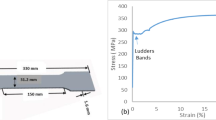
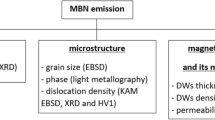
Abstract
Plastic processing operations of ferromagnetic materials may cause significant mechanical stress, which has a strong impact on its final magnetic behavior. In this paper, the magneto-mechanical correlations between the stress-strain behavior and magnetic Barkhausen noise emission in three typical steels subjected to uniaxial tension were studied comparatively, the tensile damage and fracture morphology of each sample was identified by magnetic measurements and scanning electron microscopy. The results show that the characteristics values of Barkhausen noise envelope can be approximated by a parabolic function of the carbon content experimentally and theoretically. In the elastic region, the Barkhausen noise response exhibits progressive growth with increasing strain, and reaches saturation at a critical point for the stress-induced magnetic anisotropy. However, once plastic deformation occurs, the Barkhausen noise signal intensity appears a downward trend until specimen failure, because the increasing dislocation tangles further hinder the domain wall motion. According to the mapping of Barkhausen noise eigenvalues, the location of tensile cracking is determined with a very satisfactory agreement. This indicates that the magnetic Barkhausen noise technique can be used for the nondestructive quantitative evaluation of elastoplastic deformation and failure location of ferromagnetic products.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiles DC (2015) Introduction to magnetism and magnetic materials. CRC press.
Huang H, Qian Z (2018) Recent advances in magnetic non-destructive testing and the application of this technique to remanufacturing. Insight-Non-Destructive Test Condition Monit 60(8):451–462.
Liu B, Xue XM, Li JM, Li RF, Dong SY, Fang JX (2019) Grain size effect on metal magnetic memory signal for stress damage evaluation of low carbon steel. Nondestructive Test Evaluation 34(3):267–282.
Zhang ZW, Feng YF, Tan Q, Zou JW, Li J, Zhou XM, Sun GG, Wang YD (2019) Residual stress distribution in Ni-based superalloy turbine discs during fabrication evaluated by neutron/X-ray diffraction measurement and thermomechanical simulation. Mater Design 166:107603.
Fagan P, Ducharne B, Daniel L, Skarlatos A, Domenjoud M, Reboud C (2022) Effect of stress on the magnetic barkhausen noise energy cycles: a route for stress evaluation in ferromagnetic materials. Mater Sci Engineering: B 278:115650.
Cardon M (2007) The marketing of Barkhausen noise analysis. Shot Peener 21(2):18–20.
Wolter B, Gabi Y, Conrad C (2019) Nondestructive testing with 3MA-an overview of principles and applications. Appl Sci 9(6):1068.
Moorthy V, Vaidyanathan S, Laha K, Jayakumar T, Rao KBS, Raj B (1997) Evaluation of microstructures in 2.25 Cr-1Mo and 9Cr-1Mo steel weldments using magnetic barkhausen noise. Mater Sci Engineering: A 231(1–2):98–104.
Neslušan M, Čížek J, Kolařík K, Minárik P, Čilliková M, Melikhova O (2017) Monitoring of grinding burn via Barkhausen noise emission in case-hardened steel in large-bearing production. J Mater Process Technol 240:104–117.
Zerovnik P, Grum J, Zerovnik G (2009) Determination of hardness and residual-stress variations in hardened surface layers with magnetic barkhausen noise. IEEE Trans Magn 46(3):899–904.
Stefanita CG, Atherton DL, Clapham L (2000) Plastic versus elastic deformation effects on magnetic barkhausen noise in steel. Acta Mater 48(13):3545–3551.
Pastorek F, Decký M, Neslušan M, Pitoňák M (2021) Usage of Barkhausen noise for assessment of corrosion damage on different low alloyed steels. Appl Sci 11(22):10646.
Liu J, Tian GY, Gao B, Zeng K, Zheng Y, Chen J (2020) Micro-macro characteristics between domain wall motion and magnetic barkhausen noise under tensile stress. J Magn Magn Mater 493:165719.
Ding S, Tian GY, Ruslee S (2019) Non-destructive hardness prediction for 18CrNiMo7-6 steel based on feature selection and fusion of magnetic Barkhausen noise. Ndt & E International 107:102138.
Jiles DC (2000) Dynamics of domain magnetization and the Barkhausen effect. Czech J Phys 50(8):893–988.
Jiles DC, Sipahi LB, Williams G (1993) Modeling of micromagnetic barkhausen activity using a stochastic process extension to the theory of hysteresis. J Appl Phys 73(10):5830–5832.
Jiles DC, Li L (2004) A new approach to modeling the magnetomechanical effect. J Appl Phys 95(11):7058–7060.
Kersten M (1943) Underlying theory of ferromagnetic hysteresis and coercivity. Hirzel., Leipzig.
Sakamoto H, Okada M, Homma M (1987) Theoretical analysis of Barkhausen noise in carbon steels. IEEE Trans Magn 23(5):2236–2238.
Capo-Sanchez J, Perez-Benitez JA, Padovese LR, Serna-Giraldo C (2004) Dependence of the magnetic Barkhausen emission with carbon content in commercial steels. J Mater Sci 39:1367–1370.
