Abstract
Background
The number of octogenarians or older patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) has been growing over the past several years. The aim of this study is to assess factors associated with acute renal replacement therapy (ARRT) requirement in these patients and the impact of this therapy on 90-day mortality. We also aimed to identify prognostic factors associated with mortality risk in the group of patients that required ARRT.
Methods
Retrospective study of octogenarian or older patients admitted to the ICU at Hospital Clínic de Barcelona from June 2007 to April 2019. Patients on chronic dialysis treatment or with a kidney transplant, and patients with limitation of therapeutic support or admitted for less than 48 h were excluded.
Results
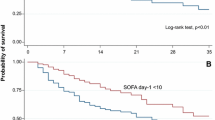
217 patients were included in the study, of whom 36.4% required ARRT. Use of vasoactive drugs (VAD) and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score on admission were higher in ARRT patients (P = 0.009 and < 0.001, respectively). Basal estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was lower in the ARRT cohort (P < 0.001). Hospital and ICU length of stay were longer in the ARRT cohort (P < 0.001). Ninety-day mortality was 58.2% in the ARRT cohort compared to 55.8% in the non-ARRT control cohort (P = NS). In the survival analysis, only female sex, sepsis and non-renal SOFA ≥ 6.5 were significantly associated with mortality (P = 0.002, 0.028 and 0.009, respectively) in the ARRT cohort.
Conclusion
Mortality was not significantly increased in the octogenarian or older population that required and received ARRT compared to control patients who did not require it. Severity scores like SOFA could help in the process of decision making about initiation of ARRT in this population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Flaatten H, de Lange DW, Artigas A et al (2017) The status of intensive care medicine research and a future agenda for very old patients in the ICU. Intens Care Med 43(9):1319–1328
Guidet B, Vallet H, Boddaert J et al (2018) Caring for the critically ill patients over 80: a narrative review. Ann Intens Care 8(1):114
Mukhopadhyay A, Tai BC, See KC et al (2014) Risk factors for hospital and longterm mortality of critically ill elderly patients admitted to an intensive care unit. Biomed Res Int 2:960575
Chao CT, Tsai HB, Lin YF, Ko WJ (2014) Acute kidney injury in the elderly: Only the tip of the iceberg. J Clin Gerontol Geriat 5(1):7–12
Akbar S, Moss AH (2014) The ethics of offering dialysis for AKI to the older patient: time to re-evaluate? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9(9):1652–1656
Borsellino P (2015) Limitation of the therapeutic effort: ethical and legal justification for withholding and/or withdrawing life sustaining treatments. Multidiscip Respir Med 10(1):5
Kaufman SR, Shim JK, Russ AJ (2004) Revisiting the biomedicalization of aging: clinical trends and ethical challenges. Gerontologist 44:731–738
Bagshaw SM, Adhikari NK, Burns K et al (2019) Selection and receipt of kidney replacement in critically ill older patientswith AKI. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 14:496–505
Teles F, Santos RO, de Moura A, Lima HM et al (2019) The impact of dialysis on critically ill elderly patients with acute kidney injuryan analysis by propensity score matching. J Bras Nefrol 41(1):14–21
Gabbay E, Zangi Y, Bnayah A, Atrash J, Slotki I, Shavit L (2018) Outcomes of very elderly treated with dialysis for acute kidney injury. Clin Nephrol 90(3):185–193
Baldyga AP, Paganini E, Chaff C, Higgins TL (1993) Acute dialytic support of the octogenarian: is it worth it? ASAIO J 39:M805–M808
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R et al (2005) Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294(7):813–818
Conroy M, Flynn J, Marsh B (2019) Mortality and long-term dialysis requirement among elderly continuous renal replacement therapy patients in a tertiary referral intensive care unit. J Intensive Care Soc 20(2):138–143
Eachempati SR, Hydo L, Barie PS (1999) Gender-based differences in outcome in patients with sepsis. Arch Surg 134(12):1342–1347
Pietropaoli AP, Glance LG, Oakes D, Fisher SG (2010) Gender differences in mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Gend Med 7(5):422–437
Hollinger A, Gayat E, Feliot E et al (2019) Gender and survival of critically ill patients: results from the FROG-ICU study. Ann Intens Care 9:43
Mayr VD, Dünser MW, Greil V (2006) Causes of death and determinants of outcome in critically ill patients. Crit Care 10(6):R154
Chawla LS, Eggers PW, Star RA, Kimmel PL (2014) Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. N Engl J Med 371(1):58–66
Acknowledgments
Hospital Clínic Intensive Care Working Group (GTMC, Grup de Treball del Malalt Crític): Sara Fernández, Josep Maria Nicolàs, Pedro Castro, Intensive Care Unit, Internal Medicine Department, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, Rut Andrea, Oriol de Diego, José Tomás Ortiz, Acute Cardiac Care, Cardiology Department, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, Enric Reverter, Javier Fernández, David Toapanta, Intensive Care Unit, Hepatology Department, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, Jordi Mercadal, Carlos Ferrando, Xavier Borrat, Surgical ICU, Anesthesiology Department, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, Antoni Torres, Joan Ramón Badia, Miquel Ferrer, Intensive Care Unit, Pneumology Department, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, Eduard Quintana, Daniel Pereda, Elena Sandoval, Irene Rovira, Intensive care unit, Cardiovascular-Surgery Department, Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
AMA conceived and designed the study. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AMA, JC and JDR. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AMA and supervised by GP and EP. EH, LFQ, MB, GP and EP interpreted the data, revised the manuscript, provided intellectual content and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Hospital Clínic de Barcelona (Reg. HCB/2020/1083). Because of the characteristics of the study patients were not able to sign informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina-Andújar, A., Casals, J., Del Risco-Zevallos, J. et al. Acute renal replacement therapy in critically ill octogenarian or older patients: prognostic factors and renal outcomes. J Nephrol 34, 1531–1536 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-021-01034-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-021-01034-w