Abstract
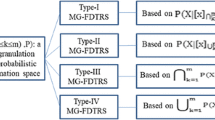
The probabilistic rough set (PRS) model, through the incorporation of error levels, represents a quantitative extension of the classical rough set model. It serves as a fundamental expansion that enables robust fault tolerance capabilities by employing relative quantitative description. However, when confronted with interval-valued fuzzy data, the PRS model is rendered ineffective. The primary reason for this lies in the absence of a unique equivalence relation in interval-valued decision systems. This paper presents a novel approach to address this limitation. In this paper, we first propose a fuzzy similarity relation based on diversity function, which establishes a viable foundation for constricting models of probabilistic rough fuzzy set and multi-granularity probabilistic rough set models for interval-valued fuzzy decision systems. Then the decision rules are derived from the presented three kinds of multi-granularity probabilistic rough fuzzy sets, respectively. In order to elucidate the concepts of interval-valued probabilistic rough fuzzy sets and multi-granularity probabilistic rough fuzzy sets, a case study is considered, which is helpful for applying these theories to deal with practical issues.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inform. Control. 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Li, W., Zhou, H., Xu, W., Wang, X.Z., Pedrycz, W.: Interval dominance-based feature selection for interval-valued ordered data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3184120
Kowalski, P.A., Jeczmionek, E.: Parallel complete gradient clustering algorithm and its properties. Inf. Sci. 600, 155–169 (2022)
Gupta, A., Das, S.: On efficient model selection for sparse hard and fuzzy center-based clustering algorithms. Inf. Sci. 590, 29–44 (2022)
Lee, C., Lee, G.G.: Information gain and divergence-based feature selection for machine learning-based text categorization. Inform. Process. Manag. 42, 155–165 (2006)
Leung, Y., Fischer, M., Wu, W., Mi, J.: A rough set approach for the discovery of classification rules in interval-valued information systems. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 47(2), 233–246 (2007)
Huang, B., Wei, D., Li, H., Zhuang, Y.: Using a rough set model to extract rules in dominance-based interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information systems. Inf. Sci. 221, 215–229 (2013)
Pan, Y., Wu, Y., Lam, H.K.: Security-based fuzzy control for nonlinear networked control systems with DoS attacks via a resilient event-triggered scheme. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(10), 4359–4368 (2022)
Wang, C., Qi, Y., Shao, M., Hu, Q., Chen, D., Qian, Y., Lin, Y.: A fitting model for feature selection with fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(4), 741–753 (2008)
Dai, J., Wang, W., Mi, J.: Uncertainty measurement for interval-valued information systems. Inf. Sci. 251, 63–78 (2013)
Lin, Y., Hu, Q., Liu, J., Li, J., Wu, X.: Streaming feature selection for multilabel learning based on fuzzy mutual information. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(6), 1491–1507 (2017)
Hosseini, S.M., Paydar, M.M., Keshteli, M.H.: Recovery solutions for ecotourism centers during the Covid-19 pandemic: utilizing fuzzy DEMATEL and fuzzy VIKOR methods. Expert Syst. Appl. 185, 115594 (2021)
Querales, M., Salas, R., Morales, Y., Allende-Cid, H., Rosas, H.: A stacking neuro-fuzzy framework to forecast runoff from distributed meteorological stations. Appl. Soft Comput. 118, 108535 (2022)
Versaci, M., Morabito, F.C.: Image edge detection: a new approach based on fuzzy entropy and fuzzy divergence. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 23(4), 918–936 (2021)
Xiao, F.: CaFtR: a fuzzy complex event processing method. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24(2), 1098–1111 (2022)
Xie, D., Xiao, F., Pedrycz, W.: Information quality for intuitionistic fuzzy values with its application in decision making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 109, 104568 (2022)
Ghosh, A., Mishra, N.S., Ghosh, S.: Fuzzy clustering algorithms for unsupervised change detection in remote sensing images. Inf. Sci. 181(4), 699–715 (2011)
Pawlak, Z.: Rough sets. J. Comput. Inf. sci. 11, 341–356 (1982)
Dubois, D., Prade, H.: Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 17(2–3), 191–209 (1990)
Dai, J., Hu, H., Wu, W.Z., Qian, Y., Huang, D.: Maxmal-discernibility-pair-based approach to attribute reduction in fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(4), 2174–2187 (2017)
