Abstract
Purpose of review
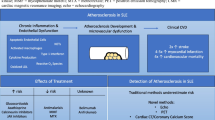
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a systemic inflammatory, autoimmune disorder characterized by diffuse fibrosis of the skin and visceral organ involvement. Endothelial dysfunction and microvascular injury dominate the pathophysiology and clinical manifestations of the disease, while the impact of macrovascular atherosclerotic disease on cardiovascular (CVD) morbidity and mortality is yet to be established. In this article, we aim to review current knowledge about CVD as well as cardiac complications in SSc and discuss the potentially implicated pathogenetic mechanisms.
Recent findings
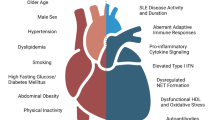
Systemic inflammation has been identified as an important trigger and contributor for the development and progression of atherosclerosis, closely associated with high cardiovascular mortality in patients with autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis. A close interplay between traditional risk factors and factors related to the disease, including inflammation, endothelial injury, and immune-mediated cytotoxicity, sharing common pathogenetic features with microvasculopathy, may be responsible for large-vessel involvement and promotion of atherosclerosis in SSc. Cardiac complications, including heart failure due to impairment of coronary microcirculation and myocardial fibrosis, are listed among the primary cause of death in SSc. Evaluation of indirect surrogate markers of CVD, namely, arterial stiffness, carotid media thickness, and flow-mediated dilation, in small studies has provided inconsistent results regarding the association between SSc and atherosclerosis, highlighting the need for further research on this field. In this article, we aim to review current knowledge about large-vessel involvement and CVD in SSc and discuss the potentially implicated pathogenetic mechanisms.
Summary
SSc conveys a higher risk for CVD associated with both vascular and fibrotic complications during the course of the disease. Increasing attention is given on the use of vasodilators, immunosuppressants, and more recently antifibrotic drugs that potentially improve myocardial function and reduce atherosclerotic disease burden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CVD:
-
cardiovascular disease
- SSc:
-
systemic sclerosis
- ESC/ERS:
-
European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society
- PAH:
-
pulmonary arterial hypertension
- SHI:
-
scleroderma heart involvement
- FMD:
-
flow-mediated dilatation
- cIMT:
-
carotid intima-media thickness
- CAD:
-
coronary artery disease
References and Recommended Reading
Katsumoto TR, Whitfield ML, Connolly MK. The pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Annu Rev. Pathol Mech Dis. 2011;6(1):509–37. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130,312.
Van Den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an american college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(11):2737–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38098.
Butt SA, Jeppesen JL, Fuchs C, Mogensen M, Engelhart M, Torp-Pedersen C, et al. Trends in incidence, mortality, and causes of death associated with systemic sclerosis in Denmark between 1995 and 2015: a nationwide cohort study. BMC Rheumatol. 2018;2:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41927-018-0043-6.
Nussinovitch U, Shoenfeld Y. Atherosclerosis and macrovascular involvement in systemic sclerosis: myth or reality. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10(5):259–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2010.09.014.
Cannarile F, Valentini V, Mirabelli G, et al. Cardiovascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.12.12.
Sherer Y, Shoenfeld Y. Mechanisms of disease: atherosclerosis in autoimmune diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0092.
Psarras A, Soulaidopoulos S, Garyfallos A. A critical view on cardiovascular risk in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Int. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-016-3530-3.
Pokeerbux MR, Giovannelli J, Dauchet L, Mouthon L, Agard C, Lega JC, et al. Survival and prognosis factors in systemic sclerosis: data of a French multicenter cohort, systematic review, and meta-analysis of the literature. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Apr 3;21(1):86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1867-1.
Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, Airo P, Cozzi F, Carreira PE, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1809–15. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.114264.
Soriano A, Afeltra A, Shoenfeld Y. Is atherosclerosis accelerated in systemic sclerosis? Novel insights. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014;26:653–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000115.
Hettema ME, Bootsma H, Kallenberg CG. Macrovascular disease and atherosclerosis in SSc. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47:578–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ken078.
