Abstract
Hydraulic fracturing is an effective technology for coal reservoir stimulation. After fracturing operation and flowback, a fraction of fracturing fluid will be essentially remained in the formation which ultimately damages the flowability of the formation. In this study, we quantified the gel-based fracturing fluid induced damages on gas sorption for Illinois coal in US. We conducted the high-pressure methane and CO2 sorption experiments to investigate the sorption damage due to the gel residue. The infrared spectroscopy tests were used to analyze the evolution of the functional group of the coal during fracturing fluid treatment. The results show that there is no significant chemical reaction between the fracturing fluid and coal, and the damage of sorption is attributed to the physical blockage and interactions. As the concentration of fracturing fluid increases, the density of residues on the coal surface increases and the adhesion film becomes progressively denser. The adhesion film on coal can apparently reduce the number of adsorption sites for gas and lead to a decrease of gas sorption capacity. In addition, the gel residue can decrease the interconnectivity of pore structure of coal which can also limit the sorption capacity by isolating the gas from the potential sorption sites. For the low concentration of fracturing fluid, the Langmuir volume was reduced to less than one-half of that of raw coal. After the fracturing fluid invades, the desorption hysteresis of methane and CO2 in coal was found to be amplified. The impact on the methane desorption hysteresis is significantly higher than CO2 does. The reason for the increasing of hysteresis may be that the adsorption swelling caused by the residue adhered on the pore edge, or the pore blockage caused by the residue invasion under high gas pressure. The results of this study quantitatively confirm the fracturing fluid induced gas sorption damage on coal and provide a baseline assessment for coal fracturing fluid formulation and technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Gas production from coal not only provide clean energy, but also improve the safe mining when coal is being mined (Yuan 2016; Cao et al. 2017; Zou et al. 2021; Tian et al. 2020). Coal is known as its low permeability due to its tight structure (Liu and Harpalani 2013; Zhai et al. 2016; Zou et al. 2015; Guo et al. 2020). Hydraulic fracturing is widely used in the coalbed methane (CBM) extraction (Montgomery and Smith 2010; Cao et al. 2017; Xu et al. 2017). In hydraulic fracturing operation, the high-pressure proppant-carrying fluid is injected into the coal formation and the proppants are trapped in the CBM fracture system to maintain high permeability pathway after the flowback (Ma et al. 2017; Lv et al. 2018; Zhai et al. 2018; Zhi et al. 2018). In CBM fracturing, fracturing fluids commonly used can be divided into slick water and gel (Li et al. 2016; Thombare et al. 2016). In recent years, the viscoelastic surfactants containing fracturing fluids have been applied (Yang 2017; Lu et al. 2015). In CBM fracturing jobs, 20%–30% of the injected fracturing fluid was observed to be permanently retained in the reservoir from the field observations (Palmer et al. 1991; Al-Ameri et al. 2018; Huang et al. 2021).
The fracturing fluid residues may have a series of effects on the reservoir flow deliverability due to physical blockage of flow pathway (Huang et al. 2020). In addition to the damage of permeability, the residual fracturing fluid may significantly modify the surface property of coal which will ultimately change sorption and diffusion behaviors of coal (Yang et al. 2019a, b; Liu et al. 2019). Chen et al. observed that the degree of influence of fracturing fluid on the adsorption of methane in CBM formation is closely related to coal rank, and Lean coal has the most evident influence among coking coal, lean coal and anthracite (Chen et al. 2009). The fracturing fluid can reduce the diffusivity of coal and the fracturing fluid as the absorbate can absorb a certain amount of gas (Kang et al. 2016). You et al. (2015) compared the performance and mechanism of anionic surfactants and cationic surfactants in the formulation of clean fracturing fluids to inhibit methane desorption. Interestingly, Lu et al. found that the clean fracturing fluid can eliminate the clay minerals in the pores through chemical reactions, thereby widening the pores for gas flow (Lu et al. 2017). When different types of fracturing fluids were applied on the coal surface, different contact angles were observed and they therefore have different influence on desorption and diffusion of methane in the coal (Chen et al. 2009). Additionally, CO2 is often used as an additive, mixed with gel or surfactant to prepare fracturing fluid to improve fracturing performance in recent years (Jing et al. 2014; Li et al. 2020). It can be inferred that the solid or liquid residues of the fracturing fluid may also cause changes in the adsorption and desorption of CO2 in the coal, thereby affecting the final fracturing stimulation effect. There are differences in the adsorption and mechanism of methane and CO2 in coal (Zhang and Liu 2017; Guan et al. 2018). Therefore, the influence of fracturing fluid residues invading to the coal on CO2 adsorption may also be different from that on methane adsorption. However, there are very few experimental studies on the impact of hydraulic fracturing on the flowability of CO2 in coal seam.
