Abstract
Objectives
The male warrior hypothesis suggests that men have evolved psychological mechanisms to form aggressive coalitions against members of outgroups, which may explain men’s propensity to engage in warfare, as well as team sports. We examined gender differences in skin conductivity and attitudes toward war after exposing participants to video imagery depicting sports and war from a sample of young adults from Slovakia.
Methods
We measured skin conductivity responses using electrodermal activity (EDA) when participants watched three short videos: Football, World War II, and Control. Then, implicit and explicit attitudes toward war and subjective arousal of the three videos were examined using questionnaires.
Results
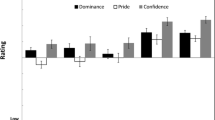
Men showed higher maximal skin conductivity when watching a team sport video, compared to a control video. Skin conductivity during a war video did not significantly differ from a sport or control video. In contrast, women showed highest maximal skin conductivity when watching a war video, followed by the sport and control videos, but these differences were not statistically significant. When the videos were subjectively rated by the same participants, men rated team sports and war as similarly arousing, but ratings of these videos were not significantly different for women.
Conclusions
These results suggest that visual cues of warfare and team sports influence skin conductivity, but we did not find support for the hypothesis that sport is a substitute for war. Because this study was based exclusively on visual cues, we discuss additional possibilities that could influence future investigations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adam, M. T., Krämer, J., & Weinhardt, C. (2012). Excitement up! Price down! Measuring emotions in Dutch auctions. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 17(2), 7–40. https://doi.org/10.2753/JEC1086-4415170201
Balish, S. M., Deaner, R. O., Rainham, D., & Blanchard, C. (2016). Sex differences in sport remain when accounting for countries’ gender inequality. Cross-Cultural Research, 50(5), 395–414. https://doi.org/10.1177/1069397116665815
Bechara, A., & Damasio, A. R. (2005). The somatic marker hypothesis: A neural theory of economic decision. Games and Economic Behavior, 52(2), 336–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geb.2004.06.010
BIOPAC. EDA electrodes. (Accessed: Aug. 1 (2020a). [Online]. Available at: https://www.biopac.com/product/eda-electrodes/?attribute_pa_size=disp-eda-electrode-100pk
BIOPAC. EDA Introductory Guide. (Accessed: Aug. 1 (2020b). [Online]. Available: https://www.biopac.com/wp-content/uploads/EDA-Guide.pdf
Boucsein, W. (2012). Principles of electrodermal phenomena. In W. Boucsein (Ed.), Electrodermal activity (pp. 1–86). Boston, MA: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-1126-0_1
Bowles, S. (2009). Did warfare among ancestral hunter–gatherer groups affect the evolution of human social behaviors. Science, 324(5932), 1293–1298. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1168112
Chagnon, N. A. (1988). Life histories, blood revenge, and warfare in a tribal population. Science, 239(4843), 985–992. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.239.4843.985
Chang, L., Lu, H. J., Li, H., & Li, T. (2011). The face that launched a thousand ships: The mating-warring association in men. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 37(7), 976–984. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167211402216
Crofoot, M. C., & Wrangham, R. W. (2010). Intergroup aggression in primates and humans: the case for a unified theory. In P. M. Kappeler, & J. B. Silk (Eds.), Mind the gap (pp. 171–195). Berlin: Springer
Dawson, M. E., Schell, A. M., & Filion, D. L. (2007). The electrodermal system. In: J.T. Cacioppo, L.G. Tassinary, and G.G. Berntson (eds.), Handbook of Psychophysiology, (pp. 159–181 and 200–223, 3rd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, New York
Deaner, R. O., Geary, D. C., Puts, D. A., Ham, S. A., Kruger, J., Fles, E. … Grandis, T. (2012). A sex difference in the predisposition for physical competition: males play sports much more than females even in the contemporary U.S. PLoS ONE, 7(11), e49168. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049168
Epting, L. K., Riggs, K. N., Knowles, J. D., & Hanky, J. J. (2011). Cheers vs. jeers: effects of audience feedback on individual athletic performance. North American Journal of Psychology, 13(2), 299–331
Escasa, M., Gray, P. B., & Patton, J. Q. (2010). Male traits associated with attractiveness in Conambo, Ecuador. Evolution and Human Behavior, 31(3), 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2009.09.008
Faurie, C., Pontier, D., & Raymond, M. (2004). Student athletes claim to have more sexual partners than other students. Evolution & Human Behavior, 25(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1090-5138(03)00064-3
FIFA (2015). 2014 FIFA World Cup ™ reached 3.2 billion viewers, one billion watched final. Retrieved from FIFA website: 2014 FIFA World Cup ™ available at: https://www.fifa.com/worldcup/news/2014-fifa-world-cuptm-reached-3-2-billion-viewers-one-billion-watched--2745519
Furley, P. (2019). What modern sports competitions can tell us about human nature. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 14(2), 138–155. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691618794912
