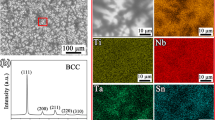
Abstract
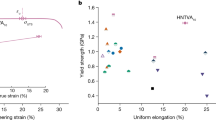
Refractory complex concentrated alloys (RCCAs) have drawn particular attention for their high yield strength and superior softening resistance at high temperatures. However, poor room-temperature ductility and high density remain the main challenges for their processing and applications. Here, using inherent material characteristics as the alloy-design principles, three novel single-phase body-centered cubic structured Ti3Zr1.5Nb(1−x)MoxVAl0.25 (x = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, marked as Mo0.1, Mo0.3, and Mo0.5, respectively) RCCAs with promising tensile ductility and relatively low density below 6 g cm−3 were developed by tailoring the Mo concentration. The introduction of Mo elements with high shear modulus promotes lattice distortion, contributing to enhanced lattice friction stress and yield strength. The Mo0.3 and Mo0.5 alloys exhibit tensile yield strengths exceeding 1100 MPa and high fracture elongation of over 15% in the as-cast state. Labusch’s model revealed that solid-solution strengthening induced by atomic size and shear modulus mismatch contributes most significantly to yield strength. Deformation microstructure observations uncovered that the formation of the kink bands, dense-dislocation walls, and Taylor lattices are highly effective in enhancing strain-hardening capacity due to their high density of dislocation boundaries, enabling the alloys to maintain high strength while yet ensuring enough ductility. This study provides new insights into the development of strong and ductile RCCAs with single-phase structures.

摘要
难熔高熵合金因其优异的高温屈服强度和抗软化性能而备受关 注. 然而, 室温延展性差和较高的密度目前仍然是其加工以及应用需要 面临的主要挑战. 本文利用材料的固有特性作为合金设计原则, 通过调 控Mo浓度, 制备了三种新型单相体心立方结构的Ti3Zr1.5Nb(1−x)−MoxVAl0.25 (x = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 标记为Mo0.1, Mo0.3和Mo0.5)合金, 这些 合金都具有良好的拉伸延展性和低于6 g cm−3的密度. 高剪切模量Mo 元素的引入促进了晶格畸变, 从而提高了合金中的晶格摩擦应力以及 屈服强度. 铸态Mo0.3和Mo0.5合金均表现出超过1100 MPa的拉伸屈服 强度, 以及大于15%的断裂延伸率. Labusch模型计算结果表明, 原子尺 寸和剪切模量失配引起的固溶强化对屈服强度的影响最为显著. 通过 观察变形微观组织发现, 由于存在高密度的位错界面, 扭折带、位错壁 以及泰勒晶格的形成能有效提高合金的应变硬化能力, 使合金在展现 高强度的同时保持足够的延展性. 该研究为开发具有高强韧的单相难 熔高熵合金提供了新的见解.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raabe D, Tasan CC, Olivetti EA. Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals. Nature, 2019, 575: 64–74
Yang T, Zhao YL, Li WP, et al. Ultrahigh-strength and ductile superlattice alloys with nanoscale disordered interfaces. Science, 2020, 369: 427–432
Ritchie RO. The conflicts between strength and toughness. Nat Mater, 2011, 10: 817–822
Gludovatz B, Hohenwarter A, Catoor D, et al. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science, 2014, 345: 1153–1158
Li Z, Pradeep KG, Deng Y, et al. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature, 2016, 534: 227–230
Zhang Y, Zuo TT, Tang Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2014, 61: 1–93
Gorsse S, Miracle DB, Senkov ON. Mapping the world of complex concentrated alloys. Acta Mater, 2017, 135: 177–187
Xiong W, Guo AXY, Zhan S, et al. Refractory high-entropy alloys: A focused review of preparation methods and properties. J Mater Sci Tech, 2023, 142: 196–215
Zhou Y, Zeng S, Zhu Y, et al. Superior tensile properties of a novel as-cast non-equimolar Zr45Ti15Nb20Ta20 complex concentrated alloy. Mater Lett, 2022, 324: 132779
Zeng S, Zhou Y, Li H, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of lightweight Ti3Zr1.5NbVAl (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75) refractory complex concentrated alloys. J Mater Sci Tech, 2022, 130: 64–74
Zeng S, Zhu Y, Li W, et al. A single-phase Ti3Zr1.5NbVAl0.25 refractory high entropy alloy with excellent combination of strength and toughness. Mater Lett, 2022, 323: 132548
Senkov ON, Woodward C, Miracle DB. Microstructure and properties of aluminum-containing refractory high-entropy alloys. JOM, 2014, 66: 2030–2042
Yurchenko NY, Stepanov ND, Gridneva AO, et al. Effect of Cr and Zr on phase stability of refractory Al−Cr−Nb−Ti−V−Zr high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2018, 757: 403–414
Senkov ON, Wilks GB, Scott JM, et al. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2011, 19: 698–706
Senkov ON, Senkova SV, Woodward C, et al. Low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr−Nb−Ti−V−Zr system: Microstructure and phase analysis. Acta Mater, 2013, 61: 1545–1557
Senkov ON, Senkova SV, Miracle DB, et al. Mechanical properties of low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr−Nb−Ti−V−Zr system. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2013, 565: 51–62
