Abstract
The present paper entails the results of the investigations carried out on the lignite deposits of Kachchh Basin. The lignite samples were drawn from five lignite seams from Panandhro lignite field (Seam-I to -V) and eight lignite seams (Seam-I to -VIII) from the Matanomadh lignite field which are currently operational. The petrographic analysis of the lignites indicates a dominance of huminite group of macerals which is mainly contributed by ulminite-A, ulminite-B, attrinite, densinite, and phlobaphinite. Liptinite (chiefly sporinite, cutinite, resinite, and liptodetrinite) and inertinite (chiefly fusinite, funginite, and inertodetrinite) groups occur in subordinated amount. The mineral matter occurs in moderate concentration. Though sulfur content is high in these lignites, there is no fixed trend of variation of sulfur from bottom seam to top seam. The investigation reveals a flooded forest swamp having high rate of degradation. However, there were a few drier periods indicated by relatively more inertinite macerals. The petrography-based models indicate that the Kachchh lignites of Gujarat evolved in coastal marshy setting under transgressive phase. However, there were few intermittent fluvial activities giving rise to supratidal flood plain. This led to the formation of the associated carbonaceous shales in the basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
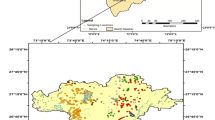
Kachchh Basin, between latitudes 22°30′–24°30′N, and longitudes 68°–72°E, covers an area of about 35,000 km2 inland and 36,000 km2 offshore in western India. The Great Rann on the north and east, Little Rann on the southeast, Gulf of Kachchh on the south, and the rest by the Arabian Sea, flank the Kachchh mainland. The name ‘Kachchh’ is given because of its tortoise-like morphology, where the central portion of this area forms a table-land sloping on all sides. There are three hill ranges, trending east–west; the Banni is formed by the sediments deposited from northern border of the mainland and is covered by soil. This area receives fluctuating rainfall (up to 88 cm) (Merh 1995). The Rann is a dry-bed, saline desert throughout the year except during the monsoon season, which formally connects the Narmada rift with Sind and separates Kachchh from the mainland. The Rann is divided into two areas, Great Rann and Little Rann, which are covered by a layer of salt and a thin layer of fine clays (Fig. 1a). The Cenozoic rocks unconformably overlie the Deccan basalt and Mesozoic rocks with an aggregate thickness of around 300 m (Biswas 1992; Sarkar et al. 1996) and contain huge lignite deposits including those of Matanomadh. Based on the foraminiferal assemblage, the age of lignite is suggested as early Eocene to early-middle Eocene (Dutta et al. 2011). The lignite deposits of Kachchh occur at Panandhro, Matanomadh, Umarsar, Akrimota, Lefri, and Lakhpat-Dhedhadi in Lakhpat Taluka (IBM 2013). The Panandhro lignite field is located in Kachchh district of Gujarat, and is surrounded by villages such as Panandhro, Fulra, and Khanot. The lignite fields are bounded within latitude 23°45′56″N and longitude 68°45′00″E (Survey of India Toposheet No. 41 F/14). It is the third largest lignite deposits of India, with reserves of 95–100 Mt. Matanomadh lignite mine is spread over an area of 1314 h with a total resource of 3.6 Mt. This lignite field lies between latitudes 23°29′00″–23°32′00″N and longitudes 68°56′00″–68°59′00″E. In the present paper, petrological and geochemical characteristics of Kachchh lignites are presented, and based on that, their evolution is discussed.