Geary, D. C. (1998). Male, female: The evolution of human sex differences. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Glowacki, L., & Wrangham, R. W. (2013). The role of rewards in motivating participation in simple warfare. Human Nature, 24(4), 444–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12110-013-9178-8
Glowacki, L., & Wrangham, R. (2015). Warfare and reproductive success in a tribal population. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(2), 348–353. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1412287112
Greem, P., & MacLeod, C. J. (2016). SIMR: an R package for power analysis of generalized linear mixed models by simulation. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 493–498. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12504
Hames, R. (2020). Cultural and reproductive success and the causes of war: A Yanomamö perspective. Evolution and Human Behavior, 41(3), 183–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2020.02.008
Henriques, G. J., Simon, B., Ispolatov, Y., & Doebeli, M. (2019). Acculturation drives the evolution of intergroup conflict. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(28), 14089–14097. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810404116
Holm, S. K., Kaakinen, J. K., Forsström, S., & Surakka, V. (2021). Self-reported playing preferences resonate with emotion-related physiological reactions during playing and watching of first-person shooter videogames. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 155, 102690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2021.102690
Huoviala, P., & Rantala, M. J. (2013). A putative human pheromone, androstadienone, increases cooperation between men. PloS One, 8(5), e62499. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone
Ji, T., Tybur, J. M., & van Vugt, M. (2021). Gendered outgroup prejudice: An evolutionary threat management perspective on anti-immigrant bias. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 24(1), 177–192. https://doi.org/10.1177/1368430219882489
Jones, M. V., Bray, S. R., & Lavallee, D. (2007). All the world’s a stage: Impact of an audience on sport performers. In S. Jowett, & D. Lavallee (Eds.), Social Psychology in Sport (pp. 103–113). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics
Kołodziej, M., Tarnowski, P., Majkowski, A., & Rak, R. (2019). Electrodermal activity measurements for detection of emotional arousal. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences, Technical Sciences, 67(4), 813–826. https://doi.org/10.24425/bpasts.2019.130190
Kreibig, S. D. (2010). Autonomic nervous system activity in emotion: a review. Biological Psychology, 84(3), 394–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2010.03.010
Lahr, M. M., Rivera, F., Power, R. K., Mounier, A., Copsey, B., et al. (2016). Inter-group violence among early Holocene hunter-gatherers of West Turkana, Kenya. Nature, 529(7586), 394–398. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16477
Lenth, R. V. (2016). Least-Squares Means: The R Package lsmeans. Journal of Statistical Software, 69(1), 1–33. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v069.i01
Livingstone Smith, D. (2007). The most dangerous animal: Human nature and the origins of war. New York:St. Martin’s Press
Lizotte, M. K. (2015). Gender differences in support for torture. Journal of Conflict Resolution, 61(4), 772–787. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022002715595698
Lombardo, M. P. (2012). On the evolution of sport. Evolutionary Psychology, 10(1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1177/147470491201000101
Macfarlan, S. J., Walker, R. S., Flinn, M. V., & Chagnon, N. A. (2014). Lethal coalitionary aggression and long-term alliance formation among Yanomamö men. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U. S. A., 111(47), 16662–16669. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1418639111
Majolo, B. (2019). Warfare in an evolutionary perspective. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews, 28(6), 321–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/evan.21806
Manson, J. H., Wrangham, R. W., Boone, J. L., Chapais, B., Dunbar, R. I. M., Ember, C. R., Irons, W., et al. (1991). Intergroup aggression in chimpanzees and humans [and comments and replies]. Current Anthropology, 32(4), 369–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12110-012-9132-1
McClure, E. B., Monk, C. S., Nelson, E. E., Zarahn, E., Leibenluft, E., Bilder, R. M., et al. (2004). A developmental examination of gender differences in brain engagement during evaluation of threat. Biological Psychiatry, 55(11), 1047–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.02.013
McDonald, M. M., Navarrete, C. D., & Van Vugt, M. (2012). Evolution and the psychology of intergroup conflict: the male warrior hypothesis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Ser. B: Biological Sciences, 367(1589), 670–679. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2011.0301
Miller, K. E., Sabo, D. F., Farrell, M. P., Barnes, G. M., & Melnick, M. J. (1998). Athletic participation and sexual behavior in adolescents: The different worlds of boys and girls. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 39(2), 108–123
Muñoz-Reyes, J. A., Polo, P., Valenzuela, N., Pavez, P., Ramírez-Herrera, O., Figueroa, et al. (2020). The Male Warrior Hypothesis: testosterone-related cooperation and aggression in the context of Intergroup Conflict. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57259-0
Pew Research Center (2013). Continued support for U.S. drone strikes. Retrieved from http://www.people-press.org/files/legacypdf/2-11-13%20Drones%20Release.pdf
