Abstract
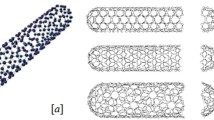
At first, we derive a series form solution of the coupled highly nonlinear equations, which includes various conditions. Then, via the method of directly defined inverse mapping with the series form solution firstly reported in this paper, we can obtain theoretical and approximate analytical analysis about the transfer of heat as well as the magnetohydrodynamic flow of Maxwell nanofluid by the influence of convective heating with effects of thermal radiation. In the energy equation, heat flux model is adopted to develop the equations for viscoelastic relaxation over boundary layer flow. For this investigation, we considered base liquid as engine oil and other forms of carbon nanotubes such as single walled nanotubes and multi-walled nanotubes. Suitable similarity transformations are applied for transformation of given boundary layer flow equations. Results are compared numerically by Keller–Box method. It is found that for both singled and multi-walled carbon nanotube based nanofluids the thermal relaxation time and temperature function are inversely proportional. More interestingly it is noted that for the two types of nanofluids, fluid relaxation parameter exactly coordinates with heat transfer rate as well as skin friction investigated. Also shown that the base functions of solutions are highly convergence.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- u′, v′:
-
Velocity components (m s−1)
- x, y :
-
Coordinates
- \( \hat{q} \) :
-
Heat flux
- T w :
-
Wall temperature (K)
- \( T_{\infty } \) :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- g :
-
Gravitational force (m s−2)
- C p :
-
Specific heat (J kg−1 K−1)
- \( \bar{V} \) :
-
Velocity vector
- q r :
-
Radiative heat flux
- k e :
-
Mean absorption coefficient
- T :
-
Fluid temperature
- f :
-
Nondimensional stream function
- Gr x :
-
Grashof number
- M :
-
Magnetic parameter
- Nr :
-
Radiation parameter
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- C fx :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- Nu x :
-
Nusselt number
- Re x :
-
Reynolds number
- λ 1 :
-
Fluid relaxation time
- \( \hat{\rho } \) :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- μ′:
-
Dynamic viscosity (N m s−1)
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (K−1)
- σ :
-
Electrical conductivity
- λ 2 :
-
Thermal relaxation time
- \( \bar{\alpha } \) :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- σ s :
-
Stefan–Bolzmann constant
- ϕ :
-
Volume fraction of nanoparticles
- \( \bar{\psi } \) :
-
Stream function
- η :
-
Similarity variable
- θ :
-
Nondimensional temperature
- ξ :
-
Velocity slip factor
- ζ :
-
Thermal slip factor
- nf :
-
Nanofluid
- f :
-
Base fluid
- w :
-
Condition at wall
- ∞:
-
Condition at infinity
References
Gupta, A.S.: Hydromagnetic flow past a porous flat plate with Hall effects. Acta Mech. 22, 281–287 (1975)
Hayat, T., Abbas, Z., Asghar, S.: Effects of Hall current and heat transfer on rotating flow of a second-grade fluid through a porous medium. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13, 2177–2192 (2018)
Saleem, A.M., Aziz, M.A.E.: Effect of Hall currents and chemical reaction on hydro magnetic flow of a stretching vertical surface with internal heat generation/absorption. Appl. Math. Model. 32, 1236–1254 (2008)
Aziz, M.A.E., Nabil, T.: Homotopy analysis solution of hydro magnetic mixed convection flow past an exponentially stretching sheet with Hall current. Math. Probl. Eng. 2012, 454023 (2012)
Pal, D.: Hall current and MHD effects on heat transfer over an unsteady stretching permeable surface with thermal radiation. Comput. Math Appl. 66(2013), 1161–1180 (2013)
Gangadhar, K., Kannan, T., Jayalakshmi, P.: Magnetohydrodynamic micropolar nanofluid past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet with Newtonian heating. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 4379–4391 (2017)
Choi, S.U.S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle. In: Siginer, D.A., Wang, H.P. (eds.), Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows, ASME FED, vol 231/MD, 66, pp. 99–105 (1995)
Choi, S.U.S., Zhang, Z.G., Yu, W., Lockwood, F.E., Grulke, E.A.: Anomalously thermal conductivity enhancement in nanotube suspensions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 2252–2254 (2001)
Hamilton, R.L., Crosser, O.K.: Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1, 187–191 (1962)
Buongiorno, J.: Convective transport in nano fluids. ASME J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006)
Xue, Q.: Model for thermal conductivity of carbon nano tube-based composites. Phys. B 368, 302–307 (2005)
Maxwell, J.C.: Electricity and Magnetism, 3rd edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1904)
Iijima, S.: Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354, 56–58 (1991)
Endo, M., Hayashi, T., Kim, Y.A., Terrones, M., Dresselhaus, M.S.: Applications of carbon nanotubes in the twenty-first century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 362, 2223–2238 (2004)