Gas desorption is the first stage of the gas migration process in coal mine gas drainage process. We used the coal samples from the Illinois Basin in the United States as testing samples and explored the influencing characteristics and mechanism of the gel fracturing fluid on the methane and CO2 ad-/desorption behavior. The finding of this study can provide a baseline reference for the optimization and improvement of coal seam fracturing fluid blending towards final effective formation stimulations.
2 Preparations of coal samples and fracturing fluids
For the CBM fracturing fluid additives, we chose the following additives and level for our experiments. We used hydroxypropyl guar (HPG) cellulose as the thickener and four concentrations were proposed and they were 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.8%, 1.2% (weight percent), respectively. The organoboron was chosen as the cross-linking agent with a concentration of 0.4%, the potassium chloride (KCl) as the anti-swelling agent with a concentration of 1.5% and the ammonium persulfate as the gel breaker with a concentration of 0.04%. For fracturing fluid preparation, the following detailed procedure was followed: (1) keep the well-mixed water in the beaker at room temperature; (2) add 1.5% KCL as anti-swelling agent to the beaker; (3) add all targeted additives and stir to make it completely dissolved; (4) finally, let it stand until the bubbles in the prepared fluids gradually rise and disappear. All the prepared fluids were then stored at the environmental chamber for future coal sample treatments.
For the sorption experiments, Illinois (IL) basin high-volatile bituminous coal samples were used. The fresh coal blocks were collected from the Illinois No. 6 coal seam from southern Illinois region in USA. Coal was pulverized and screened to 60 to 80 mesh (0.25 to 0.18 mm). We partitioned the coal sample into several portions with each portion of 50 g.
For the coal sample treatment, 500 g of each fracturing fluid was used to treat 50 g of coal sample for 5 days. To allow well mixing, the fluid and sample were stirred for 5 min for each day. After the 5-day treatment, the coal samples were dried. In order to prevent the coal sample components from chemically reacting with the fracturing fluid during the high-temperature treatment process, which would interfere with the experimental results of the study, the low-temperature drying was carried out at 60 °C. Raw coal was used as the control group. The raw coal was soaked in 500 g of clean water, and the same length of soaking and drying treatment was carried out with the coal sample after the fracturing fluid treatment. Both raw and treated coal samples were tested for gas sorption experiments for both methane and CO2. To check whether chemical structure of coal altered or not due to fracturing fluid treatment, infrared spectroscopic analyses were used to probe each group of coal samples.
3 Gas sorption experiments and modeling
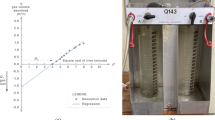
All gas sorption experiments were carried out using the HPT-SDVS sorption system, manufactured by UNGES LLC, USA. Figure 1 shows the schematic and photo of the HPT-SDVS sorption system. The system includes a reference cell and a sample cell which are used for quantifying the Gibbs gas storage capacity. In the process of carbon dioxide and methane adsorption experiments, we used the high-pressure volumetric method to determine the adsorption capacity of the gas. The specific steps are: After dehydration and drying at constant temperature, the treated dry coal sample is put into the sample cell, and then the sample cell is placed in a 30 °C constant temperature water bath, and the vacuum pump is started to degas the coal sample in the sample cell. After 8 h of continuous degassing, the sample cell is filled with 99.99% high-purity methane to maintain the internal pressure of the sample cell at about 6 MPa, and the internal pressure data of the sample cell is collected every 5 s to the range where the pressure fluctuates up and down. Within the error fluctuation range of the sensor, record the sensor data at this time, which is the equilibrium pressure at this time. The Gibbs and absolute gas sorption amounts were calculated for each equilibrium pressure, which are used for the gas sorption isotherm establishment (Adrian et al. 1998).
Gas adsorption kinetics is important for the gas storage modeling and many mathematical representations of gas sorption isotherms have been proposed and used, incluidng Langmuir model, BET model, D-R model and D-A model (Yang et al. 2019a, b; Dutta et al. 2008). The Langmuir model is a sorption model based on the monolayer sorption theory (Eq. (1)). Because of its simplicity, Langmuir model is the most widely used mathematical representation for gas sorption on coal (Levy et al. 1997). In this study, the Langmuir model was used to analyze the sorption data:
where, VGibbs is the Gibbs sorption capacity, mL/g; VL is the Langmuir volume, which represents the limit adsorption capacity of the coal sample for methane, mL/g; PL is the Langmuir pressure, representing the half of the equilibrium pressure of the gas corresponding to the limit adsorption capacity, MPa.
