Abstract
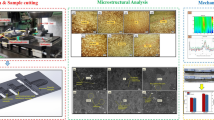
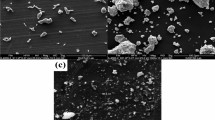
In this research work, hybrid AA2024–SiC/Si3N4 alloy composites were designed and prepared through a semi-automatic stir casting route, following industrial procedure. The ceramic (SiC/Si3N4) particulates were reinforced in the complementary manner (0–4 wt% @ step of 1%), leading to five composite specimens, namely CN04, CN13, CN22, CN31, and CN40. The samples of each composition were analyzed for their physical, mechanical, thermal conductivity, fracture toughness, and tribological behavior (steady-state sliding wear analysis) adopting ASTM standards. The Taguchi methodology was applied to optimize experimental simulations and input operating variables (like sliding velocity, sliding distance, normal load, composition, and environment temperature) with ANOVA. Worn-out surface micrograph studies were performed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) to understand wear mechanisms and elemental presence/dispersion over the surface. Further, a decision-making tool like a hybrid AHP-TOPSIS method was applied to rank the hybrid alloy composites based upon performance measures. The hybrid alloy composites shows some peculiar properties like density ~ 2.495–2.772 g/cc, voids content ~ 0.63–10.49%, Rockwell hardness (HRB) ~ 76.6 to 92.8 HRB, tensile strength ~ 191–277 MPa, flexural strength ~ 291–419 MPa, Impact strength ~ 24–100 J, thermal conductivity ~ 141–152 W/mK, fracture toughness ~ 6–41 MPa √m. Taguchi’s factorial design of the experiment shows an error of 3.5% for the S/N ratio of wear rate that validates the robustness of the experiential design. The wear rate and friction coefficient improve with sliding velocity irrespective of composition across the formulation. Further, it has been found that CN22 hybrid alloy composite having an equal amount of both ceramics tends to optimize the overall physical and mechanical properties along with steady-state sliding behavior, which is in-tune-with the results of ranking obtained hybrid AHP-TOPSIS method. The sensitivity analysis of performance criteria gives robust/stable ranking order whenever the criteria’s weight varies within ± (10–15)%.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Additional data are available on reasonable request by email to the corresponding author.
References
ASM International The Materials Information Company (1998) ASM Handbook Vol.2 Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials was published in 1990 as Volume 2 of the 1 0 Edition Metals Handbook. With the second printing (1992). Eur J Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050884
Bhaskar S, Kumar M, Patnaik A (2019) A review on tribological and mechanical properties of Al alloy composites. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.09.032
Kumar M, Kumar A (2019) Sliding wear performance of graphite reinforced AA6061 alloy composites for rotor drum/disk application. Mater Today Proc 27:1972–1976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.09.042
Singh J, Chauhan A (2016) Overview of wear performance of aluminium matrix composites reinforced with ceramic materials under the influence of controllable variables. Ceram Int 42:56–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.150
Ravindran P, Manisekar K, Vinoth Kumar S, Rathika P (2013) Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum hybrid nano-composites with the additions of solid lubricant. Mater Des 51:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.04.015
Kumar BA, Murugan N, Dinaharan I (2014) Dry sliding wear behavior of stir cast AA6061-T6/AlNp composite. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 24:2785–2795. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63410-5
Rajmohan T, Palanikumar K, Ranganathan S (2013) Evaluation of mechanical and wear properties of hybrid aluminium matrix composites. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China (English Ed) 23:2509–2517. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62762-4
Devaraju A, Kumar A, Kotiveerachari B (2013) Influence of addition of Grp/Al2O3p with SiCp on wear properties of aluminum alloy 6061–T6 hybrid composites via friction stir processing. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China (English Ed) 23:1275–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62593-5
Rao RN, Das S, Mondal DP, Dixit G (2012) Mechanism of material removal during tribological behaviour of aluminium matrix (Al–Zn–Mg–Cu) composites. Tribol Int 53:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.04.017