Saito, R., Dresselhaus, G., Dresselhaus, M.S.: Physical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes. Imperial College Press, Singapore (2001)
Murshed, S.M., Nieto de Castro, C.A., Lourenco, M.J.V., Lopes, M.L.M., Santos, F.J.V.: A review of boiling and convective heat transfer with nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(2011), 2342–2354 (2011)
Ganesh Kumar, K., Gireesha, B.J., Manjunatha, S., Rudraswamy, N.G.: Effect of nonlinear thermal radiation on double-diffusive mixed convection boundary layer flow of viscoelastic nano fluid over a stretching sheet. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 12, 18 (2017)
Khan, U., Ahmed, N., Mohyud-Din, S.T.: Heat transfer effects on carbon nano tubes suspended nano fluid flow in a channel with non-parallel walls under the effect of velocity slip boundary condition: a numerical study. Neural Comput. Appl. 28, 37–46 (2017)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Farooq, M., Alsaedi, A., Waqas, M., Yasmeen, T.: Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model in flow of variable thermal conductivity fluid over a variable thicked surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 99, 702–710 (2016)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Farooq, M., Yasmeen, T., Alsaedi, A.: Stagnation point flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. J. Mol. Liq. 220, 49–55 (2016)
Ijaz Khan, M., Waqas, M., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: A comparative study of Casson fluid with homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 498, 85–90 (2017)
Farooq, M., Ijaz Khan, M., Waqas, M., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A., Imran Khan, M.: MHD stagnation point flow of viscoelastic nanofluid with non-linear radiation effects. J. Mol. Liq. 221, 1097–1103 (2016)
Hayat, T., Waqas, M., Ijaz Khan, M., Alsaedi, A.: Analysis of thixotropic nanomaterial in a doubly stratified medium considering magnetic field effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 102, 1123–1129 (2016)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Waqas, M., Alsaedi, A., Farooq, M.: Numerical simulation for melting heat transfer and radiation effects in stagnation point flow of carbon–water nanofluid. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 315, 1011–1024 (2017)
Imran Khan, M., Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Alsaedi, A.: A modified homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions for MHD stagnation flow with viscous dissipation and Joule heating. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 113, 310–317 (2017)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Oayyum, S., Alsaedi, A.: Entropy generation in flow with silver and copper nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 539, 335–346 (2018)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Farooq, M., Alsaedi, A., Yasmeen, T.: Impact of Marangoni convection in the flow of carbon–water nanofluid with thermal radiation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 810–815 (2017)
Ijaz Khan, M., Hayat, T., Imran Khan, M., Alsaedi, A.: Activation energy impact in nonlinear radiative stagnation point flow of cross nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 91, 216–224 (2018)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Waqas, M., Alsaedi, A.: Mathematical modeling of non-Newtonian fluid with chemical aspects: a new formulation and results by numerical technique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 518, 263–272 (2017)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Farooq, M., Alsaedi, A., Imran Khan, M.: Thermally stratified stretching flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 289–294 (2017)
Qayyum, S., Ijaz Khan, M., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: A framework for nonlinear thermal radiation and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions flow based on silver–water and copper–water nanoparticles: a numerical model for probable error. Res. Phys. 7, 1907–1914 (2017)
Hayat, T., Qayyum, S., Ijaz Khan, M., Alsaedi, A.: Entropy generation in magnetohydrodynamic radiative flow due to rotating disk in presence of viscous dissipation and Joule heating. Phys. Fluids 30, 017101 (2018)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Waqas, M., Alsaedi, A., Imran Khan, M.: Radiative flow of micropolar nanofluid accounting thermophoresis and Brownian moment. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 16821–16833 (2017)
Ijaz Khan, M., Waqas, M., Hayat, T., Imran Khan, M., Alsaedi, A.: Behavior of stratification phenomenon in flow of Maxwell nanomaterial with motile gyrotactic microorganisms in the presence of magnetic field. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 131–132, 426–434 (2017)
Imran Khan, M., Ijaz Khan, M., Waqas, M., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Chemically reactive flow of Maxwell liquid due to variable thicked surface. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 86, 231–238 (2017)
