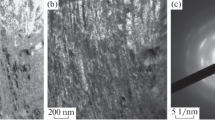
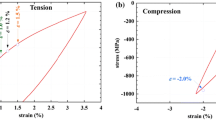
Abstract
The effect of the microstructure formed as a result of ageing in a Ti-50.7 at.% Ni alloy with different B2 austenite grain sizes on its functional properties under bending is studied. The maximum recovery strain of εr = 15.5% is obtained as a result of annealing at 600 °C for 1 h (fine-grained structure). The subsequent degradation of the functional properties after ageing is caused by the reduction of the difference between the dislocation and transformation yield stresses. The material with a coarse-grained structure and the worst combination of functional properties after recrystallisation annealing, on the contrary, represents the poorest combination and should be aged in order to improve the shape recovery characteristics. The revealed regularities can be used as an additional tool for the precise regulation of functional properties in shape memory alloys.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Serruys PW (1997) Handbook of coronary stents. Rotterdam Thoraxcentre Interventional Cardiology Group, Rotterdam
Razov AI (2004) Application of titanium nickelide-based alloys in engineering. Phys Met Metallogr 97(1):97–126
Duerig TW, Melton KN, Stockel D, Wayman CM (1990) Engineering aspects of shape memory alloys. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Prokoshkin SD, Ryklina EP, Khmelevskaya IYu, Pushin VG (2004) Application of titanium nickelide-based alloys in medicine. Phys Met Metallogr 97(1):56–96
Ryklina EP, Prokoshkin SD, Khmelevskaya IYu (2003) Medical Applications. In: Brailovski V, Prokoshkin S, Terriault P, Trochu F (eds) Shape memory alloys: fundamentals, modeling and applications. ETS, Canada, pp 775–806
Khmelevskaya I, Ryklina E, Korotitskiy A (2015) Application of thermomechanically treated Ti-Ni SMA. In: Resnina N, Rubanik V (eds) Shape memory alloys: properties, technologies, opportunities. Trans Tech Publication, Pfaffikon, pp 603–637
Ryklina EP, Khmelevskaya IYu, Prokoshkin SD (2004) Use of thermomechanically treated titanium nickelide for medical implants and tools. Met Sci Heat Treat 46(5–6):179–183
Muslov SA, Shelyakov AV, Andreev VA (2018) Shape memory alloys: properties, manufacture and application in technique and medicine. Mozartika, Moscow (in Russian)
Ryklina EP, Khmelevskaya IYu, Prokoshkin SD (2001) Some medical devices based on shape memory and superelasticity of thermomechanically treated titanium nickelide. Metallofiz Noveishie Tekhnol 23(9998):38–41
Khmelevskaya IYu, Ryklina EP, Prokoshkin SD, Markossian GA, Tarutta EP, Iomdina EN (2008) A shape memory device for the treatment of high myopia. Mater Sci Eng A 481–482:651–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.171
Prokoshkin SD, Butckevitch AC, Chadaev AP, Ryklina EP, Khmelevskaya IY (1996) Elaboration and description of the first application of nitinol extravessel corrector with the shape memory effect. Proc SPIE 2779:986–990
Ryklina, E.P., Khmelevskaya, I.Y., Morozova, T.V., Prokoshkin, S.D: Biomedical engineering in design and application of nitinol stents with shape memory effect. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 2779, 991–993 (1996)
Saburi T, Tatsumi T, Nenno S (1982) Effects of heat treatment on mechanical behavior of Ti–Ni alloys. J Phys (FY.) 43(12):261–266. https://doi.org/10.1051/jphyscol:1982435
Liu Y, McCormick PG (1989) Influence of heat treatment on the mechanical behavior of a NiTi alloy. ISIJ Int 29(5):417–422. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.29.417
Scherngell H, Kneissl AC (1998) Inducing and stability of the intrinsic two-way shape memory effect in Ni-Ti alloys. Scripta Mater. 39(2):205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(98)00155-9
Kim, J.I., Miyazaki, S.: Effect of nano-scaled precipitates on shape memory behavior of Ti-50.9at.%Ni alloy. Acta Mater. 53 (17), 4545–4554 (2005) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2005.06.009
Prokoshkin, S.D., Brailovski, V., Khmelevskaya, I.Yu., Inaekyan, K.E., Demers, V., Dobatkin, S.V., Tatyanin, E.V.: Structure and properties of Severely Cold-Rolled and Annealed Ti-Ni Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 481−482, 114−118 (2008) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.150
Wang, X., Kustov, S., Li K., Schryvers, D., Verlinden, B., Humbeeck, J.V.: Effect of nanoprecipitates on the transformation behavior and functional properties of a Ti–50.8 at.% Ni alloy with micron-sized grains. Acta Mater. 82, 224–233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.09.018
Ryklina EP, Prokoshkin SD, Chernavina AA, Perevoshchikova NN (2010) Investigation on the influence of thermomechanical conditions of induction and structure on the shape memory effects in Ti−Ni alloy. Inorg Mater Appl 1(3):188–194. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113310030032