Rao RN, Das S (2011) Effect of SiC content and sliding speed on the wear behaviour of aluminium matrix composites. Mater Des 32:1066–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.06.047
Rao RN, Das S (2010) Effect of matrix alloy and influence of SiC particle on the sliding wear characteristics of aluminium alloy composites. Mater Des 31:1200–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.09.032
Hong SJ, Kim HM, Huh D et al (2003) Effect of clustering on the mechanical properties of SiC particulate-reinforced aluminum alloy 2024 metal matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng A 347:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00593-2
Selvam JDR, Dinaharan I, Philip SV, Mashinini PM (2018) Microstructure and mechanical characterization of in situ synthesized AA6061/(TiB2 + Al2O3) hybrid aluminum matrix composites. J Alloys Compd 740:529–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.016
Sharma P, Sharma S, Khanduja D (2015) Production and some properties of Si3N4 reinforced aluminium alloy composites. J Asian Ceram Soc 3:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jascer.2015.07.002
Umanath K, Palanikumar K, Selvamani ST (2013) Analysis of dry sliding wear behaviour of Al6061/SiC/Al2O3 hybrid metal matrix composites. Composites Part B Eng 53:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.04.051
Kök M (2006) Abrasive wear of Al2O3 particle reinforced 2024 aluminium alloy composites fabricated by vortex method. Composites Part A Appl Sci Manuf 37:457–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.05.038
Ozdemir I, Muecklich S, Podlesak H, Wielage B (2011) Thixoforming of AA 2017 aluminum alloy composites. J Mater Process Technol 211:1260–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.02.008
Rajeev VR, Dwivedi DK, Jain SC (2010) Dry reciprocating wear of Al–Si–SiCp composites: a statistical analysis. Tribol Int 43:1532–1541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.02.014
Herbert MA, Maiti R, Mitra R, Chakraborty M (2008) Wear behaviour of cast and mushy state rolled Al–4.5Cu alloy and in-situ Al4.5Cu–5TiB2 composite. Wear 265:1606–1618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2008.03.010
Kurt HI (2016) Influence of hybrid ratio and friction stir processing parameters on ultimate tensile strength of 5083 aluminum matrix hybrid composites. Composites Part B Eng 93:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.02.056
Gautam G, Mohan A (2015) Effect of ZrB2 particles on the microstructure and mechanical properties of hybrid (ZrB2 + Al3Zr)/AA5052 insitu composites. J Alloys Compd 649:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.096
Bhaskar S, Kumar M (2021) Effect of graphite particulates on sliding wear performance of hybrid AA2024 alloy composites. J Mater Eng Perform 30:3976–3989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05677-5
Sreenivasa R, Mallur SB (2021) Sliding wear behavior of Cu + Sn + Cr composites by Taguchi technique. J Bio-Tribo-Corrosion 7:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-020-00465-5
Khan MM, Hajam MI, Mir ZA (2021) Optimizing the effect of solid lubricants on the sliding wear behavior of SiCp reinforced cast aluminum alloy. J Bio-Tribo-Corrosion 7:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-020-00460-w
Patnaik A, Kumar P, Biswas S, Kumar M (2012) Investigations on micro-mechanical and thermal characteristics of glass fiber reinforced epoxy based binary composite structure using finite element method. Comput Mater Sci 62:142–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.05.020
Kumar A, Patnaik A, Bhat IK (2018) Effect of titanium metal powder on thermo- mechanical and sliding wear behavior of Al7075/Ti alloy composites for gear application. Mater Today Proc 5:16919–16927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.04.095
Cui X, Wu Y, Liu X (2015) Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of VB2/A390 composite alloy. J Mater Sci Technol 31:1027–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2015.08.004
Baradeswaran A, Elaya Perumal A (2014) Study on mechanical and wear properties of Al7075/Al2O3/graphite hybrid composites. Composites Part B Eng 56:464–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.013