Ahmed Khan, W.W., Ijaz Khan, M., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Entropy generation minimization (EGM) of nanofluid flow by a thin moving needle with nonlinear thermal radiation. Phys. B Condens. Matter 534, 113–119 (2018)
Hayat, T., Ijaz Khan, M., Qayyum, S., Alsaedi, A., Imran Khan, M.: New thermodynamics of entropy generation minimization with nonlinear thermal radiation and nanomaterials. Phys. Lett. A 382, 749–760 (2018)
Hayat, T., Ahmad, S., Ijaz Khan, M., Alsaedi, A.: Simulation of ferromagnetic nanomaterial flow of Maxwell fluid. Res. Phys. 8, 34–40 (2018)
Dogonchi, A.S., Waqas, M., Ganji, D.D.: Shape effects of copper–oxide (CuO) nanoparticles to determine the heat transfer filled in a partially heated rhombus enclosure: CVFEM approach. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 107, 14–23 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Waqas, M., Seyyedi, S.M., Tilenoee, M.H., Ganji, D.D.: Numerical simulation for thermal radiation and porous medium characteristics in flow of CuO–H2O nanofluid. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41, 249 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Chamkha, A.J., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Seyyedi, S.M., Ul-Haq, R., Ganji, D.D.: Effects of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions and thermal radiation on magneto-hydrodynamic Cu–water nanofluid flow over an expanding flat plate with non-uniform heat source. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 1161–1171 (2019)
Chamka, A.J., Dogonchi, A.S., Ganji, D.D.: Magneto-hydrodynamic flow and heat transfer of a hybrid nanofluid in a rotating system among two surfaces in the presence of thermal radiation and Joule heating. AIP Adv. 9, 025103 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Armaghani, T., Chamkha, A.J., Ganji, D.D.: Natural convection analysis in a cavity with an inclined elliptical heater subject to shape factor of nanoparticles and magnetic field. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 7919–7931 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Tayebi, T., Chamkha, A.J., Ganji, D.D.: Natural convection analysis in a square enclosure with a wavy circular heater under magnetic field and nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139, 661–671 (2020)
Dogonchi, A.S., Chamkha, A.J., Seyyedi, S.M., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Ganji, D.D.: Viscous dissipation impact on free convection flow of Cu–water nanofluid in a circular enclosure with porosity considering internal heat source. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 5(4), 717–726 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Hashim, : Heat transfer by natural convection of Fe3O4–water nanofluid in an annulus between a wavy circular cylinder and a rhombus. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 130, 320–332 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Waqas, M., Seyyedi, S.M., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Ganji, D.D.: CVFEM analysis for Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid in an annulus subject to thermal radiation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 132, 473–483 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Waqas, M., Seyyedi, S.M., Animasaun, I.L., Ganji, D.D.: The influence of different shapes of nanoparticle on Cu–H2O nanofluids in a partially heated irregular wavy enclosure. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 540, 123034 (2020)
Dogonchi, A.S., Waqas, M., Seyyedi, S.M., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Ganji, D.D.: A modified Fourier approach for analysis of nanofluid heat generation within a semi-circular enclosure subjected to MFD viscosity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 111, 104430 (2020)
Mondal, S., Dogonchi, A.S., Tripathi, N., Waqas, M., Seyyedi, S.M., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Ganji, D.D.: A theoretical nanofluid analysis exhibiting hydromagnetics characteristics employing CVFEM. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42, 19 (2020)
Dogonchi, A.S., Waqas, M., Afshar, S.R., Seyyedi, S.M., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Chamka, A.J., Ganji, D.D.: Investigation of magneto-hydrodynamic fluid squeezed between two parallel disks by considering Joule heating, thermal radiation, and adding different nanoparticles. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 30, 659–680 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Waqas, M., Gulzar, M.M., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Seyyedi, S.M., Ganji, D.D.: Simulation of Fe3O4–H2O nanoliquid in a triangular enclosure subjected to Cattaneo–Christov theory of heat conduction. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 29, 4430–4444 (2019)
Dogonchi, A.S., Selimefendigil, F., Ganji, D.D.: Magneto-hydrodynamic natural convection of CuO–water nanofluid in complex shaped enclosure considering various nanoparticle shapes. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 29, 1663–1679 (2019)
