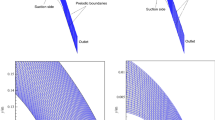
Abstract
Thermodynamic losses and blade erosion occur due to formation of wetness in the low-pressure steam turbine. By changing the trailing edge angle of turbine blade can reduce blade erosion and condensation losses. This research optimized the best of the trailing edge rotation to improve the turbine's operation at the low-pressure part of the steam turbines (thermodynamic losses and blade erosion) as passive method. In this paper, the integral of the number of droplets per volume (IND), the integral of the droplet average radius (IDR), the integral of wetness fraction (IWF), the integral of local entropy (ILE), and the integral of dynamic pressure (IDP) were considered as goals of optimization. The results introduce an optimal case (θ = − 0.84o counterclockwise) while improved IDR by 0.276%, increased IND by 0.0389%, improved IWF by 0.207%, reduced IDP by 0.054%, and increased ILE by 0.0074%. In addition, this optimization caused the erosion rate to be improved by 2.33% and the condensation losses to be decreased by 0.39%.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Area (m2)
- IWF:
-
Integral of wetness fraction (-)
- ILE:
-
Integral of local entropy (\(\frac{J}{kg K}\))
- IDP:
-
Integral of dynamic pressure (\(\frac{kg}{m {s}^{2}}\))
- IDR:
-
Integral of droplet average radius fraction (\(\mu m\))
- IND:
-
Integral of number of droplets per volume (\({m}^{-2}\))
- L:
-
Total length of blade geometry (m)
- Ma:
-
Mach number (-)
- P:
-
Pressure (Pa)
- r:
-
Droplet radius (μm)
- \(\overline{r }\) :
-
Droplet average radius (m)
- T:
-
Temperature (K)
- u:
-
Velocity (m/s)
- X:
-
Length parameter of blade geometry (m
- α:
-
Angle of second position (o)
- β:
-
Angle of first position (o)
- Γ:
-
Liquid mass fraction (kg/m3 s)
- η:
-
Number of droplets per volume (1/m2)
- θ:
-
Trailing edge rotation of blade (o
References
Li Y, Wu H, Tang Y, Fu W, Liu Z (2018) Numerical study for the influences of primary steam nozzle distance and mixing chamber throat diameter on steam ejector performance. Int J Thermal Sci 132:509–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2018.06.033
Dolatabadi AM, Lakzian E, Heydari M, Khan A (2022) A modified model of the suction technique of wetness reducing in wet steam flow considering power-saving. Energy 238:121685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121685
Keisari SJ, Shams M (2016) Shape optimization of nucleating wet-steam flow nozzle. Appl Therm Eng 103:812–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.04.134
Mirhoseini MS, Boroomand M (2017) Multi-objective optimization of hot steam injection variables to control wetness parameters of steam flow within nozzles. Energy 141:1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.138
Dykas S, Majkut M, Smolka K, Strozik M (2018) Analysis of the steam condensing flow in a linear blade cascade. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part A J Power Energy 232(5):501–514. https://doi.org/10.1177/0957650917743365
Bakhtar F, Zidi K (1989) Nucleation phenomena in flowing high-pressure steam: Experimental results. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part A J Power Eng 203(3):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1243/PIME_PROC_1989_203_027_02
Wang X, Su P, Chou L, Guan P, Li C, Zhou H (2009) Water droplets dispersion and optimization of water removal suction slot locations on stationary blades in last-stage of a 600 mw steam turbine, in: ASME Turbo Expo 2009: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, Vol. 7, American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection, pp. 1439–1446. https://doi.org/10.1115/GT2009-59490
Liu Y, Du X, Shi X, Huang D Condensation flow at the wet steam centrifugal turbine stage. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part A J Power Energy. https://doi.org/10.1177/0957650919894823.