The total gas sorption capacity should be represented by the absolute sorption volume. The occupied adsorbed phase should be corrected based on the Gibbs sorption capacity. Sudibandriyo et al. proposed the calculation formula of absolute adsorption (Huang et al. 2022; Li et al. 2019):
where, Vabs is the absolute adsorption capacity, ρgas and ρads are the gas phase and adsorption phase density. For methane, its adsorption phase density is 0.421 g/cm3, which is an assumption that the adsorbed gas is of liquid phase density. Under different pressure conditions, the density of methane is not the same, which can be calculated by the Peng-Robinson equation (Sudibandriyo et al. 2003).
4 Microscopic surface observation and infrared spectroscopy analyses of tested coals
The fracturing fluid may form colloid clusters to physically cover the sorption sites and modify the sorption characteristics of coal. It is also possible that the chemical additive of fracturing fluid can potentially react with the coal surface functional groups and radicals of coal to alter the sorption behavior of coal. To investigate the physical coverage of fracturing fluid, we used a digital microscope to observe and analyze the surface of each group of coal samples (Fig. 2).
To quantify the chemical surface property evolution, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FTIR) was used to measure the changes in the surface functional groups of the coal sample before and after fracturing fluid treatment. This experiment uses Bruker VERTEX 80v infrared spectrometer, and the probing spectrum ranges from 8000 to 350 cm−1.
In FTIR experiment, potassium bromide mainly acts as a diluent in the process of tableting. Infrared spectroscopy is used in analytical chemistry in the mid-infrared region, that is, in the range of 4000–400 cm−1. Potassium bromide has no absorption in the mid-infrared region, and it will not interfere with the sample signal when it is used to compress tablets. Therefore, the sample preparation method used is the potassium bromide tableting method. The specific experimental steps are: take 1–2 mg of coal powder in an agate mortar, add about 150 mg of potassium bromide, and grind until the two are evenly mixed, and the particle size of the mixture is approximately 2 μm. Take an appropriate amount of the mixture and move it into the tableting mold, stack it evenly, and press it on the tableting machine for about 30 s to make a transparent sample sheet for FTIR measurement. After obtaining the infrared spectrum of each sample, each peak was classified and analyzed to compare the chemical shifts.
Figure 3 shows methane adsorption and desorption isotherms for IL raw coal. There is no apparent desorption hysteresis for raw coal. Figure 4 shows the sorption isotherms with different fracturing fluids treatments. It is apparent that the fracturing fluid treatments significantly reduce the methane gas sorption capacity with comparison between Figs. 3 and 4. Among the 4 groups of treated coal samples, the sorption capacities are somewhat similar. It is worthwhile to mention that the high levels of HPG (0.8% and 1.2%) can lead to a noticeable desorption hysteresis as illustrated in Fig. 4.
5 Result analyses and discussion
5.1 Adsorption and desorption characteristics of coal sample treated by fracturing fluid
Figures 3, 4, 5 and 6 show the experimental data of adsorption and desorption isotherms for all tested coal samples. Overall, Langmuir model can describe the sorption behaviors within the tested pressure range. This confirms that the Langmuir model can be used to define the sorption capacity and pressure relationship when pressure is up to 8 MPa.
As expected, the CO2 sorption capacity is much higher than methane if we compare Figs. 3 and 5. Similar to methane sorption, the CO2 sorption capacity decrease after the fracturing fluid treatments as illustrated in Figs. 5 and 6. To quantitatively analyze the influence of fracturing fluid on the sorption of methane and CO2 on IL coal, the Langmuir volumes were estimated and compared in Fig. 7. The Langmuir volume represents the ultimate gas adsorption capacity of coal, that is, the larger the Langmuir volume, the stronger the gas adsorption capacity of coal at the infinite pressure. From Fig. 7, it was found that the Langmuir volume of the IL coal for CO2 adsorption is 42.5 mL/g, which is almost twice of methane adsorption of 22.2 mL/g. As can be seen in Fig. 7a, for the coal samples treated with 0.2%, 0.4%, and 1.2% concentration gel fracturing fluid, the Langmuir volume of the coal samples treated with the gel fracturing fluid decreases as the concentration increases. However, the Langmuir volume of coal samples treated with 0.8% concentration gel fracturing fluid was higher than that of other experimental groups. This may result from the uneven adhesion of gel residue on coal.
To quantitatively evaluate the fracturing fluid induced sorption damage, this study introduces a concept of sorption damage factor (α) as described as:
where, VL0 is the volume of Langmuir absorbed by the raw coal, and VLr is the Langmuir volume after the fracturing fluid treatment. The larger the adsorption damage factor, the more the gas adsorption capacity decreases, and the more fracturing fluid damages the gas adsorption capacity of the coal.