Wu YD, Cai YH, Chen XH, et al. Phase composition and solid solution strengthening effect in TiZrNbMoV high-entropy alloys. Mater Des, 2015, 83: 651–660
Zhang F, Xiang C, Han EH, et al. Effect of Nb content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mo0.25V0.25Ti1.5Zr0.5Nbx high-entropy alloys. Acta Metall Sin (Engl Lett), 2022, 35: 1641–1652
Zhang S, Ding X, Gao X, et al. Dual enhancement in strength and ductility of Ti−V−Zr medium entropy alloy by fracture mode transformation via a heterogeneous structure. Int J Plast, 2023, 160: 103505
Wang T, Jiang W, Wang X, et al. Microstructure and properties of Al0.5NbTi3VxZr2 refractory high entropy alloys combined with high strength and ductility. J Mater Res Tech, 2023, 24: 1733–1743
Jiang W, Wang Y, Wang X, et al. Effect of Al on microstructure and mechanical properties of lightweight AlxNb0.5TiV2Zr0.5 refractory high entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2023, 865: 144628
Chen Y, Xu Z, Wang M, et al. A single-phase V0.5Nb0.5ZrTi refractory high-entropy alloy with outstanding tensile properties. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2020, 792: 139774
Yao TT, Zhang YG, Yang L, et al. A metastable Ti−Zr−Nb−Al multi-principal-element alloy with high tensile strength and ductility Mater Sci Eng-A, 2022, 851: 143646
Pang J, Zhang H, Zhang L, et al. Ductile Ti1.5ZrNbAl0.3 refractory high entropy alloy with high specific strength Mater Lett, 2021, 290: 129428
Sohn SS, Kwiatkowski da Silva A, Ikeda Y, et al. Ultrastrong medium-entropy single-phase alloys designed via severe lattice distortion. Adv Mater, 2019, 31: 1807142
Lee C, Chou Y, Kim G, et al. Lattice-distortion-enhanced yield strength in a refractory high-entropy alloy. Adv Mater, 2020, 32: 2004029
Lee C, Song G, Gao MC, et al. Lattice distortion in a strong and ductile refractory high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater, 2018, 160: 158–172
Wang S, Wu D, She H, et al. Design of high-ductile medium entropy alloys for dental implants. Mater Sci Eng-C, 2020, 113: 110959
Li W, Xiong K, Yang L, et al. An ambient ductile TiHfVNbTa refractory high-entropy alloy: Cold rolling, mechanical properties, lattice distortion, and first-principles prediction. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2022, 856: 144046
Huang H, Wu Y, He J, et al. Phase-transformation ductilization of brittle high-entropy alloys via metastability engineering. Adv Mater, 2017, 29: 1701678
An Z, Mao S, Yang T, et al. Spinodal-modulated solid solution delivers a strong and ductile refractory high-entropy alloy. Mater Horiz, 2021, 8: 948–955
Huang W, Hou J, Wang X, et al. Excellent room-temperature tensile ductility in as-cast Ti37V15Nb22Hf23W3 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2022, 151: 107735
Wei S, Kim SJ, Kang J, et al. Natural-mixing guided design of refractory high-entropy alloys with as-cast tensile ductility. Nat Mater, 2020, 19: 1175–1181
Dirras G, Lilensten L, Djemia P, et al. Elastic and plastic properties of as-cast equimolar TiHfZrTaNb high-entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2016, 654: 30–38
Senkov ON, Semiatin SL. Microstructure and properties of a refractory high-entropy alloy after cold working. J Alloys Compd, 2015, 649: 1110–1123
Juan CC, Tsai MH, Tsai CW, et al. Simultaneously increasing the strength and ductility of a refractory high-entropy alloy via grain refining. Mater Lett, 2016, 184: 200–203
Chen S, Tseng KK, Tong Y, et al. Grain growth and Hall-Petch relationship in a refractory HfNbTaZrTi high-entropy alloy. J Alloys Compd, 2019, 795: 19–26
Wu Y, Si J, Lin D, et al. Phase stability and mechanical properties of AlHfNbTiZr high-entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2018, 724: 249–259
Wu YD, Cai YH, Wang T, et al. A refractory Hf25Nb25Ti25Zr25 high-entropy alloy with excellent structural stability and tensile properties. Mater Lett, 2014, 130: 277–280
Di Y, Wang M, Zhang L, et al. A novel Ti45V45(AlCrMo)10 lightweight medium-entropy alloy with outstanding mechanical properties. Mater Lett, 2023, 339: 134089
Yan X, Liaw PK, Zhang Y. Ultrastrong and ductile BCC high-entropy alloys with low-density via dislocation regulation and nanoprecipitates. J Mater Sci Tech, 2022, 110: 109–116
Wang J, Bai S, Tang Y, et al. Effect of the valence electron concentration on the yield strength of Ti−Zr−Nb−V high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2021, 868: 159190
