Abstract
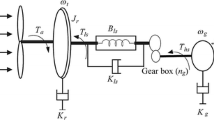
In this study, we present a method to obtain optimal control of the variable-speed fixed-pitch wind turbine using the homotopy perturbation method (HPM). In general, the optimal control problem for nonlinear systems should solve the Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman (HJB) equation. The partial differential HJB equations that arise in optimal control problem, give closed-loop control law and it is difficult to obtain an exact solution of them for nonlinear systems. The main objective of this work is to employ the homotopy perturbation method to solve the HJB equation for a two-mass model of a wind turbine to capture the maximum power from the wind in below-rated wind speed. By applying this strategy, we obtained an approximate solution of the HJB equation for a two-mass model of the wind turbine with high accuracy. In the simulation section, we compare the results of the proposed HPM strategy with the nonlinear static state feedback control (NSSFE) approach. The presented results confirm that the HPM controller produces more electrical power while minimizing low-speed shaft oscillations by improving dynamic characteristics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhandari, B., Lee, K. T., Lee, G. Y., Cho, Y. M., & Ahn, S. H. (2015). Optimization of hybrid renewable energy power systems: A review. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 2(1), 99–112.
Kavya, M., & Jayalalitha, S. (2021). A Novel Shift and Search (S&S) Algorithm for Tracking Maximum Power in PV Systems: An Approach to Increase Efficiency. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 8(6), 1699–1710.
Bhandari, B., Poudel, S. R., Lee, K. T., & Ahn, S. H. (2014). Mathematical modeling of hybrid renewable energy system: A review on small hydro-solar-wind power generation. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 1(2), 157–173.
Kim, K., Kim, H., Paek, I., Kim, H. G., & Son, J. (2019). Field validation of demanded power point tracking control algorithm for medium-capacity wind turbine. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6(5), 875–881.
Boukhezzar, B., & Siguerdidjane, H. (2010). Nonlinear control of a variable-speed wind turbine using a two-mass model. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 26(1), 149–162.
Bektache, A., & Boukhezzar, B. (2018). Nonlinear predictive control of a DFIG-based wind turbine for power capture optimization. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 101, 92–102.
Yin, X. X., Lin, Y. G., Li, W., Gu, Y. J., Lei, P. F., & Liu, H. W. (2015). Sliding mode voltage control strategy for capturing maximum wind energy based on fuzzy logic control. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 70, 45–51.
Lewis, F. L., Vrabie, D., & Syrmos, V. L. (2012). Optimal control. John Wiley & Sons.
Mangasarian, O. L. (1966). Sufficient conditions for the optimal control of nonlinear systems. SIAM Journal on control, 4(1), 139–152.
Zhang, Y., Li, S., & Liao, L. (2019). Near-optimal control of nonlinear dynamical systems: A brief survey. Annual Reviews in Control, 47, 71–80.
Chen, X., & Chen, X. (2017). An iterative method for optimal feedback control and generalized HJB equation. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 5(5), 999–1006.
Zhu, J. (2017). A feedback optimal control by Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equation. European Journal of Control, 37, 70–74.
Fakharian, A., & Hamidi Beheshti, M. T. (2010). Solving linear and nonlinear optimal control problem using modified a domian decomposition method. Journal of Computer & Robotics, 1(1), 79–86.
Shirazian, M., & Effati, S. (2012). Solving a class of nonlinear optimal control problems via He’s variational iteration method. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 10(2), 249–256.
Kafash, B., Delavarkhalafi, A., & Karbassi, S. M. (2013). Application of variational iteration method for Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equations. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37(6), 3917–3928.
Nik, H. S., Effati, S., & Shirazian, M. (2012). An approximate-analytical solution for the Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equation via homotopy perturbation method. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 36(11), 5614–5623.
Effati, S., Saberi Nik, H., & Shirazian, M. (2013). An improvement to the homotopy perturbation method for solving the Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equation. IMA Journal of Mathematical Control and Information, 30(4), 487–506.
Ganjefar, S., & Rezaei, S. (2016). Modified homotopy perturbation method for optimal control problems using the Padé approximant. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 40(15–16), 7062–7081.
He, J. H. (1999). Homotopy perturbation technique. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 178(3–4), 257–262.
He, J. H. (2003). Homotopy perturbation method: A new nonlinear analytical technique. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 135(1), 73–79.
Sakar, M. G., Uludag, F., & Erdogan, F. (2016). Numerical solution of time-fractional nonlinear PDEs with proportional delays by homotopy perturbation method. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 40(13–14), 6639–6649.
Hussain, S., Shah, A., Ayub, S., & Ullah, A. (2019). An approximate analytical solution of the Allen-Cahn equation using homotopy perturbation method and homotopy analysis method. Heliyon, 5(12), e03060.
Wu, Y., & He, J. H. (2018). Homotopy perturbation method for nonlinear oscillators with coordinate dependent mass. Results Phys, 10, 270–271.
Hur, S. H. (2018). Modelling and control of a wind turbine and farm. Energy, 156, 360–370.
Hall, J. F., & Chen, D. (2013). Dynamic optimization of drivetrain gear ratio to maximize wind turbine power generation—part 1: System model and control framework. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 135(1), 011016.
Lim, C. W. (2017). Design and manufacture of small-scale wind turbine simulator to emulate torque response of MW wind turbine. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 4(4), 409–418.
Ghorbani, A. (2009). Beyond a domian polynomials: He polynomials. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 39(3), 1486–1492.
Kirk, D. E. (2004). Optimal control theory: An introduction. Courier Corporation.
Asl, H. J., & Yoon, J. (2016). Power capture optimization of variable-speed wind turbines using an output feedback controller. Renewable Energy, 86, 517–525.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shalbafian, A., Ganjefar, S. Variable Speed Wind Turbine Control Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 10, 141–150 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-022-00422-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-022-00422-2