Abstract
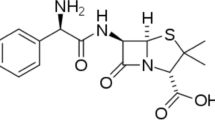
The corrosion inhibition properties of expired acetazolamide for mild steel in acidic solution were studied by gravimetric and Tafel polarization and Electrochemical Impedance spectroscopy. The inhibition efficiency evaluated by all methods was in good agreement with each other. Results suggest that the inhibition efficiency increases with increase in concentration and decreases with temperature. Inhibitor obeys Langmuir adsorption isotherm and shows inhibition efficiency up to 93% at 313 K for 500 ppm solution. Tafel polarization study suggests that it acts as mixed-type inhibitor. Thermodynamic parameters indicate that the adsorption process is spontaneous. Shifting of frequencies in FTIR spectra and SEM-EDX analysis confirms the adsorption of inhibitor on mild steel surface. Application of expired drug as corrosion inhibitor is useful to reduce environmental pollution and economically beneficial to pharmaceutical industries.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doharea P, Chauhana DS, Sorourb AA, Quraishi MA (2017) DFT and experimental studies on the inhibition potentials of expired Tramadol drug on mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid. Mater Discov 9:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.md.2017.11.001
Kamal C, Sethuraman M (2012) Spirulina platensis—A novel green inhibitor for acid corrosion of mild steel. Arab J Chem 5:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.08.006
Sherif ESM, Abbas AT, Gopi D, El-Shamy AM (2014) Corrosion and corrosion inhibition of high strength low alloy steel in 2.0 M sulfuric acid solutions by 3-amino-1,2,3-triazole as a corrosion inhibitor. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/538794
El-Etre AY, Abd El S, Wanees et al (2015) Comparison of the corrosion inhibition by drugs for the corrosion of Nickel in hydrochloric acid. J Am Sci. https://doi.org/10.7537/marsjas110215.03
Ansari KR, Quraishi MA et al (2013) Electrochemical and thermodynamic investigation of diclofenac sodium drug as a potential corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:12860–12873
Fouda S, El-Defrawy AM, El-Sherbeni MW (2013) Lornoxicam & tenoxicam drugs as green corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in 1 M H2SO4 solution. J Electrochem Sci Technol 4(2):47–56. https://doi.org/10.5229/JECST.2013.4.2.47
Naqvi I, Saleemi A, Naveed S (2011) Cefixime: a drug as efficient corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic media. Electrochemical Thermodynamic Studies. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:146–161
Prasanna B, Matad et al (2014) Ketosulfone drug as a green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic medium. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:8436–8444. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie500232g
Mahmoud N. El-Haddad (2016) Inhibitive action and adsorption behavior of cefotaxime drug at copper/hydrochloric acid interface: electrochemical, surface and quantum chemical studies. RSC Adv 6:57844–57853. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA03316D
Kumar SH, Karthikeyan S (2013) Torsemide and furosemide as green inhibitors for the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(22):7457–7469. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie400815w
Rajeswari V, Devarayan K, Viswanathamurthi P (2017) Expired pharmaceutical compounds as potential inhibitors for cast iron corrosion in acidic medium. Res Chem Intermed 43:3893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2852-9
Gökhan G (2011) Drugs: a review of promising novel corrosion inhibitors. Corros Sci 53:3873–3898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.08.006
El-Desoky AM et al (2015) Electrochemical and analytical study of the corrosion inhibitory behavior of expired pharmaceutical compounds for C-steel Corrosion. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:5112–5129
Shukla SK, Singh AK, Ebenso EE (2011) Pharmaceutically active compound as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic medium. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:4276–4285
Singh P, Chauhan DS, Srivastava K et al (2017) Expired atorvastatin drug as corrosion inhibitor for mild steelin hydrochloric acid solution. Int J Ind Chem 8:363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40090-017-0120-5
Geethamani P et al (2015) An expired non-toxic drug acts as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. IJCPS 3(1):1442–1448
Fouda AS, Etaiw SH, Wahba A (2015) Effect of acetazolamide drug as corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Nat Sci 13(9):1–8
Yadav M, Sinha RR, Sarkar TK, Tiwari N (2015) Corrosion inhibition effect of pyrazole derivatives on mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. J Adhes Sci Technol 29(16):1690–1713. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2015.1040979
