Abstract
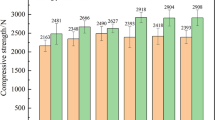
In the present study, a novel process to prepare high-strength pellets of high-calcium, high-magnesium ilmenite concentrate was investigated. Magnetite concentrate and bentonite were selected as the additive and binder of the pellet, respectively. The effects of the magnetite concentrate content, bentonite content, and roasting temperature on the compressive strength, phase transformations, and morphology were systematically investigated. The addition of magnetite concentrate is an effective way to improve the compressive strength of high-calcium, high-magnesium ilmenite concentrate pellets. A pellet with a compressive strength of more than 1800 N can be obtained through the addition of 15% magnetite concentrate and 1.5% bentonite, followed by roasting at 1100 °C. The pseudobrookite solid solution formed during the high-temperature roasting process can form crystal bridges, which contribute to the consolidation of ilmenite concentrate pellets. The hematite formed by the oxidation of magnetite concentrate, which recrystallizes during the roasting process, strengthens pellet consolidation. A long roasting time is required to form and recrystallize a large amount of hematite to prepare high-compressive-strength pellets for low roasting temperature ilmenite concentrate pellet, while the addition of magnetite concentrate to the pellet can accelerate this process.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang ZZ, Paramore JD, Sun P, Chandran KR, Zhang Y, Xia Y, Cao F, Koopman M, Free M (2018) Powder metallurgy of titanium–past, present, and future. Int Mater Rev 63(7):407–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2017.1366003
Xiong K, Wen S, Deng J, Cai J, Lv M (2019) Function and mechanism of sodium silicate in the cleaning process of ilmenite rough concentrate. Physicochem Probl Miner Process. https://doi.org/10.5277/ppmp19032
Kaur M, Singh K (2019) Review on titanium and titanium based alloys as biomaterials for orthopaedic applications. Mater Sci Eng C 102:844–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.04.064
Zhang L-C, Chen L-Y, Wang L (2020) Surface modification of titanium and titanium alloys: technologies, developments, and future interests. Adv Eng Mater 22(5):1901258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2004.11.001
Chouirfa H, Bouloussa H, Migonney V, Falentin-Daudré C (2019) Review of titanium surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater 83:37–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.10.036
Haider AJ, Jameel ZN, Al-Hussaini IH (2019) Review on: titanium dioxide applications. Energy Procedia 157:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.159
Kang X, Liu S, Dai Z, He Y, Song X, Tan Z (2019) Titanium dioxide: from engineering to applications. Catalysts 9(2):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020191
Sezer B, Bilge G, Berkkan A, Tamer U, Boyaci IH (2018) A rapid tool for determination of titanium dioxide content in white chickpea samples. Food Chem 240:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.093
Mackey TS (1994) Upgrading ilmenite into a high-grade synthetic rutile. JOM 46(4):59–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220676
Zhang W, Zhu Z, Cheng CY (2011) A literature review of titanium metallurgical processes. Hydrometallurgy 108(3):177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2011.04.005
Setiawan A, Harjanto S (2020) Effect of sulfur and sodium sulfate on phase transformation and microstructure on carbothermic reduction of Indonesian ilmenite. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering, vol 1. IOP Publishing, p 012092. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/833/1/012092
Nayak D, Ray N, Dash N, Rath S, Biswal S (2020) Reduction behaviour of Odisha Sands Complex, India ilmenite-coke composite pellets. J Central South Univ 27(6):1678–1690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4399-6
Lv W, Elliott R, Lv X, Xiang J, Wang F, Yang Y, Barati M (2021) Generation of titania-rich slag and iron from ilmenite concentrate by carbothermic reduction and magnetic separation in the presence of Na2CO3. Can Metall Q. https://doi.org/10.1080/00084433.2021.1910427
Ebadi H, Pourghahramani P (2019) Effects of mechanical activation modes on microstructural changes and reactivity of ilmenite concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 188:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.06.001
Zhang H, Zeng J, Xie H, Guan C, Chen L (2020) Enhanced separation for ilmenite tailings with a novel HGMS-flotation process. Sep Sci Technol 55(4):752–760. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1567546
Lv X-d, Huang R, Wu Q-z, Wu Q-h, Zhang J-z (2019) Volatilisation behaviour of iron, silicon and magnesium during vacuum carbothermal reduction of ilmenite concentrate. Can Metall Q 58(4):419–426. https://doi.org/10.1080/00084433.2019.1619062
Lei Y, Li Y, Peng J, Guo S, Li W, Zhang L, Wan R (2011) Carbothermic reduction of Panzhihua oxidized ilmenite in a microwave field. ISIJ Int 51(3):337–343. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.51.337
Lv W, Zhao S, Elliott R, Lv X, Barati M (2020) Influence of ferrous sulfide on carbothermic reduction of Panzhihua ilmenite concentrate. JOM 72(10):3393–3400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04295-1
Xu M, Guo M-w, Zhang J-l, Wan T-j, Kong L-t (2006) Beneficiation of titanium oxides from ilmenite by self-reduction of coal bearing pellets. J Iron Steel Res Int 13(2):6–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(06)60033-2
Song B, Huang P, Ma Y, Song Z, He Z (2019) Pelletization performance of Panzhihua ilmenite concentrate. Paper presented at the 2018 International Joint Conference on Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, 02 April 2019
