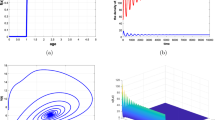
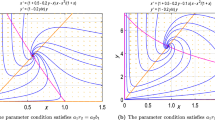
Abstract
In this study, we have analyzed a mathematical model on predator–prey interactions incorporating prey refuge and additive Allee effect on the prey species. The various dynamical behaviors of the system have analyzed, considering the prey refuge is proportional to both the prey and predator species with Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. None, single, or two coexistence equilibria can exist at the first quadrant of the phase space considering strong additive Allee effect in the system. The permanence, local stability, saddle-node bifurcation, existence of a stable limit cycle and Hopf bifurcation are examined under some parametric conditions. We have also calculated the first Lyapunov number to define the nature of Hopf bifurcating periodic solution. Moreover, it has established a parameter subset at which the dynamical system may have a cusp point of co dimension 2 (Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation). Finally, we have executed an adequate numerical simulation to authenticate our analytical findings.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allee WC (1931) Animal aggregations: a study in general sociology. Chicago Press, Chicago
Allee WC (1938) The social life of animals. WW Norton & Co, New York
Allee WC, Park O, Emerson AE, Park T, Schmidt KP (1949) Principles of animal ecology. WB Saundere Co Ltd, Philadelphia
Beddington JR (1975) Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J Anim Ecol 44(1):331–340
Berec L, Angulo E, Courchamp F (2007) Multiple Allee effects and population management. Trends Ecol Evol 22(4):185–191
Birkhoff GG, Rota (1975) Ordinary differential equations. Hafner Press, Michigan
Cai Y, Zhao C, Wang W, Wang J (2015) Dynamics of a Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with additive Allee effect. Appl Math Model 39(7):2092–2106
Carr J (1981) Applications of centre manifold theory. Springer, Berlin
Celik C, Duman O (2009) Allee effect in a discrete-time predator-prey system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40(4):1956–1962
Chen L, Chen F, Chen L (2010) Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling type ii functional response incorporating a constant prey refuge. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 11(1):246–252
Chow SN, Hale JK (1982) Methods of bifurcation theory, vol 251. Springer, Berlin
Chow SN, Li C, Wang D (1994) Normal forms and bifurcation of planar vector fields. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Collings JB (1995) Bifurcation and stability analysis of a temperature-dependent mite predator-prey interaction model incorporating a prey refuge. Bull Math Biol 57(1):63–76
Courchamp F, Clutton-Brock T, Grenfell B (1999) Inverse density dependence and the Allee effect. Trends Ecol Evol 14(10):405–410
Courchamp F, Grenfell BT, Clutton-Brock T (2000) Impact of natural enemies on obligately cooperative breeders. Oikos 91(2):311–322
Das KP (2016) Complex dynamics and its stabilization in an eco-epidemiological model with alternative food. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(4):1–12
De Angelis D, Goldstein R (1975) A model for tritrophic interactions. Ecology 56:881–892
Dennis B (1989) Allee effects: population growth, critical density, and the chance of extinction. Nat Resour Model 3(4):481–538
Freedman H, Waltman P (1984) Persistence in models of three interacting predator-prey populations. Math Biosci 68(2):213–231
Gard TC, Hallam TG (1979) Persistence in food webs Lotka-Volterra food chains. Bull Math Biol 41(6):877–891
González-Olivares E, Ramos-Jiliberto R (2003) Dynamic consequences of prey refuges in a simple model system: more prey, fewer predators and enhanced stability. Ecol Model 166(1–2):135–146
Groom MJ (1998) Allee effects limit population viability of an annual plant. Am Nat 151(6):487–496
Haque M, Sarwardi S (2016) Effect of toxicity on a harvested fishery model. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(3):122
Haque M, Rahman MS, Venturino E, Li BL (2014) Effect of a functional response-dependent prey refuge in a predator-prey model. Ecol Complex 20:248–256
Hassard B, Kazarinof D, Wan Y (1981) Theory and Applications of Hopf Bifurcation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Holling CS (1965) The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Mem Entomol Soc Can 97(S45):5–60
Indrajaya D, Suryanto A, Alghofari AR (2016) Dynamics of modified Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with Beddington-Deangelis functional response and additive Allee effect. Int J Ecol Dev 31(3):60–71
Javidi M (2013) Nematnyamorady, Allee effects in a predator prey system with a saturated recovery function and harvesting. Int J Adv Math Sci 1(2):33–44
Lai X, Liu S, Lin R (2010) Rich dynamical behaviours for predator-prey model with weak Allee effect. Appl Anal 89(8):1271–1292
Lamont BB, Klinkhamer PG, Witkowski E (1993) Population fragmentation may reduce fertility to zero in Banksia goodiia demonstration of the Allee effect. Oecologia 94(3):446–450
Ma Z, Li W, Zhao Y, Wang W, Zhang H, Li Z (2009) Effects of prey refuges on a predator-prey model with a class of functional responses: the role of refuges. Math Biosci 218(2):73–79
Manarul HM, Sarwardi S (2018) Dynamics of a harvested prey-predator model with prey refuge dependent on both species. Int J Bifurc Chaos 28(12):1830040
Merdan H, Duman O, Akın Ö, Çelik C (2009) Allee effects on population dynamics in continuous (overlapping) case. Chaos Solitons Fractals 39(4):1994–2001