Seyyedi, S.M., Dogonchi, A.S., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Asghar, Z., Waqas, M., Ganji, D.D.: A computational framework for natural convective hydromagnetic flow via inclined cavity: an analysis subjected to entropy generation. J. Mol. Liq. 287, 110863 (2019)
Seyyedi, S.M., Dogonchi, A.S., Nuraei, R., Ganji, D.D., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M.: Numerical analysis of entropy generation of a nanofluid in a semi-annulus porous enclosure with different nanoparticle shapes in the presence of a magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 268, 134 (2019)
Seyyedi, S.M., Dogonchi, A.S., Ganji, D.D., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M.: Entropy generation in a nanofluid-filled semi-annulus cavity by considering the shape of nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 138, 1607–1621 (2019)
Seyyedi, S.M., Dogonchi, A.S., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Waqas, M., Ganji, D.D.: Investigation of entropy generation in a square inclined cavity using control volume finite element method with aided quadratic Lagrange interpolation functions. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 110, 104398 (2010)
Seyyedi, S.M., Dogonchi, A.S., Hashemi-Tilehnoee, M., Waqas, M., Ganji, D.D.: Entropy generation and economic analyses in a nanofluid filled L-shaped enclosure subjected to an oriented magnetic field. Appl. Therm. Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114789
Dogonchi, A.S., Ganji, D.D.: Effect of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux on buoyancy MHD nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching sheet in the presence of Joule heating and thermal radiation impacts. Indian J. Phys. 92, 757–766 (2018)
Fourier, J.B.J.: Theorie Analytique De La Chaleur. Chez Firmin Didot, Paris (1822)
Cattaneo, C.: Sulla conduzionedelcalore. Atti del Seminario Maermatico e Fisico dell Universita di Modena e Reggio Emilia 3, 83–101 (1948)
Christov, C.I.: On frame indifferent formulation of the Maxwell–Cattaneo model of finite-speed heat conduction. Mech. Res. Commun. 36(2009), 481–486 (2009)
Tibullo, V., Zampoli, V.: A uniqueness result for the Cattaneo–Christove heat conduction model applied to incompressible fluids. Mech. Res. Commun. 38, 77–99 (2011)
Han, S.H., Zheng, L.C., Li, C.R., Zhang, X.X.: Coupled flow and heat transfer in viscoelastic fluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Appl. Math. Lett. 38, 87–93 (2014)
Mustafa, M.: Cattaneo–Christove heat flux model for rotating flow and heat transfer of upper convected Maxwell fluid. AIP Adv. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4917306
Hayat, T., Farooq, M., Alsaedi, A.: Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux in the flow over a stretching sheet with variable thickness. AIP Adv. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4929523
Hayat, T., Imtiaz, M., Alsaedi, A., Almezal, S.: On Cattaneo–Christovheat flux in MHD flow of Oldroyd-B fluid with homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 296–303 (2016)
Li, J., Zheng, L., Liu, L.: MHD viscoelastic flow and heat transfer over a vertical stretching sheet with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux effects. J. Mol. Liq. 221, 19–25 (2016)
Oyelakin, I.S., Mondal, S., Sibanda, P.: Cattaneo–Christov nanofluid flow and heat transfer with variable properties over a vertical cone in a porous medium. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 3, 1019–1034 (2017)
Farooq, M., Ahmad, S., Javed, M., Anjum, A.: Analysis of Cattaneo–Christov heat and mass fluxes in the squeezed flow embedded in porous medium with variable mass diffusivity. Res. Phys. 7, 3788–3796 (2017)
Kundu, P.K., Chakraborty, T., Das, K.: Framing the Cattaneo–Christov heat flux phenomena on CNT-based Maxwell nanofluid along stretching sheet with multiple slips. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 1177–1188 (2018)
Liao, S., Zhao, Y.: On the method of directly defining inverse mapping for nonlinear differential equations. Numer. Algorithms 72, 989–1020 (2016)
Baxter, M., Dewasurendra, M., Vajravelu, K.: A method of directly defining the inverse mapping for solutions of coupled systems of nonlinear differential equations. Numer. Algorithms 77, 1199–1211 (2018)
Dewasurendra, M., Vajravelu, K.: On the method of inverse mapping for solutions of coupled systems of nonlinear differential equations arising in nano fluid flow. Heat Mass Transf. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 3, 1–14 (2018)
Acknowledgements
We thank editor and anonymous reviewers for their comments on an earlier version of the manuscript and that greatly improved in the revised manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gangadhar, K., Keziya, K., Kannan, T. et al. Analytical Investigation on CNT Based Maxwell Nano-fluid with Cattaneo–Christov Heat Flux Due to Thermal Radiation. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 6, 124 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-020-00876-5
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-020-00876-5