2 Geological setting
Regional geological map of northern part of Gujarat showing Matanomadh and Panandhro lignite mines of Kachchh Basin is shown in Fig. 1b. Kachchh Basin is a peri-cratonic rift basin located in the western continental margin of India (Biswas 1992). It came into existence in the late Triassic, during the rifting of eastern Gondwanaland, and it is mainly formed by Mesozoic and Cenozoic sediments. The basin opens towards west and it has a general slope towards west-southwest. Cenozoic outcrops of Kachchh are exposed to the west of Deccan Trap forming semi-circular outline. Kachchh Basin mainly includes a group of E–W trending ‘uplifts’ surrounded by Little Rann and plains of the Great Rann. Seven uplifts (Patcham, Khadir, Bela, Chorar, Wagad, Kachchh Mainland, and Saurashtra) occur in three sub parallel trending E–W lines. These uplifts are bounded by monoclonal flexures/faults from one side and gently dipping peripheral plains from the other side except for the Wagad uplifts. The Mesozoic strata have suffered fault-related uplifts and consequent folding. These uplifts are surrounded by the sediments of Tertiary period which form peripheral plains. These plains conceal the Mesozoic structures and the depressions occurring between them comprise the Cenozoic Sub-Basins. The Mesozoic rocks are exposed in Kachchh Mainland, Wagad, Bela, Khadir Chorar hills, and the Patcham uplifts. The Mesozoic rocks of Kachchh are divided into Upper and Lower Series. The upper series is plant bearing while the lower one has ammonites. The Mesozoic rocks are classified into a four-fold subdivision, namely, Pachcham, Chari, Katrol, and lower part of Umia. The upper non-marine Umia is named the Bhuj Formation which is of Middle Cretaceous in age (Merh 1995). A complete sequence of rock, from Triassic to Recent, is found in this basin. Biswas (1992) has noted that the Mesozoic sequence comprises Late Triassic (Rhaetic) continental, Middle to Late Jurassic marine, and Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous fluvio-deltaic sediments. Further, Mesozoic sediments fill a major part of the basin whereas the Tertiary sediments are of a wide variety and include shallow marine-shelf sediments in the peripheral and intervening structural lows, bordering the Mesozoic uplift areas. The Quaternary sediments are mostly marine- to fluvial, eolian, and lacustrine in nature. The Kachchh Mainland exposes the major stratigraphic succession and the outcrops of Late Tertiary and Quaternary sediments are seen at the border of the lower part of the Mesozoic sequences. Sedimentological evidences indicate that Late Triassic, Jurassic, and Early Cretaceous sediments were deposited in early syn- and post-rift stages respectively (Biswas 2005). The Naredi Formation is the lignite-bearing formation. The strata including the lignite seams has a dip towards the centre of the basin. The basin appears to be a syncline with its axis in the south–south west to north-east. In Panandhro field, the border of the basin is well-marked by steep escarpments. It is elongated in NW–SE direction with a width of 3 km along the southern fringe and tapers down to 600 m towards the northern end. The lignite-bearing sedimentary succession of Matanomadh mine comprises nine lignite seams with individual seam thicknesses ranging from 0.15 to 4.88 m. However, in Panandhro mine 13 lignite seams have been reported varying in thickness from 0.10 to 10 m. The lignite encountered is dark brown in color; compact; uniform in texture; amorphous in nature; and impregnated with resin, pyrite, and marcasite. The seams are impersistent, contaminated, and exhibit splitting tendency (GSI 2012). The details of the geological succession of Kachchh Basin are given in Table 1, and the lithocolumn and the lignite seam profiles are given in Fig. 2 which shows various bands present in the lignite seams.
Litho column showing various rock units in Kachchh Basin (after Biswas 1992) along with lignite seam profiles at Matanomadh and Panandhro
3 Method of study
Lignite samples were collected from five seams (Seam-I to Seam V) from Panandhro lignite field and eight seams (Seam-I to Seam VIII) from Matanomadh lignite field of Kachchh Basin which are currently being mined. The pillar samples were drawn as per Schopf (1960) in a way to represent full-seam thickness. The lignite samples were put together to form composite bands on the basis of similar megascopic characteristics and each composite band is taken as one composite sample and has been given unique sample number. The lignite samples were crushed, and reduced in quantity through quartering and coning, and subjected to various analyses. The -18-mesh samples were used for preparation of polished lignite mounts for petrography. For proximate and other chemical analyses, the samples were further reduced to -70-mesh fraction. Maceral analysis has been performed under reflected light using a Leitz Orthoplan-Pol Microscope equipped with Wild Photoautomat MPS-45 in the Coal and Organic Petrology Laboratory, Department of Geology, Banaras Hindu University. White light was sourced from a 12 V/100 W halogen lamp while for fluorescence system, a Ploemopak with filter block I 2/3 having blue excitation filters (BP450-490), dinomatic mirror (RKP510) and suppression filter (LP520), was used. The line-to-line and point-to-point spacing was maintained at 0.4 mm and more than 600 counts were taken on each sample. The methodology described by Taylor et al. (1998) was adopted. Huminite macerals were termed and described as per ICCP-1994 (Sýkorová et al. 2005), while ICCP (2001) was followed for inertinite macerals. The vitrinite/huminite reflectance measurement was carried out at the National Metallurgical Laboratory, Jamshedpur following ISO 7404-5:2009. A minimum of 200 measurements were taken on each sample.
4 Result and discussion
4.1 Petrographic composition
Macroscopically, these lignites are generally stratified, matrix-rich, brown to black, inhomogeneous, and often contains patches of resin and pyrite specks. There are eight lignite seams in Matanomadh field and the top seam (Seam-I) is overlain by carbonaceous clay while Seam-VIII is underlain by dark grey carbonaceous clay. However, in Panandhro, out of the thirteen reported thin lignite seams only five lignite seams are mineable. Here, the roof of Seam-I comprises of carbonaceous shale while the floor of Seam-V comprises of dark grey carbonaceous clay. Petrographically, these lignites are dominantly comprised of huminite group macerals followed by the liptinite and inertinite groups while mineral matter is moderately high. The variation in the concentration of group macerals in various seams of Matanomadh and Panandhro lignite mines is shown in Fig. 3 while the characteristic macerals are shown in photomicrographs (Fig. 4).
