Abstract
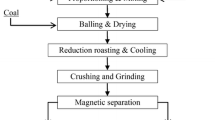
Extraction of gold from the refractory gold ores is commonly practiced by cyanide leaching, which simultaneously generates a significant amount of hazardous cyanide tailings. The cyanide tailings, still bearing certain amounts of residual gold, subsequently go through chlorination roasting to further recover Au, Ag, and other nonferrous valuable metals, and consequently, rendering the tailings inert by forming a residue containing high concentrations of Fe. This study aims at recovering Fe from the pellet-form chlorination residue by carbothermic reduction, forming magnetic Fe3O4 or metallic Fe, followed by magnetic separation. The results show that by reduction roasting at 800 °C for 4 h, a maximum amount of Fe3O4 can be generated. However, the subsequent magnetic separation was poor due to the extremely fine particle sizes and complex mineralogical associations. Notably, carbothermic reduction at 1250 °C for 4 h resulted in the formation of a metallic Fe shell on the outer surface of each residue pellet. The magnetic separation resulted in the production of an Fe concentrate containing 82.17 wt% Fe with a total Fe recovery of 79.68 wt%.
Graphical Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Song Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, Lan X (2020) Comparative experimental study on the harmless treatment of cyanide tailings through slurry electrolysis. Sep Purif Technol 251:117314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117314
Lv CC, Ding J, Qian P, Li QC, Ye SF, Chen YF (2015) Comprehensive recovery of metals from cyanidation tailing. Miner Eng 70:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2014.09.007
Li H, Yin S, Li S, Zhang L, Peng J, Yang K (2021) Investigation on the recovery of gold from pretreated cyanide tailings using chlorination leaching process. Sep Sci Technol 56(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1708108
Guo X, Zhang C, Tian Q, Yu D (2021) Liquid metals dealloying as a general approach for the selective extraction of metals and the fabrication of nanoporous metals: a review. Mater Today Commun 26:102007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.102007
Lobanov VG, Timofeev EI (2017) Development and introduction of contemporary technology of gold cyanide leaching from gravitational concentrates. Metallurgist 61(5–6):491–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-017-0522-9
Abedi-Orang B, Seifpanahi-Shabani K, Kakaie R (2020) Mathematical modeling of fate and transport of cyanide pollutant in the gold mine tailings: with emphasis on physico-chemical process. Environ Earth Sci 79(9):189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-08927-2
Qiu T, Huang X, Yang X (2016) Recovery of copper from cyanidation tailing by flotation. JOM 68(2):548–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1726-8
Long H, Li H, Pei J, Srinivasakannan C, Yin S, Zhang L, Ma A, Li S (2020) Cleaner recovery of multiple valuable metals from cyanide tailings via chlorination roasting. Sep Sci Technol 56(12):2113–2123. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2020.1812650
Anning C, Wang J, Chen P, Batmunkh I, Lyu X (2019) Determination and detoxification of cyanide in gold mine tailings: a review. Waste Manag Res 37(11):1117–1126. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242x19876691
Guo X, Qin H, Tian Q, Zhang L (2020) The efficacy of a new iodination roasting technology to recover gold and silver from refractory gold tailing. J Clean Prod 261:121147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121147
Man Y, Feng JX, Li FJ, Ge Q, Chen YM, Zhou JZ (2014) Influence of temperature and time on reduction behavior in iron ore–coal composite pellets. Powder Technol 256:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.039
Shang D, Chen F, Zhang Y, Zeng M (2011) Recovery of iron from gold-cyanide residue by reduction roasting and magnetic separation. Min Metall Eng 31(05):35–38
Zheng Y, Gong C, Sun Z (2014) New technology of iron extraction and gold recovery from cyanide tailings by cyanide process after reduction roasting and acid leaching. Chin J Nonferr Met 24(09):2426–2433
Wang W-w, Li Z-y (2020) Recovery and kinetics of gold and iron from cyanide tailings by one-step chlorination-reduction roasting. Miner Eng 155:106453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106453
Liu B, Zhang Z, Li L, Wang Y (2013) Recovery of gold and iron from the cyanide tailings by magnetic roasting. Rare Met Mater Eng 42(9):1805–1809
Zhang Y-l, Li H-m, Yu X-j (2013) Fe extraction from high-silicon and aluminum cyanide tailings by pretreatment of water leaching before magnetic separation. Trans Nonferr Met Soc China 23(4):1165–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(13)62579-0
