Abstract
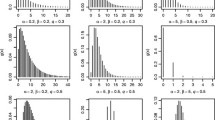
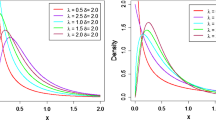
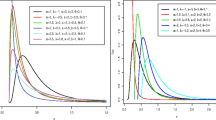
In this article, we introduced and studied exponentiated generalized Kumaraswamy distribution. We derived mathematical properties including quantile function, moment generating function, ordinary moments, probability weighted moments, incomplete moments, and Rényi entropy. The expressions of order statistics are also derived. Here we discuss the parameter estimation by using the method of maximum likelihood. We showed resilience of the introduced distribution over existing some well-known distributions by using real dataset applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya G, Elbata I (2015) On the exponentiated generalized modified Weibull distribution. Commun Stat Appl Methods 22:333–348
Alzaatreh A, Lee C, Famoye F (2013) A new method for generating families of continuous distributions. Metron 71(1):63–79
Azzalini A (1985) A class of distributions which includes the normal ones. Scand J Stat 12(2):171–178
Cordeiro GM, De Andrade TAN, Bourguignon M, da- Silva FSG (2017) The exponentiated generalized standardized half-logistic distribution. Int J Stat Probab 6(3):24–42
Cordeiro GM, de Castro M (2011) A new family of generalized distribution. J Stat Comput Simul 81(7):883–898
Cordeiro GM, Gomes AE, da-Silva CQ (2014) Another extended Burr III model: some properties and applications. J Stat Comput Simul 84(12):2524–2544
Cordeiro GM, Ortega EMM, da Cunha DCC (2013) The exponentiated generalized class of distributions. J Data Sci 11(1):1–27
De Andrade TAN, Bourguignon M, Cordeiro GM (2016) The exponentiated generalized extended exponential distribution. J Data Sci 14(3):393–414
Dumonceaux R, Antle CE (1973) Discriminating between the log-normal and Weibull Distribution. Technometrics 15(4):923–926
Elbatal I, Muhammed HZ (2014) Exponentiated generalized inverse Weibull distribution. Appl Math Sci 8:3997–4012
Elgarhy M, Hassan AS, Rashed M (2016) Garhy-generated family of distributions with application. Math Theory Model 6:1–15
Eugene N, Lee C, Famoye F (2002) Beta-normal distribution and its applications. Commun Stat Theory Methods 31(4):497–512
Gupta RC, Gupta PL, Gupta RD (1998) Modeling failure time data by Lehman alternatives. Commun Stat Theory Methods 27(4):887–904
Hassan AS, Elgarhy M (2016) Kumaraswamy Weibull-generated family of distributions with applications. Adv Appl Stat 48:205–239
Hassan AS, Elgarhy M (2016) A new family of exponentiated Weibull-generated distributions. Int J Math Appl 4:135–148
Hassan AS, Hemeda SE (2016) The additive Weibull-g family of probability distributions. Int J Math Appl 4:151–164
Haq MA, Butt NS, Usman RM, Fattah AA (2016) Transmuted power function distribution. Gazi Univ J Sci 29(1):177–185
Kumaraswamy P (1980) Generalized probability density function for double-bounded random-processes. J Hydrol 46(1–2):79–88
Lemonte AJ (2014) A new exponential-type distribution with constant, decreasing, increasing, upside-down bathtub and bathtub-shaped failure rate function. Comput Stat Data Anal 62:149–170
Mansoor M, Tahir MH, Alzaatreh A, Ghazali SSA (2016) An extended Fréchet distribution: properties and applications. J Data Sci 14:167–188
Marshall AN, Olkin I (1997) A new method for adding a parameter to a family of distributions with applications to the exponential and Weibull families. Biometrika 84(3):641–652
Oguntunde PE, Adejumo AO, Balogun OS (2014) Statistical properties of the exponentiated generalized inverted exponential distribution. Appl Math 4:47–55
Rényi A (1961) On measures of entropy and information. In: Proceedings of the fourth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability, vol 1, pp 547–561
Ristic MM, Balakrishnan N (2011) The gamma-exponentiated exponential distribution. J Stat Comput Simul 82(8):1191–1206
Shakeel M, ul Haq MA, Hussain I, Abdulhamid AM, Faisal M (2016) Comparison of Two New Robust Parameter Estimation Methods for the Power Function Distribution. PloS ONE 11(8):e0160692
Shakeel M, Rehmat N, ul Haq MA (2017) Comparison of the robust parameters estimation methods for the two-parameters Lomax distribution. Cogent Math 4(1):1279397
Sharma D, Chakrabarty TK (2016) On size biased Kumaraswamy distribution. arXiv:1609.09278
Shuaib KM, Robert K, Lena HI (2016) Transmuted Kumaraswamy distribution. Stat Transit New Ser 17(2):183–210
Shaw WT, Buckley IR (2009) The alchemy of probability distributions: beyond Gram–Charlier expansions, and a skew-kurtotic-normal distribution from a rank transmutation map. arXiv:0901.0434
Silva AO, da Silva LCM, Cordeiro GM (2015) The extended Dagum distribution: properties and application. J Data Sci 13:53–72
Zografos K, Balakrishnan N (2009) On families of beta- and generalized gamma-generated distributions and associated inference. Stat Methodol 6(4):344–362
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The elements of the observed Fisher information matrix \(I^{-1}(\Theta )\) are given by
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elgarhy, M., Haq, M.A.u. & ul Ain, Q. Exponentiated Generalized Kumaraswamy Distribution with Applications. Ann. Data. Sci. 5, 273–292 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-017-0128-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-017-0128-x