Abstract
Purpose
Growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas (GH-PAs) are common subtypes of functional PAs. Invasive GH-PAs play a key role in restricting poor outcomes. The transcriptional changes in GH-PAs were evaluated.
Methods
In this study, the transcriptome analysis of six different GH-PA samples was performed. The functional roles, co-regulatory network, and chromosome location of differentially expressed (DE) genes in invasive GH-PAs were explored.
Results
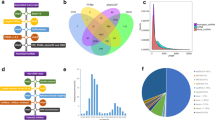
Bioinformatic analysis revealed 101 DE mRNAs and 70 DE long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) between invasive and non-invasive GH-PAs. Functional enrichment analysis showed that epithelial cell differentiation and development pathways were suppressed in invasive GH-PAs, whereas the pathways of olfactory transduction, retinol metabolism, drug metabolism-cytochrome P450, and metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 had an active trend. In the protein–protein interaction network, 11 main communities were characterized by cell- adhesion, -motility, and -cycle; transport process; phosphorus and hormone metabolic processes. The SGK1 gene was suggested to play a role in the invasiveness of GH-PAs. Furthermore, the up-regulated genes OR51B6, OR52E4, OR52E8, OR52E6, OR52N2, MAGEA6, MAGEC1, ST8SIA6-AS1, and the down-regulated genes GAD1-AS1 and SPINT1-AS1 were identified in the competing endogenous RNA network. The RT-qPCR results further supported the aberrant expression of those genes. Finally, the enrichment of DE genes in chromosome 11p15 and 12p13 regions were detected.
Conclusion
Our findings provide a new perspective for studies evaluating the underlying mechanism of invasive GH-PAs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data files can be downloaded from https://github.com/HuaChunY/GH-PA. The datasets are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Melmed S (2020) Pituitary-tumor endocrinopathies. N Engl J Med 382(10):937–950. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1810772
Cuevas-Ramos D, Carmichael JD, Cooper O, Bonert VS, Gertych A, Mamelak AN, Melmed S (2015) A structural and functional acromegaly classification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(1):122–131. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-2468
Thapar K, Kovacs K, Scheithauer BW, Stefaneanu L, Horvath E, Pernicone PJ, Murray D, Laws ER Jr (1996) Proliferative activity and invasiveness among pituitary adenomas and carcinomas: an analysis using the MIB-1 antibody. Neurosurgery 38(1):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199601000-00024 (discussion 106-107)
Zheng X, Li S, Zhang W, Zang Z, Hu J, Yang H (2016) Current biomarkers of invasive sporadic pituitary adenomas. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 77(6):658–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ando.2016.02.004
Zheng X, Li S, Zang Z, Hu J, An J, Pei X, Zhu F, Zhang W, Yang H (2016) Evidence for possible role of toll-like receptor 3 mediating virus-induced progression of pituitary adenomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol 426:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.02.009
An J, Zhang Y, He J, Zang Z, Zhou Z, Pei X, Zheng X, Zhang W, Yang H, Li S (2017) Lactate dehydrogenase A promotes the invasion and proliferation of pituitary adenoma. Sci Rep 7(1):4734. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04366-5
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10(1):57–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2484
Barrett T, Troup DB, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Rudnev D, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Soboleva A, Tomashevsky M, Edgar R (2007) NCBI GEO: mining tens of millions of expression profiles database and tools update. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Database issue):D760–D765. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl887
Consortium GT, Laboratory DA, Coordinating Center -Analysis Working G, Statistical Methods groups-Analysis Working G, Enhancing Gg, Fund NIHC, Nih/Nci, Nih/Nhgri, Nih/Nimh, Nih/Nida, Biospecimen Collection Source Site N, Biospecimen Collection Source Site R, Biospecimen Core Resource V, Brain Bank Repository-University of Miami Brain Endowment B, Leidos Biomedical-Project M, Study E, Genome Browser Data I, Visualization EBI, Genome Browser Data I, Visualization-Ucsc Genomics Institute UoCSC, Lead a, Laboratory DA, Coordinating C, management NIHp, Biospecimen c, Pathology, e QTLmwg, Battle A, Brown CD, Engelhardt BE, Montgomery SB (2017) Genetic effects on gene expression across human tissues. Nature 550(7675):204–213. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24277
Hochberg I, Harvey I, Tran QT, Stephenson EJ, Barkan AL, Saltiel AR, Chandler WF, Bridges D (2015) Gene expression changes in subcutaneous adipose tissue due to Cushing’s disease. J Mol Endocrinol 55(2):81–94. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-15-0119
Neou M, Villa C, Armignacco R, Jouinot A, Raffin-Sanson ML, Septier A, Letourneur F, Diry S, Diedisheim M, Izac B, Gaspar C, Perlemoine K, Verjus V, Bernier M, Boulin A, Emile JF, Bertagna X, Jaffrezic F, Laloe D, Baussart B, Bertherat J, Gaillard S, Assie G (2020) Pangenomic classification of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Cell 37(1):123-134.e125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2019.11.002
Cox MP, Peterson DA, Biggs PJ (2010) SolexaQA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinformatics 11:485. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-485
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25(9):1105–1111. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol 28(5):511–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1621