Fu P, Li Z, Feng J, Bian Z (2018) Recovery of gold and iron from cyanide tailings with a combined direct reduction roasting and leaching process. Metals 8(7):561. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8070561
Zhang C, Wang X, Jiang S, Zhou M, Li F, Bi X, Xie S, Liu J (2021) Heavy metal pollution caused by cyanide gold leaching: a case study of gold tailings in central China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12728-w
Li H, Li S, Ma P, Zhou Z, Long H, Peng J, Zhang L (2021) Evaluation of a cleaner production for cyanide tailings by chlorination thermal treatments. J Clean Prod 281:124195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124195
Li H, Ma A, Srinivasakannan C, Zhang L, Li S, Yin S (2018) Investigation on the recovery of gold and silver from cyanide tailings using chlorination roasting process. J Alloy Compd 763:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.298
Abd Rashid RZ, Mohd. Salleh H, Ani MH, Yunus NA, Akiyama T, Purwanto H (2014) Reduction of low grade iron ore pellet using palm kernel shell. Renew Energy 63:617–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2013.09.046
Guo D, Hu M, Pu C, Xiao B, Hu Z, Liu S, Wang X, Zhu X (2015) Kinetics and mechanisms of direct reduction of iron ore-biomass composite pellets with hydrogen gas. Int J Hydrog Energy 40(14):4733–4740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.02.065
Guo D, Zhu L, Guo S, Cui B, Luo S, Laghari M, Chen Z, Ma C, Zhou Y, Chen J, Xiao B, Hu M, Luo S (2016) Direct reduction of oxidized iron ore pellets using biomass syngas as the reducer. Fuel Process Technol 148:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.03.009
Li K, Jiang Q, Chen G, Gao L, Peng J, Chen Q, Koppala S, Omran M, Chen J (2021) Kinetics characteristics and microwave reduction behavior of walnut shell-pyrolusite blends. Biores Technol 319:124172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124172
Yu D, Zhu M, Utigard TA, Barati M (2014) TG/DTA study on the carbon monoxide and graphite thermal reduction of a high-grade iron nickel oxide residue with the presence of siliceous gangue. Thermochim Acta 575:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2013.10.015
Bandyopadhyay D, Chakraborti N, Ghosh A (1993) A study on the kinetics of iron oxide reduction by solid carbon. Steel Res 64(7):340–345
Hayashi M, Takeda K, Kashimura K, Watanabe T, Nagata K (2013) Carbothermic reduction of hematite powders by microwave heating. ISIJ Int 53(7):1125–1130. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.53.1125
Li J, Li B, Han J, Cao Z, Wang J (2014) A comparative study on the reduction mechanism of Fe2O3 under different heating methods. JOM 66(8):1529–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1083-z
Sun Y, Han Y, Gao P, Wei X, Li G (2015) Thermogravimetric study of coal-based reduction of oolitic iron ore: kinetics and mechanisms. Int J Miner Process 143:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2015.09.005
Jung S, Yi S (2013) A kinetic study on carbothermic reduction of hematite with graphite employing thermogravimetry and quadruple mass spectrometry. Steel Res Int 84(9):908–916. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201200310
Boudouard MO (1901) Recherches sur less equilibres chimiques. Ann Chim Phys 24:1–85
Kawahara M, Mitsuo T, Shirane Y (1985) Kinetics of solid state reaction in 2FeO-SiO2 and 2NiO-SiO2 systems. Trans Jpn Inst Met 26(8):542–548
Rayapudi V, Agrawal S, Dhawan N (2020) Evaluation of carbothermal reduction for processing of banded hematite jasper ore. Powder Technol 362:826–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.094
Liang Z, Yi L, Huang Z, Lu B, Dan C, Zhong R (2019) Effect of silica on reduction behaviors of hematite-carbon composite compact at 1223–1373 K. ISIJ Int 59(2):227–234. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2018-613
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Hunan Natural Science Foundation (Grant 2021JJ30854), Hunan Key Research and Development Program (Grant 2020SK2005), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 51904350).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Veena Sahajwalla.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Wang, J., Yu, D. et al. Comprehensive Reclamation of Valuable Metals from Au-Bearing Cyanide Residue by Chlorination Roasting–Carbothermic Reduction–Magnetic Separation: Recovery of Iron. J. Sustain. Metall. 7, 1748–1761 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00452-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00452-1