Abstract
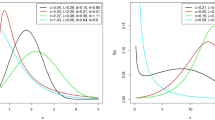
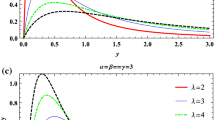
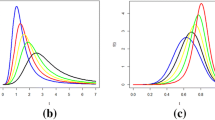
The paper proposes a new probability distribution, named inverse xgamma (IXG) distribution. Different mathematical and statistical properties, viz., reliability characteristics, inverse moments, quantile function, mean inverse residual life, stress-strength reliability, stochastic ordering and order statistics of the proposed distribution have been derived and discussed. Estimation of the parameter of IXG distribution has been approached by different methods, namely, maximum likelihood estimation, least squares estimation, weighted least squares estimation, Cramèr–von-Mises estimation and maximum product of spacing estimation (MPSE). A simulation study has been carried out to compare the performance of these estimators in terms of their mean squared errors. Asymptotic confidence interval of the parameter in terms of average widths and coverage probabilities is also obtained using MPSE of the parameter. Finally, a data set is used to demonstrate the applicability of IXG distribution in real life situations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowley AL (1920) Element of statistics. P.S. King and Son Ltd., New York
Cheng RCH, Amin NAK (1979) Maximum product-of-spacings estimation with applications to the log-normal distribution. University of Wales IST, Math Report, 79-1
Cheng RCH, Amin NAK (1983) Estimating parameters in continuous univariate distributions with a shifted origin. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 3:394–403
Ghosh K, Jammalamadaka SR (2001) A general estimation method using spacings. J Stat Plan Inference 93(1–2):71–82
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 5:299–314
Keller AZ, Kamath AR (1982) Reliability analysis of CNC machine tools. Reliab Eng 3:449–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-8174(82)90036-1
Lawless JF (2003) Statistical models and methods for lifetime data. Wiley, New York
MacDonald PDM (1971) Comment on an estimation procedure for mixtures of distributions by Choi and Bulgren. J R Stat Soc Ser B 33(2):326–329
Moors JJ (1988) A quantile alternative for kurtosis. J R Stat Soc Ser D 37:25–32
Ranneby B (1984) The maximum spacing method. An estimation method related to the maximum likelihood method. Scand J Stat 11(2):93–112
Sen S, Maiti SS, Chandra N (2016) The xgamma distribution: statistical properties and application. J Mod Appl Stat Methods 15(1):774–788
Sen S, Chandra N, Maiti SS (2018) Survival estimation in xgamma distribution under progressively type-II right censored scheme. J Model Assist Stat Appl 13(2):107–121
Sen S, Chandra N (2017) The quasi xgamma distribution with application in bladder cancer data. J Data Sci 15:61–76
Shaked M, Shanthikumar JG (1994) Stochastic orders and their applications. Academic Press, New York
Sharma VK, Singh SK, Singh U, Agarwal V (2015) The inverse Lindley distribution: a stress-strength reliability model with application to head and neck cancer data. J Ind Prod Eng 32(3):162–173
Singh SK, Singh U, Kumar M (2016) Bayesian estimation for Poisson-exponential model under progressive type-II censoring data with binomial removal and its application to ovarian cancer data. Commun Stat Simul Comput 45:3457–3475
Swain J, Venkatraman S, Wilson J (1988) Least squares estimation of distribution function in Johnsons translation system. J Stat Comput Simul 29:271–297
Voda VG (1972) On the inverse Rayleigh random variable. Pep Stat Appl Res Juse 19(4):13–21
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Editor-in-Chief and anonymous Referees for their constructive comments, which led to the present form of the paper. We also thanked Dr. Ved prakash, Dept. of English, Central University of Rajasthan for going through the manuscript and suggesting some modifications in present version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, A.S., Maiti, S.S. & Saha, M. The Inverse Xgamma Distribution: Statistical Properties and Different Methods of Estimation. Ann. Data. Sci. 8, 275–293 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-019-00211-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-019-00211-w