Kashefi M, Krause TW, Underhill PR, Saleem A, Farrell SP (2021) Decoupling the effect of stress and microstructure on MBN response in cast Q1N steel. Mater Sci Technol 37(15):1225–1235.
Wang Y, Melikhov Y, Meydan T (2022) Multifunctional induction coil sensor for evaluation of carbon content in carbon steel. IEEE Trans Magn 59(2):1–5.
Deng Y, Li Z, Chen J, Qi X (2018) The effects of the structure characteristics on magnetic barkhausen noise in commercial steels. J Magn Magn Mater 451:276–282.
Ng DHL, Cheng K, Cho KS, Ren ZY, Ma XY, Chan SLI (2001) Nondestructive evaluation of carbon contents and microstructures in plain carbon steel bars by Barkhausen emission. IEEE Trans Magn 37(4):2734–2736.
Jiles DC, Kiarie W (2020) An integrated model of magnetic hysteresis, the magnetomechanical effect, and the Barkhausen effect. IEEE Trans Magn 57(2):1–11.
Stefanita CG, Clapham L, Atherton DL (2000) Subtle changes in magnetic barkhausen noise before the macroscopic elastic limit. J Mater Sci 35(11):2675–2681.
Gorkunov E, Povoltskaya A, Solov’ev K, Zadvorkin S (2010) The influence of the magnetoelastic effect on the hysteretic properties of medium-carbon steel during uniaxial loading. Russ J Nondestr Test 46(9):638–644.
Anglada-Rivera J, Padovese LR, Capo-Sanchez J (2001) Magnetic barkhausen noise and hysteresis loop in commercial carbon steel: influence of applied tensile stress and grain size. J Magn Magn Mater 231(2–3):299–306.
Bao S, Jin P, Zhao Z, Fu M (2020) A review of the metal magnetic memory method. J Nondestr Eval 39:1–14.
Liu T, Kikuchi H, Ara K, Kamada Y, Takahashi S (2005) Relationship between magnetic properties and external stresses during in situ tensile testing. Trans Magnetics Soc Japan 5(1):35–38.
Samimi AA, Krause TW, Clapham L (2016) Multi-parameter evaluation of magnetic barkhausen noise in carbon steel. J Nondestr Eval 35(3):40–48.
Samimi AA, Krause TW, Clapham L (2016) Stress response of magnetic barkhausen noise in submarine hull steel: a comparative study. J Nondestr Eval 35(2):32–38.
Dhar A, Clapham L, Atherton DL (2001) Influence of uniaxial plastic deformation on magnetic barkhausen noise in steel. Ndt & E International 34(8):507–514.
Taylor RA, Jakubovics JP, Astié B, Degauque J (1983) Direct observation of the interaction between magnetic domain walls and dislocations in iron. J Magn Magn Mater 31:970–972.
Lambri OA, Weidenfeller B, Bonifacich FG, Pérez-Landazábal JI, Cuello GJ, Weidenfeller L, Recarte V, Zelada GI, Riehemann W (2021) Magnetic behavior in commercial iron-silicon alloys controlled by the dislocation dynamics at temperatures below 420 K. J Alloys Compd 856:157934.
Serbin ED, Kostin VN, Vasilenko ON, Ksenofontov DG, Gerasimov EG, Terentev PB (2020) Influence of the two-stage plastic deformation on the complex of the magneto-acoustic characteristics of low-carbon steel and diagnostics of its structural state. NDT & E International 116:102330.
Kleber X, Vincent A (2004) On the role of residual internal stresses and dislocations on Barkhausen noise in plastically deformed steel. NDT & E International 37(6):439–445.
Krause TW, Atherton DL, Sullivan SP (1997) Magnetic barkhausen noise indicators of cracks in steel. Nondestructive Test Evaluation 13(6):309–323.
Krause TW, Makar JM, Atherton DL (1994) Investigation of the magnetic field and stress dependence of 180 domain wall motion in pipeline steel using magnetic barkhausen noise. J Magn Magn Mater 137(1–2):25–34.
Chen L, Li DJ, Zhang MY, Shen M, Huo JH, Li YJ (2022) Strain energy evolution analysis of elastic-plastic deformation on polycarbonate by infrared radiation characteristics. Nondestructive Test Evaluation, 1–20.
Gaunkar NP, Jiles DC, Gaunkar GP (2020) Detection of surface cracks in ferromagnetic materials by C-scan mapping of residual stresses using Barkhausen emissions. AIP Adv 10(1):015246.
Franco FA, Padovese LR (2009) NDT flaw mapping of steel surfaces by continuous magnetic barkhausen noise: volumetric flaw detection case. NDT & E International 42(8):721–728.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Zhejiang Basic Public Welfare Research Project (LGF21E040003) and the Major Special Project of Ningbo Science and Technology Innovation 2025 (2022Z165) for their financial supporting this present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, J., Shen, Z., Zhong, J. et al. In-Situ Magnetic Barkhausen Noise Measurements to Identify Elastic-Plastic Deformation and Failure in Different Steels. Exp Tech 48, 381–392 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-023-00663-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-023-00663-z