Therefore, the relationship between the damage factor of methane and CO2 adsorption of each group of coal samples and the fracturing fluid concentration is plotted as shown in Fig. 8. The damage factor of gel fracturing fluid to coal methane sorption capacity is significantly higher than the damage factor to CO2 in coal as illustrated in Fig. 8. There is no direct correlation between the damage factor of methane adsorption and the concentration of the fracturing fluid, indicating that even at a lower concentration level, the fracturing fluid has decent damage on coal methane sorption capacity. As the concentration of fracturing fluid increases, the CO2 adsorption damage factor starts with 20% and increase up to 35% and then plateaued at 35%.
Figures 4, 5, 6, and 7 show that regardless of the raw coal or the coal sample treated with fracturing fluid, both adsorption and desorption processes show different degrees of hysteresis, that is, the sorption is not completely reversible, resulting in a hysteresis loop between the adsorption and desorption curves. In other words, in the process of pressure reduction, part of the previously adsorbed methane molecules failed to desorb and transport out. The hysteresis of coal adsorption and desorption of methane or CO2 has been observed for a long time (Anderson et al. 1966), scholars have proposed a variety of hypotheses about the internal mechanism of adsorption and desorption hysteresis. In the early days, Bell et al. believed that the hysteresis phenomenon was due to the excessive activation energy between gas molecules and coal macromolecules in the desorption phase (Wang et al. 2016). In addition, long-term observations have identified various factors, including temperature, moisture, and coal rank, can affect the hysteresis of coal gas sorption. For the quantitative evaluation of the degree of hysteresis, there are also many methods, such as Freundlich index (Baskaran and Kennedy 1999), solid phase equilibrium concentration (Chen et al. 2004), or evaluation based on the slope of the adsorption–desorption curve and the difference in the area under the curve (Braida et al. 2003). In this study, the average hysteresis index (AHI) index proposed by Zhu (1996) is used to quantitatively evaluate the degree of adsorption and desorption of coal samples. The essence of this method is to integrate the percentage of the area under the desorption curve and the area under the adsorption curve. The specific calculation process is as follows:
where, Aad and Ade respectively represent the area under the isotherm adsorption line and the isotherm desorption line, \(P_{\text{L}}^{\text{ad}}\) and \(P_{\text{L}}^{\text{de}}\) respectively represent the Langmuir pressure corresponding to the isotherm adsorption and desorption process, \(V_{\text{L}}^{\text{ad}}\) and \(V_{\text{L}}^{\text{de}}\) respectively represent the Langmuir volume corresponding to the isotherm adsorption and desorption process, and pf is the maximum equilibrium pressure value. The AHI value of 0 means that the adsorption and desorption process is reversible without hysteresis. The larger the AHI value, the more significant the hysteresis is.
It can be seen that the AHI value of raw coal is negative, indicating that the amount of methane desorption is greater than the actual amount of adsorption. This phenomenon is theoretically impossible, but similar reports have appeared in previous studies (Harpalani et al. 2006; Wang et al. 2014a, b). One possible reason of the negative value of AHI may be attributed to the nonequilibrium during the adsorption or desorption process. For methane sorption, the general trend for the sorption hysteresis increases with fluid treatment as illustrated in Fig. 9. After two high concentration fracturing fluids (0.8% and 1.2% concentration levels) treatments, the AHI index of methane desorption suddenly increased from negative values to 17.63 and 16.24. The calculation results of CO2 AHI show that the hysteresis occurs when the CO2 of the raw coal is desorbed, and after the raw coal is treated with fracturing fluid, the degree of hysteresis has increased to a certain extent. Compared to methane experiments, the high concentration fracturing fluid treatment did not show a sudden increase in the degree of CO2 desorption hysteresis.
5.2 The residue distribution and functional group changes of coal samples
After the coal samples were dried, 1 g of coals are randomly selected from each group, and they were evenly placed in the sample tray for microscope observation. The results are shown in Fig. 10. We observed that the surface of the raw coal particles is smooth and has less impurities (Fig. 10a). After treatment with a 0.2% concentration gel fracturing fluid, a thin coated layer of white flocculent residue was observed on the surface of the coal sample, but the overall structure of the residue is relatively loose (Fig. 10b). The coal sample treated with the 1.2% concentration fracturing fluid has extremely dense/thick surface residues, presenting a solidified colloidal film state (Fig. 10e). It can be inferred that after fracturing fluid treatment, the change of coal adsorption of methane and CO2 gas may be caused by the adhesion of residues on the coal surface.
Microscope pictures of the surface of coal particles in each group (Huang et al. 2019). Notes: a Raw coal; b Coal sample treated with 0.2% concentration fracturing fluid; c Coal sample treated with 0.4% concentration fracturing fluid; d Coal sample treated with 0.8% concentration fracturing fluid; e Coal sample treated with 1.2% concentration fracturing fluid
If fracturing fluid is reactive to the coal surface component, the greater the concentration of the fracturing fluid, the stronger the degree of chemical reaction and the more significant the functional group modifications. To observe the changes of coal surface chemical composition, we selected the highest concentration of 1.2% fracturing fluid to treat coal samples for testing. The result was shown in Fig. 11. The blue and yellow spectral lines show the distribution of functional groups of the raw coal and the coal sample treated with 1.2% fracturing fluid. It can be found that after fracturing fluid treatment, multiple peaks increase in the two wavenumber ranges of 900–1600, 2750–3000 and 3100–3700.