Oreska S, Tomcik M. Atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk in systemic sclerosis, systemic sclerosis, Mislav Radic, editors. IntechOpen. 2017.
Gikas A, Lambadiari V, Sotiropoulos A, Panagiotakos D, Pappas S. Prevalence of major cardiovascular risk factors and coronary heart disease in a sample of Greek adults: The Saronikos Study. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2016;10:69–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874192401610010069.
Zegkos T, Kitas G, Dimitroulas T. Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: assessment, management and next steps. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2016;8(3):86–101. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720X16643340.
Simeón-Aznar CP, Fonollosa-Plá V, Tolosa-Vilella C, Espinosa-Garriga G, Campillo-Grau M, Ramos-Casals M, et al. Registry of the Spanish Network for Systemic Sclerosis: survival, prognostic factors, and causes of death. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e1728. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000001728.
Ngian GS, Sahhar J, Proudman SM, Stevens W, Wicks IP, Van Doornum S. Prevalence of coronary heart disease and cardiovascular risk factors in a national cross-sectional cohort study of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1980–3. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201,176.
Man A, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Dubreuil M, Rho YH, Peloquin C, et al. The risk of cardiovascular disease in systemic sclerosis: a population- based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:1188–93. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202,007.
Chu SY, Chen YJ, Liu CJ, Tseng WC, Lin MW, Hwang CY, et al. Increased risk of acute myocardial infarction in systemic sclerosis: a nationwide population-based study. Am J Med. 2013;126:982–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.06.025.
Ali H, Ng KR, Low AH. A qualitative systematic review of the prevalence of coronary artery disease in systemic sclerosis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18:276–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12566.
Zeng Y, Li M, Xu D, Hou Y, Wang Q, Fang Q, et al. Macrovascular involvement in systemic sclerosis: Evidence of correlation with disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30:S76–80.
Butt SA, Jeppesen JL, Torp-Pedersen C, Sam F, Gislason GH, Jacobsen S, et al. Cardiovascular Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis: a Danish Nationwide Cohort Study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e013405. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.013405.
Lippi G, Caramaschi P, Montagnana M, Salvagno GL, Volpe A, Guidi G, et al. Lipoprotein[a] and the lipid profile in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;364:345–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2005.07.015.
Mok MY, Lau CS, Chiu SS, Tso AW, Lo Y, Law LS, et al. Systemic sclerosis is an independent risk factor for increased coronary artery calcium deposition. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:1387–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.30283.
Ho M, Veale D, Eastmond C, Nuki G, Belch J. Macrovascular disease and systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.59.1.39.
Avina-Zubieta JA, Man A, Yurkovich M, Huang K, Sayre EC, Choi HK. Early cardiovascular disease after the diagnosis of systemic sclerosis. Am J Med. 2016;129:324–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.10.037.
Abraham D, Distler O. How does endothelial cell injury start? The role of endothelin in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2186.
Abraham DJ, Krieg T, Distler J, Distler O. Overview of pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(Suppl 3):iii3–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ken481.
Zakopoulos NA, Kotsis VT, Gialafos EJ, Papamichael CM, Pitiriga VC, Mitsibounas DN, et al. Systemic sclerosis is not associated with clinical or ambulatory blood pressure. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21:199–204.
Sgonc R, Gruschwitz MS, Boeck G, Sepp N, Gruber J, Wick G, et al. Endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic sclerosis is induced by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity via CD95. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2550–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200011)43:11<2550::AID-ANR24>3.0.CO;2-H.
Nordin A, Jensen-Urstad K, Björnådal L, Pettersson S, Larsson A, Svenungsson E, et al. Ischemic arterial events and atherosclerosis in patients with systemic sclerosis: a population-based case-control study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15:R87. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4267.
Khurma V, Meyer C, Park GS, McMahon M, Lin J, Singh RR, et al. A pilot study of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis: coronary artery calcification in cases and controls. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:591–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23540.