Characteristic photomicrographs in the lignites of Kachchh Basin: a textinite (T); b ulminite and pyrite (Py) grains; c phlobaphinite (Ph);d densinite (D) with oxidation cracks; e densinite (D) and framboidal pyrite (Py); f densinite (D) and pyrite (Py) occurring as framboids and also in cavity; g resinite (R) and sporinite (Sp) observed under uv light; h megacutinite (Cu) as observed under uv light; i fungal bodies (F) occurring in densinitic background; j fusinite band (Fu) and densinite (D)
4.1.1 Matanomadh lignite
Maceral composition and mineral matter content in Matanomadh lignites are furnished in Tables 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Huminite varies from 41.8% to 58.6%, mean 52.2% (60.9%–78.2%, mean 69.4% on mmf basis) while liptinite varies from 11.0% to 22.0%, mean 16.3% (15.4%–29.9%, mean 21.0% on mmf basis). The inertinite content is relatively low (mean 6.9%, 9.6% on mmf basis). The mineral matter content varies from 15.1% to 37.0% (mean 24.6%). Huminite group is composed of ulminite-A (mean 12.6%; 15.6% on mmf basis), ulminite-B (mean 10.0%; 13.2% on mmf basis), attrinite (mean 12.1%; 18.0% on mmf basis), densinite (mean 13.3%; 17.3% on mmf basis), and phlobaphinite (mean 3.8%; 4.9% on mmf basis). Liptinite is represented by sporinite, cutinite, resinite, and liptodetrinite while other macerals occur in low concentration. Similarly, inertinite is mainly represented by fusinite, funginite, and inertodetrinite. Argillaceous mineral matter occurs in moderately high concentration (10.2%–29.4%, mean 17.8%) while sulphides and occur in low concentration.
Microlithotype analysis of Matanomadh lignite is given in Table 7. The analysis reveals that among the monomacerite, humite dominates (mean 46.8%) followed by liptite (mean 4.9%), and inertite (mean 1.6%). The bimacerites are contributed by clarite, huminertite, and durite. Carbominerites have a dominance of carbargilite (mean 17.1%), while carbopyrite and carbankerite occur in low concentrations.
4.1.2 Panandhro lignite
Maceral composition and mineral matter content in Panandhro lignites are given in Tables 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. In this lignite, huminite is the most dominant maceral group (mean 60.3%; 74.9% on mmf basis). Liptinite is next in dominance (mean 11.9%; 15.1% on mmf basis), followed by inertinite (mean 7.9%; 10.0% on mmf basis). The mineral matter occurs in moderate concentration (mean 19.9%) (Tables 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6). The huminite group is mainly composed of ulminite-A (mean 13.3%; 16.6% on mmf basis), ulminite-B (mean 5.2%; 6.5% on mmf basis), attrinite (mean 13.2%; 16.2% on mmf basis), densinite (mean 21.0%; 26.2% on mmf basis), and phlobaphinite (mean 7.0%; 8.6% on mmf basis). The liptinite group is mainly represented by sporinite, resinite, and liptodetrinite while other liptinitic macerals occur in very low concentrations. The inertinite group is represented chiefly by fusinite, funginite, and inertodetrinite. The mineral matter includes sulphides (mean 4.9%), carbonates (mean 0.8%), and argillaceous mineral matter (mean 14.1%).
Microlithotype analysis of Panandhro lignite is given in Table 8. The analysis reveals that among the monomacerite, humite dominates (mean 59.0%), while liptite (mean 3.5%), and inertite (mean 1.1%) occur in low concentrations. Among the bimacerites, clarite, huminertite, and durite, occur in low concentration (Table 8). The carbominerites include carbargilite (mean 13.0%), carbopyrite (mean 5.0%), and carbankerite (mean 0.4%).
Details of the reflectance values of individual lignite samples of various seams are furnished in Table 9. The huminite reflectance measurement shows that R o, min ranges from 0.20% to 0.25%, R o,max from 0.41% to 0.48%, and R o, mean from 0.31% to 0.35%.
4.2 Chemical attributes
Chemical composition of these lignites is given in Table 10. The ultimate result indicates that Matanomadh lignites contain 66.9% carbon, 4.8% hydrogen, 1.0% nitrogen, and 19.4% oxygen (daf basis). The sulfur content of this seam is high and varies from 3.8% to 11.3% (mean 7.8% on daf basis). There is no definite trend of variation of these elements from Seam-I to Seam-VIII, however, Seam-V has a relatively high carbon and low nitrogen and oxygen content. The details of these elements are furnished in Table 10.