To verify whether there is a chemical reaction between the fracturing fluid and the coal surface components, the treated coal sample was immersed in distill water for 2 h cleaning and washing. Followed by drying, the infrared green spectrum showed the distribution characteristics of functional groups of coal samples after one the infrared absorption peak decrease to some extent, especially in the wavenumber range from 3100 to 3700. After water washing again, we observed that the height and area infrared spectrum morphology tends to recover back to the raw coal. From this data, it is confirmed that a chemical reaction may indeed occur between the fracturing fluid and the coal surface, that is, during the process of treating the coal sample with the fracturing fluid, the additives contained in the fracturing fluid react chemically with the organic matter or minerals in the coal. A new substance is formed, but the new substance generated by the reaction in the washing process is diluted or cleaned up. Therefore, the FTIR results after two washings were similar.
As described in Sect. 2, the main organic components of fracturing fluid include hydroxypropyl guar and organic boron. Among them, hydroxypropyl guar is a macromolecular polymer, the chemical formula of its molecular unit is shown in Fig. 12, and its various functional groups and infrared spectrum peaks are shown in Table 1. Based on the measured data, the hydroxyl, methyl, methylene and alkyl ether contained in guar molecules in the residue should lead to multiple infrared spectral peaks in coal samples after treatment. With extensive and sufficient water washing, the residue on the surface of coal samples can be removed, and the surface components of coal samples will tend to recover back to raw coal.
5.3 Influencing mechanisms of fracturing fluid on sorption behavior of coals
The chemical modification of coal surface has been extensively studied in the literature. The surface modification of coal is usually to change the functional groups of coal by chemical agents, which can reduce the adsorption capacity of coal. It is also possible to dissolve organic matter and minerals within coal matrix through chemical reactions to enhance pore connectivity (Wang et al. 2016). A chemical reaction may occur between the fracturing fluid and the coal surface, that is, during the process of treating the coal sample with the fracturing fluid, the additives contained in the fracturing fluid reacted chemically with the organic matter or minerals in the coal. A new substance was formed, but the new substance generated by the reaction in the washing process was diluted or cleaned up. Therefore, the FTIR results after two washings were similar. This has been confirmed by the infrared spectrum data as shown in Fig. 11.
From direct microscopic observations, there are different forms of fracturing fluid residue distribution on the surface of coal particles. These residues attached to the coal surface can decrease the surface area of the coal and reduce the number of available methane adsorption sites, resulting in a decrease of sorption capacity at given pressure. Physically, the fracturing fluid residues invaded into fracture and pore structure of coal may block some pores within the coal matrix, reduce the pore interconnectivity, and then reduce the coal methane or CO2 adsorption capacity. According to the classification method specified by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) (Zdravkov et al. 2007), the pores in coal can be divided into macropores (> 50 nm), mesopores (2–50 nm) and micropores (< 2 nm). The gas in coal is mainly absorbed in the microporous structure. In actual coal seam fracturing and gas drainage projects, because gas absorbed coal reservoirs before fracturing, the fracturing fluid residues can block the coal seam microporous, which can result in decrease trends of desorption and diffusion.
Figure 8 illustrates that the damage factor of fracturing fluid to methane sorption is greater than that of CO2. According to the analysis, this may be attributed to the difference in the molecular size of methane and CO2. The dynamic diameter of methane molecule is 0.38 nm, while that of CO2 molecule is 0.33 nm. The fracturing fluid residue that enters the pore structure of the coal adheres to the pore wall and occupies the original pore space, resulting in the reduction of the pore diameter of part of the coal pores. Some narrow pores may be formed, and only CO2 molecules can pass through but hinder the transport of methane molecules. This is reflected by more damage for methane compared to CO2. Another possibility is that the solubility of CO2 in the coal matrix is significantly stronger than that of CH4, which to a certain extent leads to a stronger adsorption capacity of CO2 than CH4 (Reucroft and Sethuraman 1987). After the fracturing fluid blocks the pores and reduces the adsorption capacity, CO2 can maintain a certain adsorption capacity through better solubility when contacting the coal surface. Therefore, the damage caused by the fracturing fluid to CO2 adsorption is less than that of methane adsorption. The focus of this thesis is on the effect of gel fracturing fluid on the ad-/desorption characteristics of gaseous carbon dioxide. It is undeniable that when carbon dioxide is stored, part of the carbon dioxide injected into the coal seam will be in a supercritical state. Because gaseous carbon dioxide and supercritical carbon dioxide have significant differences in physical properties, the adsorption properties of the two in coal will be different, and the influence of gel residue on the adsorption characteristics of carbon dioxide in the two states may also be different.