Palinski W, Hörkkö S, Miller E, Steinbrecher UP, Powell HC, Curtiss LK, et al. Cloning of monoclonal autoantibodies to epitopes of oxidized lipoproteins from apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Demonstration of epitopes of oxidized low density lipoprotein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:800–14. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI118853.
Ungprasert P, Sanguankeo A, Upala S. Risk of ischemic stroke in patients with systemic sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26:128–31. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2015.1056931.
Dave AJ, Fiorentino D, Lingala B, Krishnan E, Chung L. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in hospitalized patients with systemic sclerosis: higher mortality than patients with lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66:323–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22152.
D’Angelo WA, Fries JF, Masi AT, Shulman LE. Pathologic observations in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). A study of fifty-eight autopsy cases and fifty-eight matched controls. Am J Med. 1969;46:428–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(69)90044-8.
Hesselstrand R, Scheja A, Akesson A. Mortality and causes of death in a Swedish series of systemic sclerosis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57(11):682–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.57.11.682.
Hesselvig JH, Kofoed K, Wu JJ, Dreyer L, Gislason G, Ahlehoff O. Localized scleroderma, systemic sclerosis and cardiovascular risk: a danish nationwide cohort study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:361–5. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-2842.
Youssef P, Brama T, Englert H, Bertouch J. Limited scleroderma is associated with increased prevalence of macrovascular disease. J Rheumatol. 1995;22:469–72.
Soulaidopoulos S, Triantafyllidou E, Garyfallos A, Kitas GD, Dimitroulas T. The role of nailfold capillaroscopy in the assessment of internal organ involvement in systemic sclerosis: a critical review. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(8):787–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.05.019.
Repa A, Avgoustidis N, Kougkas N, Bertsias G, Zafiriou M, Sidiropoulos P. Nailfold Videocapillaroscopy as a candidate biomarker for organ involvement and prognosis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2019;30(1):48–50. https://doi.org/10.31138/mjr.30.1.48.
Sandoo A. Important considerations for examining endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2017;28(3):112–5. https://doi.org/10.31138/mjr.28.3.112.
Jung KH, Lim MJ, Kwon SR, Kim D, Joo K, Park W. Nailfold capillary microscopic changes and arterial stiffness in Korean systemic sclerosis patients. Modern rheumatology. 2015;25(2):328–31. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2014.881955.
Rollando D, Bezante GP, Sulli A, Balbi M, Panico N, Pizzorni C, et al. Brachial artery endothelial-dependent flow-mediated dilation identifies early-stage endothelial dysfunction in systemic sclerosis and correlates with nailfold microvascular impairment. J Rheumatol. 2010;37(6):1168–73. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.091116.
Alegre Sancho JJ, Robustillo Villarino M, Albert Espí G, Vergara Dangond C, Vicens Bernabeu E, Valls Pascual È, et al. SAT0197 Capillaroscopy and macrovascular disease in patients with systemic sclerosis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2016;75(Suppl 2):739. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-eular.4652.
Soulaidopoulos S, Pagkopoulou E, Katsiki N, Triantafyllidou E, Karagiannis A, Garyfallos A, et al. Arterial stiffness correlates with progressive nailfold capillary microscopic changes in systemic sclerosis: results from a cross-sectional study. Arthritis research & therapy. 2019;21(1):253. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-2051-3.
Clements PJ, Lachenbruch PA, Furst DE, Paulus HE, Sterz MG. Cardiac score. A semiquantitative measure of cardiac involvement that improves prediction of prognosis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1991;34(11):1371–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780341105.
Kahan A, Allanore Y. Primary myocardial involvement in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2006;45(Suppl 4):iv14–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kel312.
Lambova S. Cardiac manifestations in systemic sclerosis. World journal of cardiology. 2014;6(9):993–1005. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i9.993.
Rodriguez-Reyna TS, Hinojosa-Azaola A, Martinez-Reyes C, Nunez-Alvarez CA, Torrico-Lavayen R, Garcia-Hernandez JL, et al. Distinctive autoantibody profile in Mexican Mestizo systemic sclerosis patients. Autoimmunity. 2011;44(7):576–84. https://doi.org/10.3109/08916934.2011.592886.