Panandhro lignite contains 66.1% carbon, 5.1% hydrogen, 1.0% nitrogen and 21.2% oxygen on daf basis. The sulfur content in these seams is high and varies from 3.7% to 11.6% on daf (mean 6.6%). There is no definite trend of variation in the distribution of these elements from Seam-I to Seam-V, though a little fluctuation is noticed.
4.3 Depositional environment
It is important to understand the variations in the distribution of the petrochemical constituents of Kachchh lignites along the lignite seam profiles from bottom to top in order to reconstruct their evolutionary history. The vertical variation of petrographic components is shown in Fig. 5. The black bands, in Kachchh lignites, are strongly gelified compared to the brownish bands. Owing to the sensitivity of the macerals towards varied environmetal conditions, they are useful to characterize the paleomire. Teichmüller (1989) has demonstrated that the presence or absence of macerals is indicative of the paleo-depositional environment. Nevertheless, these macerals acquire various characteristics through peat-forming plant communities, nutrient supply, bacterial activity, types of deposition, temperature, pH, and redox potential (Teichmüller et al. 1998a, b; Lin and Tian 2011). Surface inundation in the basin relates to increase in the clastic mineral matter (Singh and Singh 1996). Facies models mainly based on petrographic elements have been used to discuss the evolutionary history of the paleomires of Kachchh Basin. A number of researchers (Cohen and Spackman 1972; Styan and Bustin 1983; Cohen et al. 1987; Calder et al. 1991; Grady et al. 1993; Hawke et al. 1996; Singh and Singh 1996; Shearer and Clarkson 1998; Jasper et al. 2010; Singh et al. 2010a, b; Suárez-Ruiz et al. 2012; Singh et al. 2012a, b, 2014) have attempted paleoecological reconstructions using petrological tools. Recently, O’Keefe et al. (2013) have made a detailed discussion on ‘coal rank’ and ‘coal type’ and relation of latter to the environment of peat formation, the climate of peat formation, and the decompositional history of the mire. Systematic discussion on the paleoenvironmental interpretations and their signatures in maceral was initiated by Diessel (1982). He emphasized the presence of diagnostic macerals and proposed facies diagrams based on them. Subsequently, Diessel (1986) introduced two indices, gelification index (GI) and tissue preservation index (TPI) to characterize the paleomires of Australian Permian coals. Further, Diessel (1992) showed that less humified structured and strongly humified unstructured tissue derived macerals manifest the degree of humification and the vegetation type. High TPI values relate to a high subsidence rate of the basin and dominance of wood-derived tissues, while a low TPI value is seen as a result of a low rate of subsidence and high humification owing to the predominance of herbaceous vegetation in the peat swamp. GI values indicate the degree of gelification of huminite macerals and distinguishes gelified macerals from the ungelified ones. A continuous presence of water in the peat swamp is essential for gelification. Fluctuation in water table affects the gelification because more inertinites will form during dry periods due to increasing oxidation. Nonetheless, scientists have advised to take care while using these indices. Vertical variation of these indices along the lignite seams profiles is shown in Fig. 5. Calder (1993) and Collinson and Scott (1987) believe that palynological and paleobotanical data would provide high precision for paleoenvironment. Several researchers have raised serious remarks for using these indices for low-rank coals (Lambersen et al. 1991; Crosdale 1993; Dehmer 1995; Wust et al. 2001; Scott 2002; Moore and Shearer 2003; Amijaya and Littke 2005). Several scientists have used a combined petrographic, organic-geochemical, and/or isotope data for understanding and reconstructing the environment of paleomire (Bechtel et al. 2002, 2003; Singh et al. 2013). Kalkreuth et al. (1991), Petersen, (1993), and Flores (2002) modified these indices to broaden their usage for low-rank coals. In the present study, the indices have been taken from Flores (2002) which is a modified version of Kalkreuth et al. (1991) for brown coals. The calculations are as per the following formulae:
Very high GI values of more than 10 in several sections and even >100 in few sections of Kachchh Basin, indicate a permanently flooded forest swamp having high degradation. This type of environment is prevalent in limno-telmatic swamps where low to moderate subsidence rate occurs and there is a slow fall in the ground-water table. This type of marsh is recognized as treeless open-marsh and limnic-plant communities (Iordanidis and Georgakopoulos 2003). Intensive gelification of plant tissues in the SE Asian coals is also reported by Hoekel (1989) which is attributed to be a function of acid ground water due to marine influence. Few sections of Matanomadh and Panandhro lignites indicate spells of relatively drier periods during which the formation of inertinite macerals was relatively high. The GI and TPI values are indicative of the origin of Kachchh lignites mostly under wet forest swamp to clastic marsh having telmatic to limno-telmatic conditions (Fig. 6) with a moderate rate of subsidence and a slow fall in ground-water table. A low, but negative correlation value exists between GI and TPI values (r = −0.17 for Matanomadh lignite, and r = −0.22 for Panandhro lignite).
