Abstract
Purpose
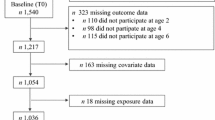
We recently reported that a high BMI and high waist circumference prevalence is present in Sicilian children and that the male gender is associated with a significant risk of obesity. Early-life and parent-related risk factors were investigated 1521 Sicilian children (752 females and 769 males, aged 9.0–14.0 years) to identify biological and environmental factors that can contribute to obesity onset.
Methods
Anthropometric measurements of children, their urban vs rural area provenience, birth weight and neonatal feeding were collected. In addition, the BMI and educational level of their parents and the perception of their child weight status were investigated.
Results
In the study cohort, the prevalence of overweight and obesity was 27.2 and 14.1 %, respectively, significantly (p < 0.05) higher in males than in females. Breastfeeding emerged as a protective factor (OR 0.64; p < 0.0005), while risk factors for developing childhood obesity were a birth weight ≥4.0 kg (OR 1.83; p < 0.05), an overweight or obese mother (OR 2.33; p < 0.0001) or father (OR 1.68; p < 0.0001) and a mother with a low/medium education level (OR 1.72; p < 0.005).
Conclusion
Understanding risk factors for pediatric obesity is a prerequisite to identify children at highly risk of being obese and to predispose early intervention strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Lamb MM, Flegal KM (2010) Prevalence of high body mass index in US children and adolescents, 2007–2008. JAMA 303:242–249
Hunsberger M, Lanfer A, Reeske A, Veidebaum T, Russo P, Hadjigeorgiou C et al (2013) Infant feeding practices and prevalence of obesity in eight European countries: the IDEFICS study. Public Health Nutr 16:219–227
Tirosh A, Shai I, Afek A, Dubnov-Raz G, Ayalon N, Gordon B et al (2011) Adolescent BMI trajectory and risk of diabetes versus coronary disease. N Engl J Med 364:1315–1325
De Giorgis T, Marcovecchio ML, Giannini C, Chiavaroli V, Chiarelli F, Mohn A et al (2016) Blood pressure from childhood to adolescence in obese youths in relation to insulin resistance and asymmetric dimethylarginine. J Endocrinol Invest 39:169–176
Binkin N, Fontana G, Lamberti A, Cattaneo C, Baglio G, Perra A, Spinelli A (2010) A national survey of the prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Italy. Obes Rev 11:2–10
Baratta R, Degano C, Leonardi D, Vigneri R, Frittitta L (2006) High prevalence of overweight and obesity in 11–15-year-old children from Sicily. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 16:249–255
Parrino C, Rossetti P, Baratta R, La Spina N, La Delfa L, Squatrito S, Vigneri R, Frittitta L (2012) Secular trends in the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Sicilian schoolchildren aged 11–13 years during the last decade. PLoS One 7(4):e34551
Han JC, Lawlor DA, Kimm SY (2010) Childhood obesity. Lancet 375:1737–1748
Verrotti A, Penta L, Zenzeri L, Agostinelli S, De Feo P (2014) Childhood obesity: prevention and strategy of intervention: a systematic review of school-based interventions in primary school. J Endocrinol Invest 37:1155–1164
Yu ZB, Han SP, Zhu GZ, Zhu C, Wang XJ, Cao XG et al (2011) Birth weight and subsequent risk of obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 12:525–542
Monasta L, Batty GD, Cattaneo A, Lutje V, Ronfani L, Van Lenthe FJ et al (2010) Early-life determinants of overweight and obesity: a review of systematic reviews. Obes Rev 11:695–708
Reilly JJ, Armstrong J, Dorosty AR, Emmett PM, Ness A, Rogers I et al (2005) Early life risk factors for obesity in childhood: cohort study. BMJ 330:1357–1359
Horta BL, Bahl R, Martines J, Victora C (2007) Evidence on the long-term effects of breastfeeding: systematic reviews and meta-analysis. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 1–57
Linabery AM, Nahhas RW, Johnson W, Choh AC, Towne B, Odegaard AO, Czerwinski SA, Demerath EW (2013) Stronger influence of maternal than paternal obesity on infant and early childhood body mass index: the Fels longitudinal study. Pediatr Obes 8:159–169
McLoone P, Morrison DS (2014) Risk of child obesity from parental obesity: analysis of repeat national cross-sectional surveys. Eur J Public Health 24:186–190