Hesselstrand R, Scheja A, Shen GQ, Wiik A, Akesson A. The association of antinuclear antibodies with organ involvement and survival in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2003;42(4):534–40. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keg170.
Kuwana M, Kaburaki J, Okano Y, Tojo T, Homma M. Clinical and prognostic associations based on serum antinuclear antibodies in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1994;37(1):75–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780370111.
Steen VD. Autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism. 2005;35(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2005.03.005.
Kahan A, Devaux JY, Amor B, Menkes CJ, Weber S, Nitenberg A, et al. Nifedipine and thallium-201 myocardial perfusion in progressive systemic sclerosis. The New England journal of medicine. 1986;314(22):1397–402. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198605293142201.
Kahan A, Devaux JY, Amor B, Menkes CJ, Weber S, Foult JM, et al. Pharmacodynamic effect of dipyridamole on thallium-201 myocardial perfusion in progressive systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986;45(9):718–25. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.45.9.718.
Kahan A, Devaux JY, Amor B, Menkes CJ, Weber S, Venot A, et al. Nicardipine improves myocardial perfusion in systemic sclerosis. The Journal of rheumatology. 1988;15(9):1395–400.
Kahan A, Devaux JY, Amor B, Menkes CJ, Weber S, Venot A, et al. The effect of captopril on thallium 201 myocardial perfusion in systemic sclerosis. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 1990;47(4):483–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.1990.61.
Ferri C, Giuggioli D, Sebastiani M, Colaci M, Emdin M. Heart involvement and systemic sclerosis. Lupus. 2005;14(9):702–7. https://doi.org/10.1191/0961203305lu2204oa.
Bulkley BH, Ridolfi RL, Salyer WR, Hutchins GM. Myocardial lesions of progressive systemic sclerosis. A cause of cardiac dysfunction. Circulation. 1976;53(3):483–90. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.53.3.483.
Tzelepis GE, Kelekis NL, Plastiras SC, Mitseas P, Economopoulos N, Kampolis C, et al. Pattern and distribution of myocardial fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: a delayed enhanced magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2007;56(11):3827–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22971.
Deswal A, Follansbee WP. Cardiac involvement in scleroderma. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America. 1996;22(4):841–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70304-5.
Ferri C, Emdin M, Nielsen H, Bruhlmann P. Assessment of heart involvement. Clinical and experimental rheumatology. 2003;21(3 Suppl 29):S24–8.
Bulkley BH, Klacsmann PG, Hutchins GM. Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death with normal coronary arteries: a clinicopathologic study of 9 patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. American heart journal. 1978;95(5):563–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-8703(78)90297-1.
Konstantopoulou P, Gialafos E, Moyssakis I, Tountas C, Konsta M, Vaiopoulos G, et al. Evolution and management of late onset cardiac involvement in a contemporary systemic sclerosis cohort. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2016;27(3):102–7.
Becker M, Graf N, Sauter R, Allanore Y, Curram J, Denton CP, et al. EUSTAR Collaborators; EUSTAR Collaborators (numerical order of centres). Predictors of disease worsening defined by progression of organ damage in diffuse systemic sclerosis: a European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Sep;78(9):1242–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215,145.
Amarnani A, Wengrofsky P, Tsui CL, Kariyanna PT, Kabani N, Salciccioli L, et al. Acute heart failure in scleroderma renal crisis: a case study for review of cardiac disease in systemic sclerosis. Am J Med Case Rep. 2020;8(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajmcr-8-1-1.
Gottdiener JS, Moutsopoulos HM, Decker JL. Echocardiographic identification of cardiac abnormality in scleroderma and related disorders. The American journal of medicine. 1979;66(3):391–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(79)91057-x.
Vacca A, Meune C, Gordon J, Chung L, Proudman S, Assassi S, et al. Cardiac arrhythmias and conduction defects in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2014;53(7):1172–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket377.