Han Z, Meng L, Yang J, et al. Novel BCC VNbTa refractory multielement alloys with superior tensile properties. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2021, 825: 141908
Li D, Dong Y, Zhang Z, et al. An as-cast Ti−V−Cr−Al light-weight medium entropy alloy with outstanding tensile properties. J Alloys Compd, 2021, 877: 160199
Wang L, Ding J, Chen S, et al. Tailoring planar slip to achieve pure metal-like ductility in body-centred-cubic multi-principal element alloys. Nat Mater, 2023, 22: 950–957
Wu M, Wang S, Xiao F, et al. Dislocation glide and mechanical twinning in a ductile VNbTi medium entropy alloy. J Mater Sci Tech, 2022, 110: 210–215
Li T, Wang S, Fan W, et al. CALPHAD-aided design for superior thermal stability and mechanical behavior in a TiZrHfNb refractory high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater, 2023, 246: 118728
Orowan E. A type of plastic deformation new in metals. Nature, 1942, 149: 643–644
Wang S, Wu M, Shu D, et al. Kinking in a refractory TiZrHfNb0.7 medium-entropy alloy. Mater Lett, 2020, 264: 127369
Zheng Y, Zeng W, Wang Y, et al. Kink deformation in a beta titanium alloy at high strain rate. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2017, 702: 218–224
Wang S, Wu M, Shu D, et al. Mechanical instability and tensile properties of TiZrHfNbTa high entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures. Acta Mater, 2020, 201: 517–527
Castany P, Pettinari-Sturmel F, Douin J, et al. TEM quantitative characterization of short-range order and its effects on the deformation micromechanims in a Ti−6Al−4V alloy. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2017, 680: 85–91
He F, Wei S, Cann JL, et al. Composition-dependent slip planarity in mechanically-stable face centered cubic complex concentrated alloys and its mechanical effects. Acta Mater, 2021, 220: 117314
Lei Z, Liu X, Wu Y, et al. Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes. Nature, 2018, 563: 546–550
Sudmanns M, El-Awady JA. The effect of local chemical ordering on dislocation activity in multi-principle element alloys: A three-dimensional discrete dislocation dynamics study. Acta Mater, 2021, 220: 117307
Hsiung LL. On the mechanism of anomalous slip in bcc metals. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2010, 528: 329–337
Senkov ON, Scott JM, Senkova SV, et al. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509: 6043–6048
Labusch R. A statistical theory of solid solution hardening. Physica Status Solidi (b), 1970, 41: 659–669
Wang SP, Xu J. (TiZrNbTa)−Mo high-entropy alloys: Dependence of microstructure and mechanical properties on Mo concentration and modeling of solid solution strengthening. Intermetallics, 2018, 95: 59–72
Hall EO. The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results. Proc Phys Soc B, 1951, 64: 747–753
Petch NJ. The cleavage strength of polycrystals. J Iron Steel Inst, 1953, 174: 25–28
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52074257) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (ZDBS-LY- JSC023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions Zhu ZW conceived the research. Zeng S, Zhou YK, Li H, and Chen JQ designed the experiments. Zeng S performed the experiments with assistance from Zhou YK, Li H, and Chen JQ. Zeng S, Zhu ZW, Gao HQ, Zhang HW, Fu HM, and Wang AM analyzed the date. Zeng S and Zhu ZW wrote the paper with input from Zhang HF and Zhao HW. All anthors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Shuai Zeng is a PhD candidate at Shi-changxu Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences. His current research focuses on the design and deformation mechanism of high-performance lightweight refractory high-entropy alloy materials.
Zhengwang Zhu received his PhD degree from the Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences. From 2009 to 2010, he conducted research at Tohoku University (Japan). He joined the Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences as an assistant professor in 2010, was promoted to professor in 2016, and now moved to Northeastern University. His research focuses on the development and application of high-performance alloys, in particular, metallic glasses and high-entropy alloys.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, S., Zhou, Y., Gao, H. et al. Novel as-cast Ti-rich refractory complex concentrated alloys with superior tensile properties. Sci. China Mater. 67, 311–320 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-023-2705-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-023-2705-2