Yadav M, Sinha RR, Kumar S, Sarkar TK (2015) Corrosion inhibition effect of spiropyrimidinethiones on mild steel in 15% HCl solution: insight from electrochemical and quantum studies. RSC Adv 5:70832–70848. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA14406J
Akbarzadeh E, Ibrahim MNM, Rahim AA (2011) Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in near neutral solution by kraft and soda lignins extracted from oil palm empty fruit bunch. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:5396–5416
Thanapackiam P et al (2016) Electrochemical evaluation of inhibition efficiency of ciprofloxacin on the corrosion of copper in acid media. Mater Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.02.059
Verma C, Quraishi MA, Ebenso EE et al (2018) A green and sustainable approach for mild steel acidic corrosion inhibition using leaves extract: experimental and DFT studies. J Bio Tribo Corros 4:33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-018-0150-3
Saman Zehra M, Mobin JA, Parveen M (2018) Assessment of glycine derivative N-benzylidine-2((2-oxo-2-(10H-phenothiazine-10yl)ethyl)amino) acetohydrazide as inhibitor for mild steel corrosion in 1 M HCl solution: electrochemical and theoretical approach. J Adhes Sci Technol 32(3):317–342. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2017.1354669
Eddy NO, Ebenso EE (2010) Adsorption and quantum chemical studies on cloxacillin and halides for the corrosion of mild steel in acidic medium. Int J Electrochem Sci 5:731–750
Emeka E, Oguzie (2008) Evaluation of the inhibitive effect of some plant extracts on the acid corrosion of mild steel. Corros Sci 50:2993–2998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2008.08.004
Nathiya RS, Perumal S, Murugesan V et al (2018) Expired drugs: environmentally safe inhibitors for aluminium corrosion in 1 M H2SO4. J Bio Tribo Corros 4:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-017-0120-1
de Souza FS, Spinelli A (2009) Caffeic acid as a green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel, Corros Sci 51:642–649, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2008.12.013
Karthik G, Sundaravadivelu M (2016) Studies on the inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution by atenolol drug. Egypt J Pet 25:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.04.003
Praveen BM, Prasanna BM, Hebbar N et al (2018) Experimental and theoretical studies on inhibition effect of the praziquantel on mild steel corrosion in 1 M HCl. J Bio Tribo Corros 4:21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-018-0137-0
Ansari KR, Ramkumar S, Nalini D, Quraishi MA, Slawin AMZ (2016) Studies on adsorption and corrosion inhibitive properties of quinoline derivatives on N80 steel in 15% hydrochloric acid. Cogent Chem 2:1. https://doi.org/10.1080/23312009.2016.1145032
Shukla SK, Singh AK, Ahamad I, Quraishi MA (2009) Streptomycin: a commercially available drug as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Mater Lett 63:819–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.01.020
Shukla SK, Ebenso EE (2011) Corrosion inhibition, adsorption behavior and thermodynamic properties of streptomycin on mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:3277–3291
Vinutha MR, Venkatesha TV, Nagaraja C (2018) Anticorrosive ability of electrochemically synthesized 2,2′-disulfanediyldianiline for mild steel corrosion: electrochemical and thermodynamic studies. Int J Ind Chem 9:185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40090-018-0149-0
Ameh PO, Sani UM (2016) Cefuroxime axetil: a commercially available drug as corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in hydrochloric acid solution. Portugaliae Electrochim Acta 34(2):131–141. https://doi.org/10.4152/pea.201602131
Nnaji NJ, Obi-Egbedia NO, Nnabugwu MA (2012) Kinetics and thermodynamics of aluminium corrosion inhibition by anthocleista djalonensis leaf extract in hydrochloric acid solution. Int J Chem Sci 10(1):182–194
Umoren SA (2016) Biomaterials for corrosion protection: evaluation of mustard seed extract as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for X60 steel in acid media. J Adhes Sci Technol 30:17,1858–1879. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2016.1168339
Acknowledgements
Mr Lakhan Prakash Chaudhari gratefully acknowledges the research grant provided by the North Maharashtra University Jalgaon under Vice Chancellor Research Motivational Scheme [VCRMS] (Grant No. NMU/11A/VCRMS/Budjet-2015/Science-8/65/2016). Authors are also thankful to Head of the U.I.C.T. department of North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon for SEM-EDX analysis facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhari, L.P., Patel, S.N. Corrosion Inhibition Study of Expired Acetazolamide on Mild Steel in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Solution. J Bio Tribo Corros 5, 20 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-018-0212-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-018-0212-6