It is worth noting that the results of isothermal adsorption and desorption experiments show that the treatment of fracturing fluid will aggravate the hysteresis effect of gas desorption in coal (Fig. 9). Regarding the mechanism of this phenomenon, this article proposes two possible explanations.
The first is that the residue adheres to the orifice, causing the coal to adsorb gas to swell and deform leading to a pore blocking (Fig. 13). For this phenomenon, at the low-pressure adsorption stage, a small amount of fracturing fluid residue adheres to the narrower orifice, but the orifice is not completely blocked. Due to the swelling and deformation effect of methane adsorption by coal (Wang et al. 2014a, b), the aperture of the pore can be progressively reduced with solid matrix swelling as shown in Fig. 13. When the aperture reduces to some critical value, the gas will not be able to freely transport, and the desorption and diffusion eventually cease. This induces the notable hysteresis for the desorption process. It should be noted that in the actual process of fracturing and enhancing the permeability of the coal seam, since methane invades and adsorbs in the coal seam before the fracturing residue, the residue does not participate in the early methane adsorption stage, so it is different from the experimental design of isothermal adsorption. Therefore, the conclusion that incomplete plugging caused by adsorption expansion turns into a fully blockage has no direct guiding significance for gas drainage. But this does prove a kind of retention characteristic of fracturing fluid residue in the pores.
The second explanation is that the fracturing fluid residue can potentially invade into the pore by the high-pressure gas, causing it to be blocked, and cannot be discharged during the pressure reduction process (Fig. 13). The fracturing fluid residue is attached to the pores. For low pressure, methane can normally enter the pores and be adsorbed. At the higher pressure, the pressure in the sample cell increases, pushing the residue attached to the pore into a narrower area deep in the pore, forming a stable blockage structure. In the later desorption stage, due to the adhesion of the residue on the pore wall and the frictional resistance between the two, the residue will not be come off from the pore entry, and the gas molecules that have entered the deep part of the pore cannot be desorbed normally, resulting in the hysteresis. It can be speculated that in the actual fracturing process, fluid pressures of up to tens of megapascals are very likely to drive fracturing fluid into the pores and fractures of the coal seam, hindering the normal desorption and flow of gas, and adversely affecting gas drainage.
From the perspective of coal seam gas drainage, to eliminate the gel-based fluid formation damage, the fracturing fluid gel breaking process should be further improved toward a fully gel breaking and flowback. After fracturing is promoted, the fracturing fluid can be fully retreated from the coal seam borehole, reducing the amount of retention in the reservoir. We can also consider to continuously improve the fracturing fluid formula, effectively control the size of fracturing fluid residue particles, change its rheological characteristics and physical interaction characteristics with coal, and prevent fracturing fluid residues from entering the coal pores, to minimize the impact of fracturing fluid on gas drainage efficiency.
6 Summary and conclusions
-
(1)
The gel fracturing fluid causes serious damage to the gas adsorption and desorption capacity of coal, which may adversely affect the mining and carbon dioxide storage effects of coalbed methane. As the concentration of fracturing fluid increases, the density of coal residues increases and the adhesion structure becomes denser. The adhesion of residues on the coal wall surface will reduce the number of adsorption sites for gas molecules, and the clogging of pores will reduce the connectivity of the pore network in the coal and the fluidity of gas.
-
(2)
FTIR results show that after the treatment of fracturing fluid, the composition of the functional groups on the coal surface does not change significantly, there is no obvious chemical reaction between the coal surface and the fracturing fluid, or the new substance produced by the reaction is diluted or cleaned by two water washes.
-
(3)
With the intrusion of gel fracturing fluid, the desorption hysteresis effect of methane and CO2 in coal is intensified, and the impact on methane desorption hysteresis is obviously greater than that on CO2 desorption hysteresis. The reason for the increasing of hysteresis may be that the adsorption swelling caused by the residue adhered on the pore edge, or the pore blockage caused by the residue invasion under high gas pressure.