Coal facies determined from Gelification Index (GI) and the Tissue Preservation Index (TPI) in relation to depositional setting and type of mire for the lignites of Kachchh Basin, Gujarat (modified from Diessel 1986)
Calder et al. (1991) gave more credence to the influence of ground water and how it characterized the environment of a paleomire. They have used the ground water index (GWI) and vegetation index (VI) for the reconstruction of paleoenvironment. Mires form in rheotrophic to ombrotrophic hydrological conditions. Ombrotrophic to mesotrophic paleoenvironments have low GWI values (<1) whereas values more than 1 prevail in the rheotrophic hydrological condition. Drowning of peat is indicated by GWI values more than 5. Following formulae were used in the present study:
The GWI and VI values of investigated lignites of Kachchh Basin are suggestive of mesotrophic to rheotrophic hydrological conditions (Fig. 7), having the dominance of herbaceous to marginal aquatic vegetation. Variation of GI, TPI, GWI, and VI values with depth in the lignite seams of Kachchh Basin is shown in Fig. 5. It is evident from the figure that in Panandhro area maximum gelification occurred during the formation of Seam-II while in Matanomadh area high gelification was observed during the formation of Seams I, II, and V. Further, in Panandhro area, GWI was high during the formation of seams I, II, and V while in Matanomadh area the GWI was high during the formation of seams I and VI. Singh et al. (2012a) proposed a ternary model for understanding the paleomires of the Eocene lignite deposit of Rajpardi. This is based on maceral composition as well as clastic minerals. While the former is sensitive to varying environmental conditions, the latter directly relates to the water cover in the basin and would provide a better clue to the paleoenvironment. It is evident from the plots of Kachchh lignites, on this model, (Fig. 8) that these lignites evolved under wet moor with moderate to high flooding having variable levels of tissue preservation. Yet another facies model has been used to understand the paleomires of Kachchh lignites. Singh et al. (2010a) initially proposed this ternary facies model, based on microlithotype and carbominerite composition, for Vastan lignites located closely in the Cambay Basin in Gujarat. The plots of the lignites of Kachchh (Matanomadh and Panandhro) Basin, in this model also, point toward a wet-moor environment with moderate flooding where increasing bacterial activity prevailed (Fig. 9). The results obtained through these ternary models compare well with the ones shown by GI, TPI, GWI, and VI indices. The physical break down is prominent at the margins of peat beds (Kuder et al. 1998). Framboidal pyrite indicates increasing activity of sulphate-reducing bacteria which thrive in carbonate- and sulphate-rich waters (Kuder et al. 1998; Teichmüller et al. 1998a). These conditions lead to adsorption of iron on clays and pyrite is seen adjacent to clay zones (Cabrera et al. 1995). Clay-rich layers in the lignite of Kachchh Basin have been confirmed by X-ray diffraction. This is indicative of marine influence in the basin which led to the formation of pyrite framboids. Haq et al. (1987) have noted that there was a eustatic rise of 70–140 in the sea level during Early Paleogene. This has also been indicated by global transgressions during 58.5–52.8 Ma (Hardenbol et al. 1998). Recently, Srivastava and Singh (2017) have discussed about the initial marine transgression during Late Paleocene sedimentation in Kachchh Basin. Prasad et al. (2013) also believe that the lignite-bearing sequences in western India evolved in consequence of extensive transgressive event. The investigation of the Kachchh lignites of Gujarat points that these lignites of Gujarat evolved under coastal marshy setting which prevailed in transgressive phase but there were intermittent fluvial activity which gave rise to supratidal flood plain as indicated by the associated carbonaceous shales.
Plots of ground water influence index (GWI) versus vegetation index (VI) for the lignites of Kachchh Basin, Gujarat (after Calder et al. 1991)
Peat forming environment of lignites of Kachchh Basin, Gujarat, based on macerals and mineral matter (after Singh et al. 2012a)
Peat forming environment of lignites of Kachchh Basin, Gujarat, based on microlithotype (after Singh et al. 2010a)
5 Conclusions
-
1.
The lignites are dominantly rich in huminite group macerals with subordinate liptinite and inertinite groups. The mineral matter is moderately high. In these lignites, huminite group is mainly contributed by ulminite-A, ulminite-B, attrinite, densinite, and phlobaphinite. Sporinite, cutinite, resinite, and liptodetrinite chiefly contribute to liptinite group while fusinite, funginite, and inertodetrinite are the main inertinite macerals.
-
2.
The sulfur content in the seams of Matanomadh and Panandhro fields is high but there is no definite trend of variation of sulfur or other elements from bottom to the top of the seam.