Kim DH, Kim TS, Heo JH, Park HS, Park JH (2019) Influence of temperature on reaction mechanism of ilmenite ore smelting for titanium production. Metall Mater Trans B 50(4):1830–1840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01604-1
Firth AR, Manuel JR (2005) Thermal implications of phase transformations during induration of iron ore pellets produced from hematite. ISIJ Int 45(11):1561–1566. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.45.1561
Wang C, Xu C, Liu Z, Wang Y, Wang R, Ma L (2021) Effect of organic binders on the activation and properties of indurated magnetite pellets. Int J Miner Metall Mater 28(7):1145–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2055-7
Sandeep Kumar TK, Viswanathan NN, Ahmed H, Dahlin A, Andersson C, Bjorkman B (2019) Developing the oxidation kinetic model for magnetite pellet. Metall Mater Trans B 50(1):162–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1423-4
Dishwar RK, Mandal AK, Sinha OP (2019) Studies on highly fluxed iron ore pellets hardened at 1100 °C to 1200 °C. Metall Mater Trans B 50(2):617–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01506-2
Chiwandika EK, Jung S-M (2020) Effects of ilmenite ore on phase development of hematite ore sinter. Metall Mater Trans B 51(4):1469–1484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01856-2
Santos FE, Borgert CH, Neto LR, de Oliveira JR, Filho HJF, Alves JO, Machado JP, Grillo FF, Telles VB, Junca E (2021) Physical characterization and kinetic analysis of the iron ore pellets produced with marble waste. Metall Mater Trans B 52(3):1664–1680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02131-8
Gou H-P, Zhang G-H, Chou K-C (2015) Influence of Pre-oxidation on Carbothermic Reduction Process of Ilmenite Concentrate. ISIJ Int 55(5):928–933. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.55.928
Lv W, Lv X, Xiang J, Wang J, Lv X, Bai C, Song B (2017) Effect of pre-oxidation on the carbothermic reduction of ilmenite concentrate powder. Int J Miner Process 169:176–184
Lv W, Lv X, Xiang J, Hu K, Zhao S, Dang J, Han K, Song B (2019) Effect of preoxidation on the reduction of ilmenite concentrate powder by hydrogen. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(8):4031–4040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.139
Nayak D, Ray N, Dash N, Rath SS, Pati S, De PS (2021) Induration aspects of low-grade ilmenite pellets: Optimization of oxidation parameters and characterization for direct reduction application. Powder Technol 380:408–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.11.018
Pyung-Hwa K (2015) Impurities in Ilmenite: Magnesium. Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, master's thesis
Marius S (2012) Organic binder as a substitute for bentonite in ilmenite pelletization. Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, master's thesis
Gan M, Ji Z, Fan X, Lv W, Zheng R, Chen X, Liu S, Jiang T (2018) Preparing high-strength titanium pellets for ironmaking as furnace protector: optimum route for ilmenite oxidation and consolidation. Powder Technol 333:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.04.042
Limiao H, Jun Z (2012) Pangang Group successfully solved the technical problem of preparation of ilmenite concentrate pellets. Titan Ind Prog 29(06):14
Forsmo SPE, Forsmo SE, Samskog PO, Björkman BMT (2008) Mechanisms in oxidation and sintering of magnetite iron ore green pellets. Powder Technol 183(2):247–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2007.07.032
Lv W, Lv X, Zhang Y, Li S, Tang K, Song B (2017) Isothermal oxidation kinetics of ilmenite concentrate powder from Panzhihua in air. Powder Technol 320:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.07.058
Chen Y (1997) Low-temperature oxidation of ilmenite (FeTiO3) induced by high energy ball milling at room temperature. J Alloy Compd 257(1):156–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(97)00012-1
Gupta SK, Rajakumar V, Grieveson P (1991) Phase transformations during heating of llmenite concentrates. Metall Trans B 22(5):711–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02679027
Fu X, Wang Y, Wei F (2010) Phase transitions and reaction mechanism of ilmenite oxidation. Metall Mater Trans A 41(5):1338–1348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0173-y
Chen X, Deng J, Yu R, Chen J, Hu P, Xing X (2010) A simple oxidation route to prepare pseudobrookite from Panzhihua raw ilmenite. j Am Ceram Soc 93(10):2968–2971. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03937.x
Li G, Jiang T, Zhang Y, Tang Z (2012) Recrystallization of Fe2O3 during the induration of iron ore oxidation pellets. In: Recrystallization. IntechOpen
Lobo S, Kolbeinsen L, Seim S (2013) Pre-reduction of ilmenite with natural gasmodel development and use. Paper presented at the The thirteenth International Ferroalloys Congress, Almaty, Kazakhstan
Bhogeswara Rao D, Rigaud M (1975) Kinetics of the oxidation of ilmenite. Oxid Met 9(1):99–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613496
Li GH, Li XQ, Zhang YB, He GQ, Jiang T (2009) Induration mechanisms of oxidised pellets prepared from mixed magnetite–haematite concentrates. Ironmak Steelmak 36(5):393–396. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328109X410325
Papanastassiou D, Bitsianes G (1973) Mechanisms and kinetics underlying the oxidation of magnetite in the induration of iron ore pellets. Metall Trans 4(2):487–496
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52104325).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Il Sohn.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, W., Zhou, G., Chen, F. et al. A Novel Process for Preparing High-Strength Pellets of Ilmenite Concentrate. J. Sustain. Metall. 8, 551–565 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-022-00508-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-022-00508-w