Mohammad Sharafi E, Kermanpur A (2018) Superelastic behavior of nanostructured Ti50Ni48Co2 shape memory alloy with cold rolling processing. Trans Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64773-9
Lim, Y.G., Han, S.H., Choi, E., Kim, W.J.: Shape memory and superelasticity of nanograined Ti–51.2 at.% Ni alloy processed by severe plastic deformation via high-ratio differential speed rolling. Mater. Charact. 145, 284–293 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.08.017
Ryklina, E.P., Prokoshkin, S.D., Chernavina, A.A.: Shape-memory behavior of nanostructured Ti–Ni alloy. ESOMAT 0502516 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1051/esomat/200905025
Ryklina EP, Prokoshkin SD, Chernavina AA (2013) Peculiarities of implementation of abnormally high shape memory effects in thermomechanically treated Ti−Ni alloys. Inorg Mater Appl 4(4):348–355
Ryklina EP, Prokoshkin SD, Kreytsberg AY (2013) Abnormally high recovery strain in TiNi-based shape memory alloys. J Alloys Compd 577:255258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.138
Ryklina, E., Prokoshkin, S., Vachiyan, K.: Nanostructured titanium nickelide: realization of abnormally high recovery strain, IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 63 (2014) https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/63/1/012110
Ryklina EP, Polyakova KA, Tabachkova NYu, Resnina NN, Prokoshkin SD (2018) Effect of B2 austenite grain size and aging time on microstructure and transformation behavior of thermomechanically treated titanium nickelide. J Alloys Compd 764:626–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.102
Kolobova AYu, Ryklina EP, Prokoshkin SD, Inaekyan KE, Brailovskii V (2018) Study of the evolution of the structure and kinetics of martensitic transformations in a titanium nickelide upon isothermal annealing after hot helical rolling. Phys Met Metallogr 119(2):134–145. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X17120079
Khmelevskaya I, Ryklina E, Prokoshkin S, Soutorine M (2013) Peculiarities of behaviour of Ti−50.7% Ni alloy for suturing of blood vessels. J Alloys Compd 577:752–755
Ryklina E, Korotitskiy A, Khmelevskaya I, Prokoshkin S, Polyakova K, Kolobova A, Soutorine M, Chernov A (2017) Control of phase transformations and microstructure for optimum realization of one-way and two-way shape memory effects in removable surgical clips. Mater Des 136:174–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.09.024
Ryklina EP, Khmelevskaya IYu, Prokoshkin SD, Ipatkin RV, Turilina VYu, Inaekyan KE (2004) Device for urgent bleeding control produced from titanium nickelide with reversible shape memory effect. Met Sci Heat Treat 46(7–8):319–323
Ryklina EP, Khmelevskaya IYu, Prokoshkin SD (2004) Application of thermomechanically treated titanium nickelide to development of medical implants and tools. Met Sci Heat Treat 5:3–7
Ryklina EP, Khmelevskaya IY, Prokoshkin SD, Ipatkin RV (2003) The device «Klyost» for clipping vessels and soft-elastic tubular structures. J Phys IV 112:1129–1132
Polyakova-Vachiyan KA, Ryklina EP, Prokoshkin SD, Dubinskii SM (2016) Dependence of the functional characteristics of thermomechanically processed titanium nickelide on the size of the structural elements of austenite. Phys Met Metallogr 117:817–827. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X16080123
Prokoshkin SD, Korotitskiy AV, Dubinskiy SM, Brailovski V, Inaekyan KE (2011) Crystal lattice of martensite and the reserve of recoverable strain of thermally and thermomechanically treated Ti-Ni shape-memory alloys. Phys Met Metallogr 112:170–187. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X11020244
Chumlyakov Yu, Kireeva I, Panchenko E, Karaman I, Maier HJ, Timofeeva E (2013) Shape memory effect and high-temperature superelasticity in high-strength single crystals. J Alloys Compd 577:393398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.003
Chumlyakov YI, Kireeva IV, Panchenko EY, Timofeeva EE, Kretinina IV, Kuts OA (2015) Physics of thermoelastic martensitic in transformation in high-strength single crystals in shape memory alloys. In: Resnina N, Rubanik V (eds) Shape memory alloys: properties, technologies, opportunities. Trans Tech Publication, Pfaffikon, pp 107–173
Brailovski V, Prokoshkin S, Terriault P, Trochu P (2003) Shape memory alloys: fundamentals, modeling and applications. ETS Publ., Montreal
Acknowledgements
The work was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation, Project No. 19-79-00365.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polyakova, K.A., Ryklina, E.P. & Prokoshkin, S.D. Effect of Grain Size and Ageing-Induced Microstructure on Functional Characteristics of a Ti-50.7 at.% Ni Alloy. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 6, 139–147 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-020-00269-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-020-00269-z