Assassi S, Del Junco D, Sutter K, McNearney TA, Reveille JD, Karnavas A, et al. Clinical and genetic factors predictive of mortality in early systemic sclerosis. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2009;61(10):1403–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24734.
Sebestyen V, Szucs G, Pall D, Ujvarosy D, Otvos T, Csige I, et al. Electrocardiographic markers for the prediction of ventricular arrhythmias in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2020;59(3):478–86. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez644.
Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Bournia VK, Panopoulos S, Koutsogeorgopoulou L, Kanoupakis G, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance identifies high-risk systemic sclerosis patients with normal echocardiograms and provides incremental prognostic value. Diagnostics (Basel). 2019;9(4):pii: E220. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040220.
Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Karvounis H, Settas L, Kitas GD. Systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary hypertension: unique characteristics and future treatment targets. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(11):1457–64. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212799504704.
Mavrogeni S, Gargani L, Pepe A, Monti L, Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Santis M, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance predicts ventricular arrhythmias in scleroderma: the Scleroderma Arrhythmia Clinical Utility Study (SAnCtUS). Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez494.
Nordin A, Svenungsson E, Björnådal L, Elvin K, Larsson A, Jensen-Urstad K. Troponin I and echocardiography in patients with systemic sclerosis and matched population controls. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017 May;46(3):226–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009742.2016.1192217.
Bissell LA, Dumitru RB, Erhayiem B, Abignano G, Fent G, Kidambi A, et al. Abnormal electrophysiological testing associates with future incidental significant arrhythmia in scleroderma. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Apr 1;59(4):899–900. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez434.
Morrisroe K, Stevens W, Proudman S, Nikpour M. A systematic review of the epidemiology, disease characteristics and management of systemic sclerosis in Australian adults. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(11):1728–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13203.
Hachulla E, Gressin V, Guillevin L, Carpentier P, Diot E, Sibilia J, et al. Early detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: a French nationwide prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(12):3792–800.
Arvanitaki A, Boutsikou M, Anthi A, Apostolopoulou S, Avgeropoulou A, Demerouti E, et al. Epidemiology and initial management of pulmonary arterial hypertension: real-world data from the Hellenic pulmOnary hyPertension rEgistry (HOPE). Pulm Circ. 2019;9(3):2045894019877157. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045894019877157.
Simonneau G, Montani D, Celermajer DS, Denton CP, Gatzoulis MA, Krowka M, et al. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2019;53(1). https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01913-2018.
Hassoun PM, Mouthon L, Barbera JA, Eddahibi S, Flores SC, Grimminger F, et al. Inflammation, growth fators, and pulmonary vascular remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(1 Suppl):S10–9.
Morrisroe K, Stevens W, Huq M, Prior D, Sahhar J, Ngian GS, et al. Survival and quality of life in incident systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-017-1341-x.
Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, Bertocchi M, Habib G, Gressin V, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in France: results from a national registry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173(9):1023–30. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200510-1668OC.
McGoon MD, Miller DP. REVEAL: a contemporary US pulmonary arterial hypertension registry. Eur Respir Rev. 2012;21(123):8–18.
Escribano-Subias P, Blanco I, Lopez-Meseguer M, Lopez-Guarch CJ, Roman A, Morales P, et al. Survival in pulmonary hypertension in Spain: insights from the Spanish registry. Eur Respir J. 2012;40(3):596–603. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00101211.
Chung L, Domsic RT, Lingala B, Alkassab F, Bolster M, Csuka ME, et al. Survival and predictors of mortality in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension: outcomes from the pulmonary hypertension assessment and recognition of outcomes in scleroderma registry. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(3):489–95.
Kolstad KD, Li S, Steen V, Chung L, Investigators P. Long-term outcomes in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension From the Pulmonary Hypertension Assessment and Recognition of Outcomes in Scleroderma Registry (PHAROS). Chest. 2018;154(4):862–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2018.05.002.
