Anderson, K., Bonmassar, G. & Graham, S. J. (2017). Parallel transmission for heating reduction in realistic deep brain stimulation lead trajectories: Proceedings of the 25 scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 2633). Honolulu.
Nyenhuis, J. A., Kildishev, A. V., Bourland, J. D., Foster, K. S., & Graber, G. (1999). Heating near implanted medical devices by the MRI RF-magnetic field. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 35(5), 4133–4135.
Baker, K. B., Tkach, J. A., Phillips, M. D., & Rezai, A. R. (2006). Variability in RF induced heating of a deep brain stimulation implant across MR systems. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 24, 1236–1242.
Amjad, A., Kamondetdacha, R., Kildishev, A. V., Park, S. M., & Nyenhuis, J. A. (2005). Power deposition inside a phantom for testing of MRI heating. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 41(10), 4185–4187.
Katscher, U., Bornert, P., Leussler, C., & van den Brink, J. (2003). Transmit sense. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 49, 144–150.
Zhang, Z., Yip, C., Grissom, W., Noll, D., Boada, F., & Stenger, V. (2007). Reduction of transmitter B1 inhomogeneity with transmit SENSE slice-select pulses. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 57, 842–847.
Ullmann, P., Junge, S., Wick, M., Seifert, F., Ruhm, W., & Hennig, J. (2005). Experimental analysis of parallel excitation using dedicated coil setups and simultaneous RF transmission on multiple channels. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 54, 994–1001.
Zhu, Y. (2004). Parallel excitation with an array of transmit coils. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 51, 775–784.
Katscher, U., Rӧhrs, J., & Bӧrnert, P. (2005). Basic considerations on the impact of the coil array on the performrance of transmit sense. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, 18, 81–88.
Tse, D. H. Y., Wiggins, C. J., & Poser, B. A. (2017). High-resolution gradient-recalled echo imaging at 9.4T using 16-channel parallel transmit simultaneous multislice spokes excitations with slice-by-slice flip angle homogenization. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 78, 1050–1058.
Setsompop, K., Wald, L. L., Alagappan, V., Gagoski, B., Hebrank, F., Fontius, U., et al. (2006). Parallel RF transmission with eight channels at 3 Tesla. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 56, 1163–1171.
Etezadi-Amoli, M., Stang, P., Kerr, A., Pauly, J., & Scott, G. (2015). Controlling radiofrequency-induced currents in guidewires using parallel transmit. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 74, 1790–1802.
Vaughan, J., Snyder, C., DelaBarre, L., Bolan, P., Tian, J., Bolinger, L., et al. (2009). Whole-body imaging at 7 T: Preliminary results. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 61, 244–248.
Rahbar, H., Partridge, S. C., DeMartini, W. B., Gutierrez, R. L., Parsian, S., & Lehman, C. D. (2012). Improved B1 homogeneity of 3 Tesla breast MRI Using dual-source parallel radiofrequency excitation. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 35(5), 1222–1226.
Ishizaka, K., Kato, F., Terae, S., Mito, S., Oyama-Manabe, N., Kamishima, T., et al. (2015). Bilateral breast MRI by use of dual-source parallel radiofrequency excitation and image-based shimming at 3 Tesla: Improvement in homogeneity on fat-suppression imaging. Radiological Physics and Technology, 8, 4–12.
Kim, H. J., Jeon, B. S., Lee, J. Y., Paek, S. H., & Kim, D. G. (2012). The benefit of subthalamic deep brain stimulation for pain in parkinson disease: A 2-year follow-up study. Neurosurgery, 70, 18–24.
Koller, W. C., Lyons, K. E., Wilkinson, S. B., Troster, A. I., & Pahwa, R. (2001). Long-term safety and efficacy of unilateral deep brain stimulation of the thalamus in essential tremor. Movement Disorders, 16, 464–468.
Tysnes, O. B., & Storstein, A. (2017). Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet Neurology, 124(8), 901–905.
Kazemivalipour E., Keil B., Vali A., Rajan S., Elahi B., et al. (2019). Reconfigurable MRI technology for low-SAR imaging of deep brain stimulation at 3T: Application in bilateral leads, fully-implanted systems, and surgically modified lead trajectories. NeuroImage, 199, 18–29.
Eryaman, Y., Guerin, B., Akgun, C., Herraiz, J. L., Martin, A., Torrado-Carvajal, A., et al. (2014). Parallel transmit pulse design for patients with deep brain stimulation implants. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 73, 1896–1903.
Martin, A., Schiavi, E., Eryaman, Y., Herraiz, J. L., Gagoski, B., Adalsteinsson, E., et al. (2016). Parallel transmission pulse design with explicit control for the specific absorption rate in the presence of radiofrequency errors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 75, 2493–2504.