References
Adrian T, Wendland M, Hasse H et al (1998) High-pressure multiphase behaviour of ternary systems carbon dioxide–water–polar solvent: review and modeling with the Peng-Robinson equation of state. J Supercrit Fluid 12(3):185–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-8446(98)00087-4
Al-Ameri A, Gamadi T, Ispas I (2018) Evaluation of the near fracture face formation damage caused by the spontaneously imbibed fracturing fluid in unconventional gas reservoirs. J Petrol Sci Eng 171:23–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.07.021
Anderson RB, Bayer J, Hofer LJE (1966) Equilibrium sorption studies of methane on Pittsburgh seam and Pocahontas No. 3 seam coal. Advances in chemistry. ACS Publications, Washington, DC
Baskaran S, Kennedy IR (1999) Sorption and desorption kinetics of diuron, fluometuron, prometryn and pyrithiobac sodium in soils. J Environ Sci Health Part B 34(6):943–963. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601239909373238
Braida WJ, Pignatello JJ, Lu Y et al (2003) Sorption hysteresis of benzene in charcoal particles. Environ Sci Technol 37(2):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020660z
Cao Y, Zhang Z, Zhai H et al (2017) CO2 gas fracturing: a novel reservoir stimulation technology in low permeability gassy coal seams. Fuel 203:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.053
Chen HL, Zhang JY, Chen YK et al (2004) Delayed adsorption and desorption behavior of pentachlorophenol in sediments. J Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2004.01.006
Chen SB, Zhu YM, Liu TY et al (2009) Effect of clean fracturing fluid on adsorption performance of coalbed methane. J Coal Ind 34(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2009.01.008
Dutta P, Harpalani S, Prusty B (2008) Modeling of CO2 sorption on coal. Fuel 87(10):2023–2036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2007.12.015
Guan C, Liu S, Li C et al (2018) The temperature effect on the methane and CO2 adsorption capacities of Illinois coal. Fuel 211:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.09.046
Guo D, Lv P, Zhao J, Zhang C (2020) Research progress on permeability improvement mechanisms and technologies of coalbed deep-hole cumulative blasting. Int J Coal Sci Technol 7(2):329–336
Harpalani S, Prusty BK, Dutta P (2006) Methane/CO2 sorption modeling for coalbed methane production and CO2 sequestration. Energy Fuel 20(4):1591–1599. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef050434l
Huang QM, Liu SM, Wang G et al (2019) Gas sorption and diffusion damages by guar-based fracturing fluid for CBM reservoirs. Fuel 251:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.031
Huang QM, Liu SM, Cheng WM et al (2020) Fracture permeability damage and recovery behaviors with fracturing fluid treatment of coal: an experimental study. Fuel 282:118809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118809
Huang QM, Liu SM, Wang G et al (2021) Evaluating the changes of sorption and diffusion behaviors of Illinois coal with various water-based fracturing fluid treatments. Fuel 283:118884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118884
Huang Q, Wu B, LiuY (2022) Experimental and simulation investigations of the impact of polyacrylamide on CBM ad-/desorption. J Pet Sci Eng 208:109300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109300.
Jing ZF, Wang SZ, Luo XR et al (2014) Experimental study on frictional resistance characteristics of CO2-emulsified viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluid. Appl Mech Mater 3282:35–38. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.577.35
Kang YL, Huang FS, You LJ et al (2016) Impact of fracturing fluid on multi-scale mass transport in coalbed methane reservoirs. Int J Coal Geol 154:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2016.01.003
Levy JH, Day SJ, Killingley JS (1997) Methane capacities of Bowen Basin coals related to coal properties. Fuel 76(9):813–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(97)00078-1
Li L, Al-Muntasheri GA, Liang F et al (2016) A review of crosslinked fracturing fluids prepared with produced water. Petroleum 2(4):313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petlm.2016.10.001
Li SG, Zhao B, Zhao PX et al (2019) Experiment on influencing factors of gas adsorption characteristics of coal-like materials. J China Univ Min Technol Soc Sci 7(5):943–954. https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.001051
Li SH, Zhang SC, Zou YS et al (2020) Experimental study on the feasibility of supercritical CO2-gel fracturing for stimulating shale oil reservoirs. Eng Fract Mech 238:107276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107276
Liu S, Harpalani S (2013) Permeability prediction of coalbed methane reservoirs during primary depletion. Int J Coal Geol 113:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2013.03.010
Liu YQ, Zhang SL, Shu LY (2019) Mechanism of coalbed methane migration in adsorption-desorption state. Coalf Geol Explor 47(4):12–18. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.04.003
Lu YY, Yang F, Ge ZL et al (2015) Comparative experimental study on the influence of clean fracturing fluid and water on coal seam permeability. J Coal Ind 40(1):93–97. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.0209
Lu Y, Yang F, Ge Z et al (2017) Influence of viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluid on permeability of coal seams. Fuel 194:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.12.078
Lv HY, Liu F, Li LH et al (2018) Study on directional hydraulic fracturing of prefabricated cracks in top coal. J Min Sci 3(6):553–560. https://doi.org/10.19606/j.cnki.jmst.2018.06.006