R Core Team (2020). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Ramirez, A. V., Hornero, G., Royo, D., Aguilar, A., & Casas, O. (2020). Assessment of emotional states through physiological signals and its application in music therapy for disabled people. IEEE Access: Practical Innovations, Open Solutions, 8, 127659–127671. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3008269
Ravaja, N., Saari, T., Salminen, M., Laarni, J., & Kallinen, K. (2006). Phasic emotional reactions to video game events: A psychophysiological investigation. Media Psychology, 8(4), 343–367. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532785xmep0804_2
Ravaja, N., Turpeinen, M., Saari, T., Puttonen, S., & Keltikangas-Järvinen, L. (2008). The psychophysiology of James Bond: Phasic emotional responses to violent video game events. Emotion, 8(1), 114–120. https://doi.org/10.1037/1528-3542.8.1.114
Romero-Martínez, A., Lila, M., Williams, R. K., González-Bono, E., & Moya-Albiol, L. (2013). Skin conductance rises in preparation and recovery to psychosocial stress and its relationship with impulsivity and testosterone in intimate partner violence perpetrators. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 90(3), 329–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.10.003
Scalise Sugiyama, M. (2014). Fitness costs of warfare for women. Human Nature, 25(4), 476–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12110-014-9216-1
Scalise Sugiyama, M., Mendoza, M., & Sugiyama, L. (2020). War games: Intergroup coalitional play fighting as a means of comparative coalition formidability assessment. Evolutionary Behavioral Sciences, 15(2), 91–110. https://doi.org/10.1037/ebs0000251
Schulte-Hostedde, A. I., Eys, M. A., & Johnson, K. (2008). Female mate choice is influenced by male sport participation. Evolutionary Psychology, 6(1), 113–124. https://doi.org/10.1177/147470490800600113
Schwarz, A., Mertens, L., Simons, M., Spook, J. E., Thompson, D., Cardon, G., et al. (2019). Which game narratives do adolescents of different gameplay and sociodemographic backgrounds prefer? a mixed-methods analysis. Games for Health Journal, 8(3), 195–204. https://doi.org/10.1089/g4h.2017.0178
Shavers, T., Baghurst, T., & Finkelstein, M. (2015). The influence of social status and power on the sexual behavior of male collegiate football athletes. Journal for the Study of Sports and Athletes in Education, 9(2), 86–101. https://doi.org/10.1179/1935739715Z.00000000037
Strauss, B., & MacMahon, C. (2014). Audience influences on athlete performances. In A. Papaioannou, & D. Hackfort (Eds.), Routledge Companion to Sport and Exercise Psychology. Global Perspectives and Fundamental Concepts (pp. 213–216). New York, NY: Routledge
Sulikowski, D., & Burke, D. (2014). Threat is in the sex of the beholder: men find weapons faster than do women. Evolutionary Psychology, 12(5), 913–931. https://doi.org/10.1177/147470491401200505
Thirer, J., & Wright, S. D. (1985). Sports and social status for adolescent males and females. Sociology of Sport Journal, 2(2), 164–171. https://doi.org/10.1123/ssj.2.2.164
Thornhill, R., & Palmer, C. T. (2000). A natural history of rape: Biological bases of sexual coercion. Cambridge, MA: The MIT press
TIBCO Software Inc (2017). Statistica (data analysis software system), version 13. http://statistica.io
Torgler, B. (2003). Why do people go to war? Defence and Peace Economics, 14(4), 261–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/10242690302929
van Vugt, M., Cremer, D. D., & Janssen, D. P. (2007). Gender differences in cooperation and competition: The male-warrior hypothesis. Psychological Science, 18(1), 19–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01842.x
Wilcox, C., Hewitt, L., & Allsop, D. (1996). The gender gap in attitudes toward the Gulf War: A cross-national perspective. Journal of Peace Research, 33(1), 67–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022343396033001005
Wilson, M. L., & Wrangham, R. W. (2003). Intergroup relations in chimpanzees. Annual Review of Anthropology, 32(1), 363–392. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.anthro.32.061002.120046
Winegard, B., & Deaner, R. O. (2010). The evolutionary significance of Red Sox Nation: Sport fandom as a by-product of coalitional psychology. Evolutionary Psychology, 8(3), 432–446. https://doi.org/10.1177/147470491000800310
Wu, X. J., Schepartz, L. A., Liu, W., & Trinkaus, E. (2011). Antemortem trauma and survival in the late middle Pleistocene human cranium from Maba, South China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 108 (49), 19558–19562. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1117113108
Wu, X., & Trinkaus, E. (2015). Neurocranial trauma in the late archaic human remains from Xujiayao, northern China. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 25(2), 245–252. https://doi.org/10.1002/oa.2283
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Professor Mark van Vugt, the Editor and two anonymous referees for their critical comments on an earlier draft of the MS. PP was partly funded by VEGA no. 1/0286/2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosťovecký, M., Riegert, J., Pazda, A. et al. Skin Conductivity Responses to Images of War and Sports in Men and Women: An Evolutionary Perspective. Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology 8, 263–279 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40750-022-00186-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40750-022-00186-8