-
3.
Very high GI values (>100 in few sections) in Kachchh Basin, indicate a permanently flooded forest swamp having high degradation. Such environment prevails in limno-telmatic swamps where low to moderate subsidence rate occurs and there is a slow fall in the ground water table. This is supported by GWI and VI values of the investigated lignites, indicating mesotrophic to rheotrophic hydrological conditions. Nevertheless, few sections of Matanomadh and Panandhro lignites underwent spells of relatively drier periods, as indicated by relatively more inertinite macerals. Further, maximum gelification in the Panandhro field was observed during the formation of Seam-II while it was high during the formation of Seams I, II, and V in the Matanomadh field. The Panandhro field also witnessed a high GWI during the formation of seams I, II, and V while the Matanomadh field witnessed high GWI during the formation of seams I and VI.
-
4.
The investigation of the Kachchh lignites of Gujarat indicates that the Gujarat lignites formed under a coastal marshy environment during a transgressive phase. However, there was intermittent fluvial activity, which gave rise to a supratidal flood plain which led to the formation of the associated carbonaceous shales.
References
Amijaya H, Littke R (2005) Microfacies and depositional environment of Tertiary Tanjung Enim low rank coal, South Sumatra basin Indonesia. Int J Coal Geol 61(3–4):197–221
Bechtel A, Sachsenhofer RF, Kolcon I, Gratzer R, Otto A, Puttmann W (2002) Organic geochemistry of the Lower Miocene Oberdorf lignite (Styrian Basin, Austria); its relation to petrography, palynology and the peleoenvironment. Int J Coal Geol 51:31–57
Bechtel A, Gruber W, Sachsenhofer RF, Gratzer R, Lucke A, Puttmann W (2003) Depositional environment of the Late Miocene Hausruck lignite (Alpine Foreland Basin); insights from petrography, organic geochemistry and stable carbon isotopes. Int J Coal Geol 53:153–180
Biswas SK (1992) Tertiary stratigraphy of Kutch. J Palaeontol Soc India 37:1–29
Biswas SK (2005) A review of structure and tectonics of Kutch basin, Western India, with special reference to earthquakes. Curr Sci 88:1592–1600
Biswas SK, Raju DSN (1973) The rock-stratigraphic classification on the Tertiary sediments of Kutch. Bull ONGC 10:37–46
Cabrera L, Hagemann HW, Pickel W, Sa´ez A (1995) The coalbearing, Cenozoic As Pontes Basin (northwestern Spain): geological influence on coal characteristics. Int J Coal Geol 27:201–226
Calder JH (1993) The evolution of a ground-water influenced (Westphalian B) peat-forming ecosystem in a piedmont setting: the no. 3 seam, Springhill coalfield, Cumberland Basin, Nova Scotia. In: Cobb JC, Cecil CB (eds), Modern and ancient coal-forming environments, Geological Society of America, Special Paper, Boulder, CO, pp 153–180
Calder JH, Gibbing MR, Mukhopadhay PK (1991) Peat formation in a Westphalian B piedmont setting, Cumberland Basin, Nova Scotia: implication for the maceral-based interpretation of rheotrophic and raised paleomires. Bulletin de la Societe Geologigue de France 162(2):283–298
Cohen AD, Spackman W (1972) Methods in peat petrology and their application to reconstruction of paleoenvironments. Geol Soc Am Bull 83(1):129–142
Cohen AD, Spackman W, Raymond R (1987) Interpreting the characteristics of coal seams from chemical, physical and petrographic studies of peat deposits. In: Scott AC (ed), Coal and coal-bearing strata: recent advances. The Geological Society Special Publication No. 32, Blackwell, Oxford, UK, pp 107–126
Collinson ME, Scott AC (1987) Implications of vegetational change through the geological record on models of coal-forming environments, In: Scott AC (ed.), Coal and coal-bearing strata: recent advances, Geological Society of America, Special Paper, Boulder, CO, 67–85
Crosdale PJ (1993) Coal maceral ratios as indicators of environment of deposition: do they work for ombrogenous mires? An example from the Miocene of New Zealand. Organ Geochem 20(6):797–809
Dehmer J (1995) Petrological and organic geochemical investigation of recent peats with known environments of deposition. Int J Coal Geol 28(2–4):111–138
Diessel CFK (1982) An appraisal of coal facies based on maceral characteristics. Aust Coal Geol 4:474–483
Diessel CFK (1986) On the correlation between coal facies and depositional environments. In: Proceeding 20th symposium of department geology, University of New Castle, New South Wales, pp 19–22