Yang, B., Tam, F., McElcheran, C., & Graham, S. J. (2017). Another alternate integrated circuit approach to modulation of radiofrequency transmission signals in magnetic resonance imaging. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance Part B, 47B, e21359. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmr.b.21359.
Yang, B. & Graham, S. J. (2018). A low cost prototype pre-gate amplifier to study radiofrequency power amplification for parallel transmission MRI at 3 T: Proceedings of the 26 scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 1694) Paris.
Gudino, N., Duan, Q., de Zwart, J. A., Murphy-Boesch, J., Dodd, S. J., Merkle, H., et al. (2016). Optically controlled switch-mode current-source amplifiers for on-coil implementation in high-field parallel transmission. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 76, 340–349.
Twieg, M., Mehta, B., Coppo, S., Ruff, J., Gumbrecht, R. & Griswold, M. (2017). A 16 channel head-only pTx array using high efficiency in-bore RFPAs at 3T: Proceedings of the 25th scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 1054) Honolulu.
Filci, F., Dogan, A., Cansiz, G., Sen, B., Acikel, V. & Atalar, E. (2017). Prototype hardware of FPGA controlled multi-channel all-digital RF transmitter for parallel magnetic resonance imaging: Proceedings of the 25th scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 4347) Honolulu.
Stang, P., Kerr, A., Pauly, J., & Scott, G. (2008). An extensible transmit array system using vector modulation and measurement: Proceedings of the 16th scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 145) Toronto.
Scott, G., Stang, P., Overall, W., Kerr, A. & Pauly, J. (2006). A vector modulation transmit array system: Proceedings of the 14th scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 128) Miami.
Feng, K., Hollingsworth, N., McDougall, M., & Wright, S. (2012). A 64-channel transmitter for investigating parallel transmit MRI. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 59–8, 2152–2160.
Shooshtary, S., Gratz, M., Ladd, M. & Solbach, K. (2014). High-speed RF modulation system for 32 parallel transmission channels at 7T: Proceedings of the 22nd scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. (p. 544) Milan.
Tam, F., Yang, B. & Graham, S. J. (2018). Software defined radio-based platform for parallel transmit MRI research at high field: Proceedings of the 26th scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. (p. 1690) Paris.
Kurpad, K. N., Boskamp, E. B., & Wright, S. M. (2014). Eight channel transmit array volume coil using in-coil radiofrequency current sources. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery, 4(2), 71–78.
Yang, B., Tam, F., Wei, P. S., McElcheran, C. E. & Graham, S. J. (2018). A prototype four-channel parallel transmission system to investigate MRI safety at 3 T: Proceedings of the 26th scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. (p. 1695) Paris.
Eryaman, Y., Akin, B., & Atalar, E. (2011). Reduction of implant RF heating through modification of transmit coil electric field. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 65, 1305–1313.
Grainger, D. (2014). Safety guidelines for magnetic resonance imaging equipment in clinical use. Resource document. Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Retrieved March 25, 2019, from https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/safety-guidelines-for-magnetic-resonance-imaging-equipment-in-clinical-use.
Delfino, J. G. (2015). U.S. federal safety standards, guidelines and regulations for MRI systems: An overview. Resource document. Appl Radiol. Retrieved March 25, 2019, from https://appliedradiology.com/articles/u-s-federal-safety-standards-guidelines-and-regulations-for-mri-systems-an-overview.
Graesslin, I., Falaggis, K., Vernickel, P., Röschmann, P., Leussler, C., Zhai, Z., Morich, M. & Katscher, U. (2006). Safety considerations concerning SAR during RF amplifier malfunctions in parallel transmission: Proceedings of the 14th scientific meeting, Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med (p. 2041) Seattle.
McElcheran, C. E. (2017). Parallel radiofrequency transmission for the reduction of heating in deep brain stimulation leads at 3T. PhD Thesis Dissertation, University of Toronto.
Funding
Canada Foundation for Innovation (grant number: 30729), Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (Grant Number: 238911).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: Yang, Wei, McElcheran, Tam, Graham. Simulation and Acquisition of data: Yang, Wei, McElcheran. Analysis and interpretation of data: Yang. Manuscript Writing: Yang, Graham.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Wei, PS., McElcheran, C.E. et al. A Platform for 4-Channel Parallel Transmission MRI at 3 T: Demonstration of Reduced Radiofrequency Heating in a Test Object Containing an Implanted Wire. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 39, 835–844 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-019-00478-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-019-00478-7