Beheshti KM, Amiri H (2015) The effect of inlet stagnation supercooling degree on the aerodynamics of the steam flow field around a rotor tip section. Heat Mass Transfer 51:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-014-1402-5
Su J, Li Q, Hu P, Cao L, Li Y (2020) Distribution characteristics of salt-out particles in steam turbine stage. Energy 192:116626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116626
Bhattacharya, Chittatosh, Sengupta, Bidesh Investigation of energy loss on fractional deposition in last stages of condensing steam turbine due to blade shape and moisture droplet size. J Eng Gas Turbines Power 140 (7). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4038544
Lakzian E, Wen C, Wang C, Ding H, Li Y (2019) Entropy generation and exergy destruction in condensing steam flow through turbine blade with surface roughness. Energy Convers Manag 196:1089–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.06.066
Zhang G, Zhang X, Wang F, Wang D, Jin Z, Zhou Z (2019) Numerical investigation of novel dehumidification strategies in nuclear plant steam turbine based on the modified nucleation model. Int J Multiph Flow 120:103083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2019.103083
Alekseev R, Gribin V, Tishchenko A, Gavrilov IY, Tishchenko V, Popov V (2019) Investigation of the influence of intra-channel liquid film suction on the structure of the droplet flow downstream a stator blades cascade of a steam turbine. J Phy Conf Ser 1359:012024
Gribin V, Tishchenko A, Gavrilov IY, Popov V, Sorokin IY, Tishchenko V, Khomyakov S (2016) Experimental study of intrachannel separation in a flat nozzle turbine blade assembly with wet stream flow. Power Technol Eng 50(2):180–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10749-016-0680-0
Amiri HB, Salmaniyeh F, Izadi A (2016) The influence of incidence angle on the aerodynamics of condensing flow around a rotor tip section of steam turbine. Heat Mass Transf 52(11):2423–2436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1736-7
Bagheri-Esfe H, Kermani MJ, Saffar-Avval M (2016) Effects of nonequilibrium condensation on deviation angle and efficiency in a steam turbine stage. J Mech Sci Technol 30(3):1351–1361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-016-0242-2
Mahmoud NH, Singh UK (2000) Wetness and Losses Control Using Geometry Considerations in Low Pressure Stages of Steam Turbines. ERJ Eng Res J 23(2):119–149
Havakechian S, Greim R (1999) Aerodynamic design of 50 per cent reaction steam turbines. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci 213(1):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1243/0954406991522158
Han X, Han Z, Zeng W, Li P, Qian J Numerical simulation of wet steam transonic condensation flow in the last stage of a steam turbine. Int J Num Methods Heat Fluid Flow. https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-10-2017-0415
Nowak G, Wr´oblewski W, Nowak I (2012) Convective cooling optimization of a blade for a supercritical steam turbine. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 55(17):4511–4520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.03.072
Vatanmakan M, Lakzian E, Mahpeykar MR (2018) Investigating the entropy generation in condensing steam flow in turbine blades with volumetric heating. Energy 147:701–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.097
Hosseini R, Lakzian E (2019) Optimization volumetric heating in condensing steam flow by a novel method. J Thermal Anal Calorimetry: 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09001-1
Bagheri-Esfe H, Safikhani H (2017) Modeling of deviation angle and performance losses in wet steam turbines using gmdh-type neural networks. Neural Comput Appl 28(1):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2389-2
Farnam M, Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Asadollahzadeh MJ (2018) Heat transfer intensification of agitated U-tube heat exchanger using twisted-tube and twisted-tape as passive techniques. Chem Eng Processi Process Intensif 133:137–147
Guodong Y, Zhou H, Qiu L, Wu J (2020) Geometry-Load Based Hybrid Correction Method for the Pre-Deformation Design of a Steam Turbine Blade. Energies 13(10):2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102471
Ebrahimi-Fizik A, Lakzian E, Hashemian A (2019) Entropy generation analysis of wet-steam flow with variation of expansion rate using nurbs-based meshing technique. Int J Heat Mass Transf 139:399–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.05.010
Zhonghe H, Zeng W, Han X, Xiang P (2018) Investigating the dehumidification characteristics of turbine stator cascades with parallel channels. Energies 11(9):2306. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092306
Sieverding C, Manna M (2020) A review on turbine trailing edge flow. Int J Turbomach Propuls Power 5(2):10
Wei W, Rong M, Zhang Y (2011) Multi-objective aerodynamic optimization design method of compressor rotor based on Isight. Procedia Eng 15:3699–3703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.08.693
Papila N, Shyy W, Griffin L, Dorney D (2016) Shape optimization of supersonic turbines using response surface and neural network methods, in: 39th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, p. 1065. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2001-1065
Huppertz A, Flassig PM, Flassig RJ, Swoboda M (2007) Knowledge based 2d blade design using multi-objective aerodynamic optimization and a neural network, in: ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection, pp. 413–423. https://doi.org/10.1115/GT2007-28204
Özhan Ö, Akmandor İS (2010) Multi-objective aerodynamic optimization of axial turbine blades using a novel multilevel genetic algorithm: 041009
Hoseinzade D, Lakzian E, Hashemian A (2021) A blackbox optimization of volumetric heating rate for reducing the wetness of the steam flow through turbine blades. Energy 220:119751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119751
Bakhtar F, Mahpeykar MR, Abbas KK (1995) An investigation of nucleating flows of steam in a cascade of turbine blading-theoretical treatment. J Fluids Eng 117(1):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2816803
Byeong-Eun L, Riu K, Shin S, Kwon S (2003) Development of a water droplet erosion model for large steam turbine blades. KSME Int J 17(1):114–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984292
Aliabadi MAF, Lakzian E, Jahangiri A, Khazaei I (2020) Numerical investigation of effects polydispersed droplets on the erosion rate and condensation loss in the wet steam flow in the turbine blade cascade. Appl Thermal Eng 164:114478
Coello CCA, Lamont GB, Veldhuizen DAV (2007) Evolutionary algorithms for solving multi-objective problems, vol 5. Springer, New York
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Prof. Ali Hashemian (BCAM – Basque Center for Applied Mathematics, Bilbao, Basque Country, Spain) for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoseinzade, D., Lakzian, E. & Dykas, S. Optimization of the Trailing Edge Inclination of Wet Steam Turbine Stator Blade Towards the Losses Reduction. Exp Tech 47, 269–279 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-021-00534-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-021-00534-5