Bahrami M, Helmi N, Dehghani K, Givi MKB (2014) Exploring the effects of SiC reinforcement incorporation on mechanical properties of friction stir welded 7075 aluminum alloy: fatigue life, impact energy, tensile strength. Mater Sci Eng A 595:173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.11.068
Bhaskar S, Kumar M, Patnaik A (2019) Silicon carbide ceramic particulate reinforced AA2024 alloy composite—part I: evaluation of mechanical and sliding tribology performance. SILICON 12:843–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00181-x
Bhaskar S, Kumar M, Patnaik A (2020) Microstructure, thermal, thermo-mechanical and fracture analyses of hybrid AA2024–SiC alloy composites. Trans Indian Inst Met 73:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01819-5
Mohan Krishna SA (2014) An investigative review on thermal characterization of hybrid metal matrix composites. IJMER 4:53–62
Bhaskar S, Kumar M, Patnaik A (2019) Mechanical and Tribological overview of ceramic particulates reinforced aluminium alloy composites. Rev Adv Mater Sci 58:280–294
Kumar A, Patnaik A, Bhat IK (2017) Investigation of nickel metal powder on tribological and mechanical properties of Al-7075 alloy composites for gear materials. Powder Metall 60:371–383. https://doi.org/10.1080/00325899.2017.1318481
Janssen G-J. Information on the FESEM. Radboud University Nijmegen, Nijmegen. www.sem.com/analytic/sem.html
Kumar A, Patnaik A, Bhat IK (2018) Tribology analysis of cobalt particulate filled Al 7075 alloy for gear materials: a comparative study. SILICON. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9920-2
Bhaskar S, Kumar M, Patnaik A (2019) Application of hybrid AHP-TOPSIS Technique in analyzing material performance of silicon carbide ceramic particulate reinforced AA2024 alloy composite. SILICON. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00211-8
Kiliç Delice E, Güngör Z (2009) The usability analysis with heuristic evaluation and analytic hierarchy process. Int J Ind Ergon 39:934–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ergon.2009.08.005
Shyur HJ, Shih HS (2006) A hybrid MCDM model for strategic vendor selection. Math Comput Model 44:749–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2005.04.018
Lin MC, Wang CC, Chen MS, Chang CA (2008) Using AHP and TOPSIS approaches in customer-driven product design process. Comput Ind 59:17–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2007.05.013
Joshi R, Banwet DK, Shankar R (2011) A Delphi-AHP-TOPSIS based benchmarking framework for performance improvement of a cold chain. Expert Syst Appl 38:10170–10182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.02.072
Satapathy BK, Majumdar A, Tomar BS (2010) Optimal design of flyash filled composite friction materials using combined analytical hierarchy process and technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solutions approach. Mater Des 31:1937–1944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.10.047
Yousefpour M, Rahimi A (2014) Characterization and selection of optimal parameters to achieve the best tribological performance of the electrodeposited Cr nanocomposite coating. Mater Des 54:382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.08.017
Kumar M, Kumar R, Tak Y et al (2020) Parametric optimization and ranking analysis of hybrid epoxy polymer composites based on mechanical, thermo-mechanical and abrasive wear performance. High Perform Polym. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954008320959412
Pazhouhanfar Y, Eghbali B (2018) Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of TiB2 reinforced Al6061 matrix composites produced using stir casting process. Mater Sci Eng A 710:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.10.087
Rana RS, Purohit R, Soni VK, Das S (2015) Characterization of mechanical properties and microstructure of aluminium alloy-SiC composites. Mater Today Proc 2:1149–1156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.026
Mamatha TG, Patnaik A, Biswas S et al (2012) Thermo-mechanical and crack position on stress intensity factor in particle-reinforced zinc-aluminium alloy composites. Comput Mater Sci 55:100–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2011.11.028
Muralidharan N, Chockalingam K, Dinaharan I, Kalaiselvan K (2018) Microstructure and mechanical behavior of AA2024 aluminum matrix composites reinforced with in situ synthesized ZrB2 particles. J Alloys Compd 735:2167–2174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.371
Mathan Kumar N, Senthil Kumaran S, Kumaraswamidhas LA (2016) Aerospace application on Al 2618 with reinforced—Si3N4, AlN and ZrB2 in-situ composites. J Alloys Compd 672:238–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.155