Michelfelder M, Becker M, Riedlinger A, Siegert E, Drömann D, Yu X, et al. Interstitial lung disease increases mortality in systemic sclerosis patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension without affecting hemodynamics and exercise capacity. Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Feb;36(2):381–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3504-6.
Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Respir J. 2015;46(4):903–75. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317.
Demerouti ETI, Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Katsimpri P, Mitrouska I, Orfanos S, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in connective tissue disorders. The emerging role of screening and early diagnosis. A position paper for Greek Rheumatologists. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2019;30(2):90–3. https://doi.org/10.31138/mjr.30.2.90.
McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(17):1573–619. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192230.
Coghlan JG, Denton CP, Grunig E, Bonderman D, Distler O, Khanna D, et al. Evidence-based detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: the DETECT study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1340–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203,301.
Thakkar V, Stevens WM, Prior D, Moore OA, Byron J, Liew D, et al. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in a novel screening algorithm for pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: a case-control study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(3):R143. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3876.
Avouac J, Lepri G, Smith V, Toniolo E, Hurabielle C, Vallet A, et al. Sequential nailfold videocapillaroscopy examinations have responsiveness to detect organ progression in systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2017;47(1):86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2017.02.006.
Argula RG, Ward C, Feghali-Bostwick C. Therapeutic challenges and advances in the management of systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary arterial hypertension (SSc-PAH). Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019;15:1427–42.
Galie N, Channick RN, Frantz RP, Grunig E, Jing ZC, Moiseeva O, et al. Risk stratification and medical therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2019;53(1). https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01889-2018.
Kylhammar D, Kjellstrom B, Hjalmarsson C, Jansson K, Nisell M, Soderberg S, et al. A comprehensive risk stratification at early follow-up determines prognosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(47):4175–81.
Benza RL, Gomberg-Maitland M, Elliott CG, Farber HW, Foreman AJ, Frost AE, et al. Predicting survival in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: the REVEAL Risk Score Calculator 2.0 and Comparison With ESC/ERS-Based Risk Assessment Strategies. Chest. 2019;156(2):323–37.
Ahmed S, Pattanaik SS, Rai MK, Nath A, Agarwal V. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: insights into pathogenesis and evolving therapies. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2018;29(3):140–7. https://doi.org/10.31138/mjr.29.3.140.
Allanore Y, Meune C, Vonk MC, Airo P, Hachulla E, Caramaschi P, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with left ventricular dysfunction in the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research group (EUSTAR) database of patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jan;69(1):218–21. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.103382.
Sato T, Ambale-Venkatesh B, Lima JAC, Zimmerman SL, Tedford RJ, Fujii T, et al. The impact of ambrisentan and tadalafil upfront combination therapy on cardiac function in scleroderma associated pulmonary arterial hypertension patients: cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking study. Pulm Circ. 2018 Jan-Mar;8(1):2045893217748307. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045893217748307.
Mavrogeni S, Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Koutsogeorgopoulou L, Dimitroulas T, Bratis K, Kitas GD, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging pattern at the time of diagnosis of treatment naïve patients with connective tissue diseases. Int J Cardiol. 2017 Jun 1;236:151–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.01.104.
Gargani L, Todiere G, Guiducci S, Bruni C, Pingitore A, De Marchi D, et al. Early detection of cardiac involvement in systemic sclerosis: the added value of magnetic resonance imaging. JACC Cardiovascular imaging. 2019;12(5):927–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.09.025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Eleni Angeloudi declares that she has no conflict of interest. Eleni Pagkopoulou declares that she has no conflict of interest. Alexandra Arvanitaki declares that she has no conflict of interest. Stergios Soulaidopoulos declares that he has no conflict of interest. Alexandros Garyfallos declares that he has no conflict of interest. George Kitas declares that he has no conflict of interest. Theodoros Dimitroulas declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Scleroderma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angeloudi, E., Pagkopoulou, E., Arvanitaki, A. et al. Cardiovascular Risk in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr Treat Options in Rheum 6, 282–298 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40674-020-00152-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40674-020-00152-z