Lazzeri G, Pammolli A, Pilato V, Giacchi MV (2011) Relationship between 8/9-yr-old school children BMI, parents’ BMI and educational level: a cross sectional survey. Nutr J. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-10-76
Vanhala ML, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi SM, Kaikkonen KM, Laitinen JH, Korpelainen RI (2011) Factors associated with parental recognition of a child’s overweight status: a cross sectional study. BMC Public Health. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-11-665
Garrett-Wright D (2011) Parental perception of preschool child body weight. J Pediatr Nurs 26:435–445
Santoro N, Amato A, Grandone A, Brienza C, Savarese P, Tartaglione N, Marzuillo P, Perrone L, Miraglia Del Giudice E (2013) Predicting metabolic syndrome in obese children and adolescents: look, measure and ask. Obes Facts 6(1):48–56
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 320:1240–1243
Cole TJ, Flegal KM, Nicholls D, Jackson AA (2007) Body mass index cut offs to define thinness in children and adolescents: international survey. BMJ 335:194–197
Lobstein T, Baur L, Uauy R, IASO International Obesity TaskForce (2004) Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obes Rev 5(suppl. 1):4–104
Maffeis C, Banzato C, Talamini G (2008) Waist-to-height ratio, a useful index to identify high metabolic risk in overweight children. J Pediatr 152:207–213
Oldroyd J, Renzaho A, Skouteris H (2011) Low and high birth weight as risk factors for obesity among 4 to 5-year-old Australian children: does gender matter? Eur J Pediatr 170:899–906
Word Health Organization (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. World Health Organization: technical report series,894, pp i–xii, 1–253
Rosati P, Triunfo S, Scambia G (2013) Child nutritional status: a representative survey in a metropolitan school. J Obes. doi:10.1155/2013/395671
Birbilis M, Moschonis G, Mougios V, Manios Y (2013) Obesity in adolescence is associated with perinatal risk factors, parental BMI and sociodemographic characteristics. Eur J Clin Nutr 67:115–121
Owen CG, Martin RM, Whincup PH, Davey-Smith G, Gillman MW, Cook DG (2005) The effect of breastfeeding on mean body mass index throughout life: a quantitative review of published and unpublished observational evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 82:1298–1307
Owen CG, Martin RM, Whincup PH, Smith GD, Cook DG (2005) Effect of infant feeding on the risk of obesity across the life course: a quantitative review of published evidence. Pediatrics 115:1367–1377
Harder T, Bergmann R, Kallischnigg G, Plagemann A (2005) Duration of breastfeeding and risk of overweight: a meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol 162:397–403
Grube MM, von der Lippe E, Schlaud M, Brettschneider AK (2015) Does breastfeeding help to reduce the risk of childhood overweight and obesity? a propensity score analysis of data from the KiGGS study. PLoS One 10(3):e0122534. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122534
Casazza K, Fontaine KR, Astrup A, Birch LL, Brown AW, Bohan Brown MM et al (2013) Myths, presumptions, and facts about obesity. N Engl J Med 368:446–454
Kramer MS, Matush L, Vanilovich I, Platt RW, Bogdanovich N, Sevkovskaya Z et al (2007) Effects of prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding on child height, weight, adiposity, and blood pressure at age 6.5 y: evidence from a large randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr 86:1717–1721
Binkin N, Spinelli A, Baglio G, Lamberti A (2013) What is common becomes normal: the effect of obesity prevalence on maternal perception. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 23:410–416
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the schoolchildren, their parents, teachers and the local school authorities for the collaboration to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
The Institutional Board of the school approved the study, and informed written consent was obtained from parents for children examination and anonymous recording of their data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parrino, C., Vinciguerra, F., La Spina, N. et al. Influence of early-life and parental factors on childhood overweight and obesity. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 1315–1321 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0501-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0501-1