Diessel CFK (1992) Coal bearing depositional system. Springer-Verlag, New York, p 721
Dutta S, Mathews RP, Singh BD, Tripathi SKM, Singh A, Saraswati PK, Banerjee S, Mann U (2011) Petrology, palynology and organic geochemistry of Eocene lignite of Matanomadh, Kutch Basin, western India: implications to depositional environment and hydrocarbon source potential. Int J Coal Geol 85:91–102
Flores D (2002) Organic facies and depositional palaeoenvironment of lignites from Rio Maior Basin (Portugal). Int J Coal Geol 48(3–4):181–195
Grady WC, Eble CF, Neuzil SG (1993) Brown coal maceral distributions in a modern domed tropical Indonesian peat and a comparison with maceral distributions in Middle Pennsylvanian- age Appalachian bituminous coal beds. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 286:63–82
GSI (2012) Geological and mineral map of Gujarat, Daman and Diu (Published under the Direction of the Director General, Geological Survey of India; Government of India Copyright 2012)
Haq BU, Hardenbol J, Vail PR (1987) Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic. Science 235:1156–1167
Hardenbol J, Thierry J, Farley MB, Jacquin T, de Graciansky PC, Vail PR (1998) Mesozoic and Cenozoic sequence chronostratigraphic framework of European basins. In: de Graciansky PC, Hardenbol J, Jacquin T and Vail PR (eds) Mesozoic and Cenozoicsequence stratigraphy of European basins, SEPM Special Publication 60: 763–786
Hawke MI, Martini IP, Stasiuk LD (1996) Petrographic characteristics of selected Ontario peats: possible modern analogues for coals. In: 13th annual meeting TSOP, abstracts and program. Southern Illinois University, Carbondale Illinois pp 22–23
Hoekel A (1989) On the plate tectonic setting of the coal deposits of Indonesia and the Phillippines. Mitteilungen des Österreichische Geologische Gesellschaft 82:119–133
Indian Minerals Year book 2013 (Part-III: mineral reviews) 53rd Edition (2015) Coal and lignite. Government of India, Ministry of Mines, IBM, Indira Bhavan, Civil lines, Nagpur, pp 1–36
International Committee for Coal and Organic Petrology (1998) The new vitrinite classification (ICCP System 1994). Fuel 77:349–558
International Committee for Coal Petrology (2001) The new inertinite claasification (ICCP System 1994). Fuel 80:459–471
Iordanidis A, Georgakopoulos A (2003) Pliocene lignites from Apofysis mine, Amynteo basin, Northwestern Greece: petrographical characteristics and depositional environment. Int J Coal Geol 54:57–68
ISO 7404-5:2009. Methods for the petrographic analysis of coals—Part 5: Method of determining microscopically the reflectance of vitrinite, pp 1–14
Jasper K, Hartkopf-Froder C, Flajs G, Littke R (2010) Evolution of Pennsylvanian (Late Carboniferous) peat swamps of the Ruhr Basin, Germany: comparison of palynological, coal petrographical and organic geochemical data. Int J Coal Geol 83(4):346–365
Kalkreuth WD, Marchioni DL, Calder JH, Lamberson MN, Naylor RD, Paul J (1991) The relationship between coal petrography and depositiona environments from selected coal basins in Canada. In: Kalkreuth WD, Bustin RM, Cameron AR (eds.) Recent Advances in Organic Petrology and Geochemistry. A Symposium honouring Dr. P. Hacquebard. International Journal of Coal Geology 19: 21–76
Kuder T, Kruge MA, Shearer JC, Miller SL (1998) Environmental and botanical controls on peatification—a comparative study of two New Zealand restiad bogs using Py-GC/MS, petrography and fungal analysis. Int J Coal Geol 37:3–27
Lamberson MN, Bustin RM, Kalkreuth W (1991) Lithotype (maceral) composition and variation as correlated with paleo-wetland environment, gates formation, Northeastern British Columbia, Canada. Int J Coal Geol 18:87–124
Lin MY, Tian L (2011) Petrographic characteristics and depositional environment of the No. 9 Coal (Pennsylvanian) from the Anjialing Mine, Ningwu Coalfield, China. Energy Explor Exploit 29(2):197–204
Merh SS (1995) Geology of Gujarat. Geological Society of India, Publisher, Gavipuram, Banglore, pp 1–220
Moore TA, Shearer JC (2003) Peat/coal type and depositional environment-are they related? Int J Coal Geol 56(3–4):233–252
O’Keefe JMK, Bechtel A, Christanis K, Dai S, DiMichele WA, Eble CF, Esterle JS, Mastalerz M, Raymond AL, Valentim BV, Wagner NJ, Ward CR, Hower JC (2013) On the fundamental difference between coal rank and coal type. Int J Coal Geol 118:58–87
Petersen HI (1993) Petyrographic facies analysisof Lower and Middle Jurassic coal seams on the island of Bomholm, Denmark. Int J Coal Geol 22(3–4):189–216