Lee CM, Barber GP, Casper J, Clawson H, Diekhans M, Gonzalez JN, Hinrichs AS, Lee BT, Nassar LR, Powell CC, Raney BJ, Rosenbloom KR, Schmelter D, Speir ML, Zweig AS, Haussler D, Haeussler M, Kuhn RM, Kent WJ (2020) UCSC genome browser enters 20th year. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D756–D761. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1012
Lopes MBS (2017) The 2017 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the pituitary gland: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 134(4):521–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1769-8
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26(1):139–140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Chen J, Bardes EE, Aronow BJ, Jegga AG (2009) ToppGene suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res 37(Web Server issue):W305–W311. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp427
Walter W, Sanchez-Cabo F, Ricote M (2015) GOplot: an R package for visually combining expression data with functional analysis. Bioinformatics 31(17):2912–2914. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv300
Nie X, Wei J, Hao Y, Tao J, Li Y, Liu M, Xu B, Li B (2019) Consistent biomarkers and related pathogenesis underlying asthma revealed by systems biology approach. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164037
Zhou G, Soufan O, Ewald J, Hancock REW, Basu N, Xia J (2019) NetworkAnalyst 3.0: a visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W234–W241. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz240
Su G, Morris JH, Demchak B, Bader GD (2014) Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 47:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0813s47
Paci P, Colombo T, Farina L (2014) Computational analysis identifies a sponge interaction network between long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs in human breast cancer. BMC Syst Biol 8:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-83
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT, Lin CY (2014) cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol 8(Suppl 4):S11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11
Bader GD, Hogue CW (2003) An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 4:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-2
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(43):15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Gel B, Serra E (2017) karyoploteR: an R/Bioconductor package to plot customizable genomes displaying arbitrary data. Bioinformatics 33(19):3088–3090. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx346
van Rijn SJ, Riemers FM, van den Heuvel D, Wolfswinkel J, Hofland L, Meij BP, Penning LC (2014) Expression stability of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR of healthy and diseased pituitary tissue samples varies between humans, mice, and dogs. Mol Neurobiol 49(2):893–899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8567-7
Thomas G, Jacobs KB, Kraft P, Yeager M, Wacholder S, Cox DG, Hankinson SE, Hutchinson A, Wang Z, Yu K, Chatterjee N, Garcia-Closas M, Gonzalez-Bosquet J, Prokunina-Olsson L, Orr N, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Ziegler RG, Berg CD, Buys SS, McCarty CA, Feigelson HS, Calle EE, Thun MJ, Diver R, Prentice R, Jackson R, Kooperberg C, Chlebowski R, Lissowska J, Peplonska B, Brinton LA, Sigurdson A, Doody M, Bhatti P, Alexander BH, Buring J, Lee IM, Vatten LJ, Hveem K, Kumle M, Hayes RB, Tucker M, Gerhard DS, Fraumeni JF Jr, Hoover RN, Chanock SJ, Hunter DJ (2009) A multistage genome-wide association study in breast cancer identifies two new risk alleles at 1p11.2 and 14q24.1 (RAD51L1). Nat Genet 41(5):579–584. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.353
Lekva T, Berg JP, Lyle R, Heck A, Ringstad G, Olstad OK, Michelsen AE, Casar-Borota O, Bollerslev J, Ueland T (2013) Epithelial splicing regulator protein 1 and alternative splicing in somatotroph adenomas. Endocrinology 154(9):3331–3343. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2013-1051
Lekva T, Berg JP, Fougner SL, Olstad OK, Ueland T, Bollerslev J (2012) Gene expression profiling identifies ESRP1 as a potential regulator of epithelial mesenchymal transition in somatotroph adenomas from a large cohort of patients with acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(8):E1506-1514. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-1760
Bujko M, Kober P, Boresowicz J, Rusetska N, Paziewska A, Dabrowska M, Piascik A, Pekul M, Zielinski G, Kunicki J, Bonicki W, Ostrowski J, Siedlecki JA, Maksymowicz M (2019) USP8 mutations in corticotroph adenomas determine a distinct gene expression profile irrespective of functional tumour status. Eur J Endocrinol 181(6):615–627. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-19-0194
Neuhaus EM, Zhang W, Gelis L, Deng Y, Noldus J, Hatt H (2009) Activation of an olfactory receptor inhibits proliferation of prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 284(24):16218–16225. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.012096
Rodriguez M, Luo W, Weng J, Zeng L, Yi Z, Siwko S, Liu M (2014) PSGR promotes prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer xenograft growth through NF-kappaB. Oncogenesis 3:e114. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2014.29
Weber L, Massberg D, Becker C, Altmuller J, Ubrig B, Bonatz G, Wolk G, Philippou S, Tannapfel A, Hatt H, Gisselmann G (2018) Olfactory receptors as biomarkers in human breast carcinoma tissues. Front Oncol 8:33. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00033