Yang, Y., Chen, D., Wang, H., Wang, X.: Incremental perspective for feature selection based on fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(3), 1257–1273 (2018)
Wang, C., Huang, Y., Shao, M., Fan, X.: Fuzzy rough set-based attribute reduction using distance measures. Knowl.-Based Syst. 164, 205–212 (2019)
Yang, X., Zhang, M.: Dominance-based fuzzy rough approach to an interval-valued decision system. Front. Comput. Sci. 5(2), 195–204 (2011)
Yao, Y.: Probabilistic rough set approximations. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 49(2), 255–271 (2008)
Yao, Y.: The superiority of three-way decisions in probabilistic rough set models. Inf. Sci. 181, 1080–1096 (2011)
Yao, Y.: Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf. Sci. 180, 341–353 (2010)
Yao, Y.: Information granulation and rough set approximation. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 16, 87–104 (2001)
Peters, J.F., Pawlak, Z., Skowron, A.: A rough set approach to measuring information granules. Comput. Softw. Appl. Conf. pp. 1135-1139, (2002)
Rasiowa, H.: Mechanical proof systems for logic: reaching consensus by groups of intelligent systems. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 5(4), 415–432 (1991)
Qian, Y., Liang, J.: Rough set method based on multi-granulations In: Proc. 5th IEEE Conf. Cogn. Inf., vol. 1, pp. 297-304, (2006)
Li, W., Xu, W., Zhang, X., Zhang, J.: Updating approximations with dynamic objects based on local multigranulation rough sets in ordered information systems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 55(8), 1821–1855 (2021)
Mandal, P., Ranadive, A.S.: Fuzzy multigranulation decision-theoretic rough sets based on fuzzy preference relation. Soft Comput. 23(1), 85–99 (2019)
Qian, Y., Liang, X., Lin, G., Guo, Q., Liang, J.: Local multigranulation decision-theoretic rough sets. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 82, 119–137 (2017)
Zhou, H., Li, W., Zhang, C., Zhan, T.: Dynamic maintenance of approximations based on dominance-based rough set approach in interval-valued information system. Appl. Intell. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04655-9
Wang, Z., Xiao, F., Ding, W.: Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy jenson-shannon divergence and its application in multi-attribute decision making. Appl. Intell. 52, 16168–16184 (2022)
Liu, J., Huang, B., Li, H., Bu, X., Zhou, X.: Optimization-based three-way decisions with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information. IEEE Trans. Cyb. 53(6), 3829–3843 (2023)
Sun, L., Zhu, L., Li, W., Zhang, Ch., Balezentis, T.: Interval-valued functional clustering based on the Wasserstein distance with application to stock data. Inf. Sci. 606, 910–926 (2022)
Rico, N., Huidobro, P., Bouchet, A., Diaz, I.: Similarity measures for interval-valued fuzzy sets based on average embeddings and its application to hierarchical clustering. Inf. Sci. 615, 794–812 (2022)
Yang, L., Qin, K., Sang, B., Xu, W.: Dynamic maintenance of variable precision fuzzy neighborhood three-way regions in interval-valued fuzzy decision system. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 13, 1797–1818 (2022)
Du, C., Ye, J.: Decision-making strategy for slope stability using similarity measures between interval-valued fuzzy credibility sets. Soft Comput. 26, 5105–5114 (2022)
Zhang, X., Li, J.: Incremental feature selection approach to interval-valued fuzzy decision information systems based on \(\lambda\)-fuzzy similarity self-information. Inf. Sci. 625, 593–619 (2023)
Chang, W., Fu, C., Chang, L.: Triangular bounded consistency of interval-valued fuzzy preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzz. Syst. 30(12), 5511–5525 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Associate Editor and the reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Funding
This paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 12201518), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2023T160401), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (No. CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0152), the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Education Commission (Nos. KJQN202300202, KJQN202100205, KJQN202100206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Authors are ethical for data used.
Informed Consent
Authors are informed consent for data used.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Zhan, T. Multi-Granularity Probabilistic Rough Fuzzy Sets for Interval-Valued Fuzzy Decision Systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 25, 3061–3073 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-023-01577-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-023-01577-z