Prasad V, Thakur B, Kapur VV, Singh IB, Singh A, Bajpai S, Garg R, Saravanam N (2013) Palynofacies and sedimentology-based high-resolution sequence stratigraphy of the lignite-bearing muddy coastal deposits (early Eocene) in the Vastan Lignite Mine, Gulf of Cambay, India. Facies 59:737–761
Sarkar A, Ray AK, Bhattacharya SK (1996) Stable isotope studies of fossiliferous Palaeogene sequence of Kutch, western India: palaeoenvironmental implications. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 121:65–77
Schopf JM (1960) Field description and sampling of coal beds. U.S. Geol Survey Bull B 1111:25–69
Scott AC (2002) Coal petrology and the origin of coal macerals: a way ahead? Int J Coal Geol 50(1–4):119–134
Shearer JC, Clarkson BR (1998) Whangamarino wetland: effects of lowered river levels on peat and vegetation. Int Peat J 8:52–65
Singh MP, Singh PK (1996) Petrographic characterization and evolution of the Permian coal deposits of the Rajmahal basin, Bihar, India. Int J coal Geol 29(1–3):93–118
Singh PK, Singh MP, Singh AK (2010a) Petro-chemical characterization and evolution of Vastan Lignite, Gujarat, India. Int J Coal Geol 82(1–2):1–16
Singh PK, Singh MP, Singh AK, Arora M (2010b) Petrographic characteristics of coal from the Lati Formation, Tarakan basin, East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Int J Coal Geol 81(2):109–116
Singh PK, Singh MP, Singh AK, Naik AS, Singh Vikas K, Singh Vijay K, Rajak PK (2012a) Petrological and geochemical investigations of Rajpardi lignite deposit, Gujarat, India. Energy Explor Exploit 30(1):131–152
Singh PK, Singh MP, Singh AK, Naik AS (2012b) Petrographic and geochemical characterization of coals from Tiru valley, Nagaland, NE India. Energy Explor Exploit 30(2):171–192
Singh PK, Singh MP, Singh AK, Arora M, Naik AS (2013) The prediction of the liquefaction behavior of the East Kalimantan Coals of Indonesia: an appraisal through petrography of selected coal samples. Energy Sources Part A 35:1728–1740
Singh AL, Singh PK, Kumar A, Yadav A, Singh MP (2014) Experimental study on demineralization of coal with Pseudomonas mendocina strain B6-1 bacteria to obtain clean fuel. Energy Explor Exploit 32(5):831–846
Srivastava VK, Singh BP (2017) Shoreface to estuarine sedimentation in the late Paleocene Matanomadh Formation, Kachchh, western India. J Asian Earth Sci 136:1–15
Styan WB, Bustin RM (1983) Petrography of some Fraser Delta peat deposits: coal maceral and microlithotype precursors in temperate-climate peats. Int J Coal Geol 2(4):321–370
Suárez-Ruiz I, Flores D, Filho JGM, Hackley PC (2012) Review and update of the applications of organic petrology: part 1, geological applications. Int J Coal Geol 99:54–112
Sýkorová I, Pickel W, Christanis M et al (2005) Classification of huminite. ICCP System 1994. Int J Coal Geol 62(1):85–106
Taylor GH, Teichmuller M, Davis A et al (1998) Organic petrology. Gebruder Borntraeger, Berlin, Stuttgart, p 704
Teichmüller M (1989) The genesis of coal from the viewpoint of coal petrology. Int J coal Geology 12:1–87
Teichmuller M, Taylor GH, Littke R (1998) The nature of organic matter-macerals associated minerals. In: Taylor GH, Teichmuller M, Davis A, Diessel CFK, Littke R, Robert P (eds) Organic petrology. Gebruder Borntraeger, Berlin, p 704
Teichmüller M, Littke R, Taylor GH (1998) The origin of organic matter in sedimentary rocks. In: Taylor GH, Teichmüller M, Davis A, Diessel CFK, Littke R, Robert P (eds) Organic Petrology. Gebru¨der Borntraeger, Berlin, p 704
Wust RAJ, Hawke MI, Bustin RM (2001) Comparing maceral ratios from tropical peatlands with assumption from coal studies; do classic coal petrographic interpretation methods have to be discarded. Int J Coal Geol 48:115–132
Acknowledgements
The authors thankfully acknowledge the Department of Geology, Banaras Hindu University for extending the laboratory and other facilities and to the National Metallurgical Laboratory, Jamshedpur for permission to take vitrinite reflectance measurements. The help rendered by the officials in the Panandhro and Matanomadh mines is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P.K., Singh, V.K., Singh, M.P. et al. Understanding the paleomires of Eocene lignites of Kachchh Basin, Gujarat (Western India): petrological implications. Int J Coal Sci Technol 4, 80–101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-017-0165-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-017-0165-2