Mikko Kuussaari MC, Saccheri Ilik, Hanski I (1998) Allee effect and population dynamics in the Glanville fritillary butterfly. Oikos 82(2):384–392
Molla H, Rahman MS, Sarwardi S (2019) Dynamics of a predator-prey model with Holling type ii functional response incorporating a prey refuge depending on both the species. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 20(1):1–16
Molla H, Rahman MS, Sarwardi S (2020) Incorporating prey refuge in a prey-predator model with Beddington-Deangelis type functional response: a comparative study on intra-specific competition. Discontin Nonlinear Complex 9(1):395–419
Murray JD (1989) Mathematical Biology I: An Introduction, Springer, New York
Pal PJ, Mandal PK (2014) Bifurcation analysis of a modified Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with Beddington-Deangelis functional response and strong Allee effect. Math Comput Simul 97:123–146
Pal PJ, Saha T, Sen M, Banerjee M (2012) A delayed predator-prey model with strong Allee effect in prey population growth. Nonlinear Dyn 68(1–2):23–42
Perko L (2001) Differential equations and dynamical systems. Springer, Berlin
Pusawidjayanti K, Suryanto A, Wibowo R (2015) Dynamics of a predator-prey model incorporating prey refuge, predator infection and harvesting. Appl Math Sci 9(76):3751–3760
Ramos-Jiliberto R (2003) Population dynamics of prey exhibiting inducible defenses: the role of associated costs and density-dependence. Theor Popul Biol 64(2):221–231
Rocha JL, Fournier-Prunaret D, Taha AK (2013) Strong and weak Allee effects and chaotic dynamics in Richards’ growths. Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems-B 18(9):2397
Rudin W (1976) Principles of Mathematical Analysis: International Series in Pure and Applied Mathematics, McGraw-Hill Education
Sahoo B (2015) Role of additional food in eco-epidemiological system with disease in the prey. Appl Math Comput 259:61–79
Sahoo B, Poria S (2016) Effects of additional food in a susceptible-exposed-infected prey-predator model. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(3):160
Sarwardi S, Mandal PK, Ray S (2012) Analysis of a competitive prey-predator system with a prey refuge. Biosystems 110(3):133–148
Sarwardi S, Mandal MR, Gazi NH (2016) Dynamical behaviour of an ecological system with Beddington-Deangelis functional response. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(2):106
Schreiber SJ (2003) Allee effects, extinctions, and chaotic transients in simple population models. Theor Popul Biol 64(2):201–209
Shi J, Shivaji R (2006) Persistence in reaction diffusion models with weak Allee effect. J Math Biol 52(6):807–829
Sotomayor J (1973) Generic bifurcations of dynamical systems. In: Dynamical systems, Elsevier, pp 561–582
Stephens PA, Sutherland WJ (1999) Consequences of the Allee effect for behaviour, ecology and conservation. Trends Ecol Evol 14(10):401–405
Stephens PA, Sutherland WJ, Freckleton RP (1999) What is the allee effect? Oikos 87(1):185–190
Tewa JJ, Djeumen VY, Bowong S (2013) Predator-prey model with Holling response function of type ii and sis infectious disease. Appl Math Model 37(7):4825–4841
Trisdiani P, Trisilowati AS (2014) Dynamics of harvested predator-prey system with disease in predator and prey in refuge. Int J Ecol Econ Stat 33:47–57
Van Voorn GA, Hemerik L, Boer MP, Kooi BW (2007) Heteroclinic orbits indicate overexploitation in predator-prey systems with a strong Allee effect. Math Biosci 209(2):451–469
Venturino E (1995) Epidemics in predator-prey models: diseases in the prey. Math Popul Dyn Anal Heterog 1:381–393
Wang MH, Kot M (2001) Speeds of invasion in a model with strong or weak Allee effects. Math Biosci 171(1):83–97
Wang W, Yn Zhu, Cai Y, Wang W (2014) Dynamical complexity induced by Allee effect in a predator-prey model. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 16:103–119
Wiggins S (1991) Introd Appl Nonlinear Dyn Syst Chaos. Springer-Verlag, USA
Zhou SR, Liu YF, Wang G (2005) The stability of predator-prey systems subject to the Allee effects. Theor Popul Biol 67(1):23–31
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author Dr. Sarwardi is grateful to the Department of Mathematics & Statistics, Aliah University for extending support to perform the present work. Mr. Molla is highly thankful to Department of Mathematics, Manbhum Mahavidyalaya for giving opportunity to do this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix
A1. The values of the coefficients A, B, C, D and E used in Eq. (5) are given bellow
A2. The constants \(\alpha _{i}\) \((i=1,2,3,4)\) given in local stability section are as follows
A3. The Jacobian matrix of the system (1) at \((x^{*},y^{*})\) is as follows
where
A4 The expressions of \(D^{2}F(E^{*},\delta _{sn})(\chi ,\chi )\) and \(D^{3}F(E^{*},\delta _{sn})(\chi ,\chi ,\chi )\) are defined by the following quantities
A5. The expressions of \(l_{ij}\) and \(m_{ij}\) \((i,j=0,1,2,3)\), shown in "Behavior of Hopf bifurcation periodic solution" section are as follows
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molla, H., Rahman, M.S. & Sarwardi, S. Dynamical study of a prey–predator model incorporating nonlinear prey refuge and additive Allee effect acting on prey species. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 7, 749–765 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01049-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01049-5
Keywords
- Refuge
- Additive Allee
- Stability
- Saddle-node and Hopf bifurcation
- Lyapunov number
- Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation
- Numerical simulation