Ma HF, Cheng ZH, Zhang KX (2017) Experimental study on enhanced anti-permeability of W-S-W hydraulic fracturing in high gassy coal seam of 1000 meters deep well. J Coal Ind 42(7):1757–1764. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.0153
Montgomery CT, Smith MB (2010) Hydraulic fracturing: history of an enduring technology. J Pet Technol 62:26–40. https://doi.org/10.2118/1210-0026-JPT
Palmer ID, Fryar RT, Tumino KA et al (1991) Water fracs outperform gel fracs in coalbed pilot, vol 89. PennWell Publishing Corp, Tulsa, p 71
Reucroft PJ, Sethuraman AR (1987) Effect of pressure on carbon dioxide induced coal swelling. Energy Fuel 1(1):72–75
Sudibandriyo M, Pan Z, Fitzgerald JE et al (2003) Adsorption of methane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and their binary mixtures on dry activated carbon at 318.2 K and pressures up to 13.6 MPa. Langmuir 19(13):5323–5331. https://doi.org/10.1021/la020976k
Thombare N, Jha U, Mishra S et al (2016) Guar gum as a promising starting material for diverse applications: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 88:361–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.001
Tian L, Cao Y, Liu S et al (2020) Coalbed methane reservoir fracture evaluation through the novel passive microseismic survey and its implications on permeable and gas production. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 76:103181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103181
Wang HF, Ji M, Pan J et al (2014a) Study on surface modification of different rank coals under the action of chlorine dioxide. Coal Mine Saf 45(3):21–23. https://doi.org/10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2014.03.006
Wang K, Wang G, Ren T et al (2014b) Methane and CO2 sorption hysteresis on coal: a critical review. Int J Coal Geol 132:60–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2014.08.004
Wang GD, Ren TX, Qi QX et al (2016) Mechanism of adsorption and desorption hysteresis and its influence on deep coalbed methane development. J Coal Ind 41(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.9022
Xu JZ, Zhai C, Liu SM et al (2017) Feasibility investigation of cryogenic effect from liquid carbon dioxide multi cycle fracturing technology in coalbed methane recovery. Fuel 206:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.05.096
Yang F (2017) Study on gas desorption and seepage characteristics of coal seam enhanced by clean fracturing fluid. Chongqing University, Chongqing
Yang Y, Liu SM, Zhao W et al (2019a) Intrinsic relationship between Langmuir sorption volume and pressure for coal: experimental and thermodynamic modeling study. Fuel 241:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.12.008
Yang X, Zhang JY, Wang GD et al (2019b) Experimental study on the influence of gas pressure on gas diffusion in coal. J China Univ Min Technol Soc Sci 48(3):503–510, 519. https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.001004
You Q, Wang C, Ding Q et al (2015) Impact of surfactant in fracturing fluid on the adsorption–desorption processes of coalbed methane. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 26:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.06.003
Yuan L (2016) Strategic thinking on deep coal and gas co mining in China. J Coal Ind 41(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.9027
ZdravkovCermak BJ, Sefara M, Jank J (2007) Pore classification in the characterization of porous materials: a perspective. Open Chem 5(2):385–395
Zhai C, Qin L, Liu SM et al (2016) Pore structure in coal: pore evolution after cryogenic freezing with cyclic liquid nitrogen injection and its implication on coalbed methane extraction. Energy Fuel 30(Jul. Spec.):6009–6020. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00920
Zhai C, Xu J, Liu S et al (2018) Fracturing mechanism of coal-like rock specimens under the effect of non-explosive expansion. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 103:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.01.037
Zhang R, Liu S (2017) Experimental and theoretical characterization of methane and CO2 sorption hysteresis in coals based on Langmuir desorption. Int J Coal Geol 171:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2016.12.007
Zhi S, Elsworth D, Wang J et al (2018) Hydraulic fracturing for improved nutrient delivery in microbially-enhanced coalbed-methane (MECBM) production. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 60:294–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2018.10.012
Zhu Z (1996) Improvement of isothermal adsorption experiment by high pressure volumetric method. Coalf Geol Explor 13(5):28–30
Zou Q, Lin B, Zheng C et al (2015) Novel integrated techniques of drilling–slotting–separation-sealing for enhanced coal bed methane recovery in underground coal mines. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 26:960-973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.07.033
Zou Q, Liu H, Jiang Z et al (2021) Gas flow laws in coal subjected to hydraulic slotting and a prediction model for its permeability-enhancing effect. Energy Sources Part A 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2021.1936692
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by the open fund by Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control (MDPC201911), and the Independent Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Industrial Dust Prevention and Control & Occupational Health and Safety, Ministry of Education Anhui University of Science and Technology (EK20201001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Q., Li, J., Liu, S. et al. Experimental study on the adverse effect of gel fracturing fluid on gas sorption behavior for Illinois coal. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8, 1250–1261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-021-00463-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-021-00463-z