Molina JM, Rhême M, Carron J, Weber L (2008) Thermal conductivity of aluminum matrix composites reinforced with mixtures of diamond and SiC particles. Scr Mater 58:393–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.10.020
Sun K, Zhang ZD, Qian L et al (2016) Dual percolation behaviors of electrical and thermal conductivity in metal–ceramic composites. Appl Phys Lett 108:061903. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4941758
Oddone V, Boerner B, Reich S (2017) Composites of aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy with graphite showing low thermal expansion and high specific thermal conductivity. Sci Technol Adv Mater 18:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2017.1286222
Asano K, Yoneda H, Agari Y et al (2014) Thermal and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy composite reinforced with potassium hexatitanate short fiber. Mater Trans 56:160–166. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2014284
Wang Z, Sun K, Xie P et al (2020) Epsilon-negative BaTiO3/Cu composites with high thermal conductivity and yet low electrical conductivity. J Mater 6:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2020.01.007
Vldson DLDA (1993) Fatigue and fracture toughness of aluminium alloys reinforced with SiC and alumina particles. Composites 24:248–255
Pandey AB, Majumdar BS, Miracle DB (2000) Deformation and fracture of a particle-reinforced aluminum alloy composite: Part I. Experiments. Metall Mater Trans A 31:921–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-000-1011-4
Ravindran P, Manisekar K, Rathika P, Narayanasamy P (2013) Tribological properties of powder metallurgy—processed aluminium self lubricating hybrid composites with SiC additions. Mater Des 45:561–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.09.015
Rao RN, Das S, Mondal DP, Dixit G (2010) Effect of heat treatment on the sliding wear behaviour of aluminium alloy (Al–Zn–Mg) hard particle composite. Tribol Int 43:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2009.06.013
Kumar R, Dhiman S (2013) A study of sliding wear behaviors of Al-7075 alloy and Al-7075 hybrid composite by response surface methodology analysis. Mater Des 50:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.02.038
Bai M, Xue Q, Ge Q (1996) Wear of 2024 Al-Mo-SiC composites under lubrication. Wear 195:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(95)06808-2
Ashby MF (1999) Material properties chart. Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford
Jha K, Kumar R, Verma K et al (2018) Application of modified TOPSIS technique in deciding optimal combination for bio-degradable composite. Vacuum 157:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.08.063
Yue Z (2011) A method for group decision-making based on determining weights of decision makers using TOPSIS. Appl Math Model 35:1926–1936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2010.11.001
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere gratitude to the Department of Mechanical Engineering of Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur-302017, Rajasthan, INDIA for their all kinds of financial as well as other miscellaneous infrastructural support. The authors also acknowledge the aid and facilities provided by the Advanced Research Lab for Tribology and Material Research Centre of the Institute for experimentation and characterization work.
Funding
Not applicable, no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MK—Supervisor, conceptualization, methodology, editing the manuscript. RK—M.Tech. student, original or first draft of the manuscript. SB—Editing and some characterization work. AK—Methodology and editing of the manuscript. SH—Hybrid AHP-TOPSIS method and its calculations.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest concerning the research, authorship, and publication of these articles have been declared by the authors.
Consent to Participate
All authors consented to participate.
Consent for Publication
All authors consented for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Kumar, R., Bhaskar, S. et al. Parametric Optimization and Ranking Analysis of Hybrid AA2024–SiC/Si3N4 Alloy Composites Based on Mechanical and Sliding Wear Performance. J Bio Tribo Corros 8, 24 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-021-00619-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-021-00619-z