Masjedi S, Zwiebel LJ, Giorgio TD (2019) Olfactory receptor gene abundance in invasive breast carcinoma. Sci Rep 9(1):13736. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50085-4
Weon JL, Potts PR (2015) The MAGE protein family and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 37:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2015.08.002
Yacqub-Usman K, Richardson A, Duong CV, Clayton RN, Farrell WE (2012) The pituitary tumour epigenome: aberrations and prospects for targeted therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8(8):486–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2012.54
Cheng S, Xie W, Miao Y, Guo J, Wang J, Li C, Zhang Y (2019) Identification of key genes in invasive clinically non-functioning pituitary adenoma by integrating analysis of DNA methylation and mRNA expression profiles. J Transl Med 17(1):407. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-02148-3
Qian ZR, Sano T, Yoshimoto K, Asa SL, Yamada S, Mizusawa N, Kudo E (2007) Tumor-specific downregulation and methylation of the CDH13 (H-cadherin) and CDH1 (E-cadherin) genes correlate with aggressiveness of human pituitary adenomas. Mod Pathol 20(12):1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800965
Seltzer J, Ashton CE, Scotton TC, Pangal D, Carmichael JD, Zada G (2015) Gene and protein expression in pituitary corticotroph adenomas: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 38(2):E17. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.FOCUS14683
Orlacchio A, Ranieri M, Brave M, Arciuch VA, Forde T, De Martino D, Anderson KE, Hawkins P, Di Cristofano A (2017) SGK1 is a critical component of an AKT-independent pathway essential for PI3K-mediated tumor development and maintenance. Cancer Res 77(24):6914–6926. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2105
Liu W, Wang X, Wang Y, Dai Y, Xie Y, Ping Y, Yin B, Yu P, Liu Z, Duan X, Liao Z, Chen Y, Liu C, Li X, Tao Z (2018) SGK1 inhibition-induced autophagy impairs prostate cancer metastasis by reversing EMT. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0743-1
Chiu HS, Somvanshi S, Patel E, Chen TW, Singh VP, Zorman B, Patil SL, Pan Y, Chatterjee SS, Cancer Genome Atlas Research N, Sood AK, Gunaratne PH, Sumazin P (2018) Pan-cancer analysis of lncRNA regulation supports their targeting of cancer genes in each tumor context. Cell Rep 23(1):297-3122.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.064
Zhang H, Wang Z, Wu J, Ma R, Feng J (2019) Long noncoding RNAs predict the survival of patients with colorectal cancer as revealed by constructing an endogenous RNA network using bioinformation analysis. Cancer Med 8(3):863–873. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1813
Jiang N, Wang X, Xie X, Liao Y, Liu N, Liu J, Miao N, Shen J, Peng T (2017) lncRNA DANCR promotes tumor progression and cancer stemness features in osteosarcoma by upregulating AXL via miR-33a-5p inhibition. Cancer Lett 405:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.009
Jeong G, Bae H, Jeong D, Ham J, Park S, Kim HW, Kang HS, Kim SJ (2018) A Kelch domain-containing KLHDC7B and a long non-coding RNA ST8SIA6-AS1 act oppositely on breast cancer cell proliferation via the interferon signaling pathway. Sci Rep 8(1):12922. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31306-8
Shen FF, Pan Y, Yang HJ, Li JK, Zhao F, Su JF, Li YY, Tian LQ, Yu PT, Cao YT, Zhang YW, Zhou FY (2019) Decreased expression of SPINT1-AS1 and SPINT1 mRNA might be independent unfavorable prognostic indicators in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 12:4755–4763. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S206448
Dekker J, Mirny L (2016) The 3D genome as moderator of chromosomal communication. Cell 164(6):1110–1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.007
Li S, Wu C, Gao H, Wu X, Yu L, Tao B, Hong Y (2018) CD151 up-regulation contributes to the invasion of pituitary adenomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 11(3):1538–1545
Lu T, Yu C, Ni H, Liang W, Yan H, Jin W (2018) Expression of the long non-coding RNA H19 and MALAT-1 in growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas and its relationship to tumor behavior. Int J Dev Neurosci 67:46–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.03.009
Lv J, Qiu M, Xia W, Liu C, Xu Y, Wang J, Leng X, Huang S, Zhu R, Zhao M, Ji F, Xu L, Xu K, Yin R (2016) High expression of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 promotes proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0352-9
Wang J, Wang H, Liu A, Fang C, Hao J, Wang Z (2015) Lactate dehydrogenase A negatively regulated by miRNAs promotes aerobic glycolysis and is increased in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 6(23):19456–19468. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3318
Acknowledgments
We want to thank and acknowledge all participants of the study.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81801369), Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (No.cstc2019jcyj-msxmX0475), Nursery Project of Army Medical University (No.2019R054), and Clinical Research Project of Army Military Medical University (2018XLC3049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The collection procedure of patient tissue samples in this study was approved by laboratory animal welfare and ethics committee of Xinqiao Hospital (the ethical review number: 2018-049-012). All procedures performed involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, H., Zheng, X., Tang, X. et al. Potential biomarkers and lncRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in invasive growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas. J Endocrinol Invest 44, 1947–1959 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01510-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01510-x