Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the performance of various indexes of insulin sensitivity and secretion and to identify the most useful indicator of deterioration of glucose metabolism in a cohort of children with growth hormone (GH) deficiency (GHD) during GH treatment.
Methods
In 73 GHD children (55 M, 18 F; mean age 10.5 years) at baseline and after 12 months of treatment, we evaluated a number of surrogate indexes of insulin secretion and sensitivity. In a subgroup of 11 children we also performed an euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp.
Results
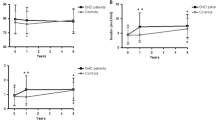
After 12 months, a significant increase in fasting glucose (p < 0.001) and HbA1c levels (p < 0.001) was documented, despite all children remained with a normal glucose tolerance. With regard the insulin secretion, Homa-β did not show any significant change (p = 0.073), while oral disposition index (DIo) showed a significant decrease (p = 0.031). With regard the insulin sensitivity, Homa-IR significantly increased (p < 0.001) with a concomitant decrease in QUICKI (p < 0.001). ISI Matsuda showed a decrease, although not statistically significant (p = 0.069). In the subgroup of 11 children, the M value derived from clamp showed a significant decrease (p = 0.011) and a significant positive correlation was found between M value and ISI Matsuda both at baseline (ρ 0.950; p = 0.001) and after 12 months (ρ 0.980; p = 0.001) but not with Homa-IR and QUICKI.
Conclusions
12 months of GH treatment lead to a decrease in insulin sensitivity and impairment in insulin secretion relative to insulin sensitivity even without evident changes in glucose tolerance. DIo has proven to be the most useful indicator of deterioration of glucose metabolism even in cases in which the overt glucose abnormalities have not yet appeared.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vijayakumar A, Novosyadlyy R, Wu Y, Yakar S, LeRoith D (2010) Biological effects of growth hormone on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Growth Horm IGF Res 20(1):1–7
Boot AM, Engels MA, Boerma GJ, Krenning EP, De Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM (1997) Changes in bone mineral density, body composition, and lipid metabolism during growth hormone (GH) treatment in children with GH deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82(8):2423–2428
Capalbo D, Mattace Raso G, Esposito A, Di Mase R, Barbieri F, Meli R, Bruzzese D, Salerno M (2013) Cluster of cardiometabolic risk factors in children with GH deficiency: a prospective, case-control study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 80(6):856–862
Capalbo D, Esposito A, Di Mase R, Barbieri F, Parenti G, Vajro P, Pignata C, Salerno M (2012) Update on early cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors in children and adolescents affected with growth hormone deficiency. Minerva Endocrinol 37(4):379–389
Zahnd GR, Steinke J, Renold AE (1960) Early metabolic effects of human growth hormone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 105:455–459
Fineberg SE, Merimee TJ (1974) Acute metabolic effects of human growth hormone. Diabetes 23(6):499–504
Daughaday WH, Kipnis DM (1966) The growth-promoting and anti-insulin actions of somatotropin. Recent Prog Horm Res 22:49–99
Rizza RA, Mandarino LJ, Gerich JE (1982) Effects of growth hormone on insulin action in man. Mechanisms of insulin resistance, impaired suppression of glucose production, and impaired stimulation of glucose utilization. Diabetes. 31(8 Pt 1):663–669
Bratusch-Marrain PR, Smith D, DeFronzo RA (1982) The effect of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 55(5):973–982
MacGorman LR, Rizza RA, Gerich JE (1981) Physiological concentrations of growth hormone exert insulin-like and insulin antagonistic effects on both hepatic and extrahepatic tissues in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 53(3):556–559
Møller N, Butler PC, Antsiferov MA, Alberti KG (1989) Effects of growth hormone on insulin sensitivity and forearm metabolism in normal man. Diabetologia 32(2):105–110
Heptulla RA, Boulware SD, Caprio S, Silver D, Sherwin RS, Tamborlane WV (1997) Decreased insulin sensitivity and compensatory hyperinsulinemia after hormone treatment in children with short stature. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82(10):3234–3238
Child CJ, Zimmermann AG, Scott RS, Cutler GB Jr, Battelino T, Blum WF, GeNeSIS International Advisory Board (2011) Prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus in GH-treated children and adolescents: analysis from the GeNeSIS observational research program. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96(6):E1025–E1034
Cutfield WS, Wilton P, Bennmarker H, Albertsson-Wikland K, Chatelain P, Ranke MB, Price DA (2000) Incidence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in children and adolescents receiving growth-hormone treatment. Lancet 355:610–613
Marshall WA, Tanner JM (1969) Variations in pattern of pubertal changes in girls. Arch Dis Child. 44(235):291–230
Growth Hormone Research Society (2000) Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of growth hormone (GH) deficiency in childhood and adolescence: summary statement of the GH Research Society. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3990–3993
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7):412–419
Utzschneider KM, Prigeon RL, Faulenbach MV, Tong J, Carr DB, Boyko EJ, Leonetti DL, McNeely MJ, Fujimoto WY, Kahn SE (2009) Oral disposition index predicts the development of future diabetes above and beyond fasting and 2-h glucose levels. Diabetes Care 32(2):335–341
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G, Quon MJ (2000) Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(7):2402–2410
Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA (1999) Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 22:1462–1470
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R (1979) Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol 237:E214–E223
Jorgensen JO, Pedersen SA, Thuesen L, Jorgensen J, Ingermann-Hansen T, Skakkebaek NE, Christiansen JS (1989) Beneficial effect of growth hormone treatment in GH-deficient adults. Lancet 1:1221–1225
Salomon F, Cuneo RC, Hesp R, So¨nksen PH (1989) The effects of treatment with recombinant human growth hormone on body composition and metabolism in adults with growth hormone deficiency. N Engl J Med 321:1797–1803
Giavoli C, Porretti S, Ronchi CL, Cappiello V, Ferrante E, Orsi E, Arosio M, Beck-Peccoz P (2004) Long-term monitoring of insulin sensitivity in growth hormone-deficient adults on substitutive recombinant human growth hormone therapy. Metabolism 53:740–743
Saenger P (2000) Metabolic consequences of growth hormone treatment in paediatric practice. Horm Res 53:60–69
Ciresi A, Amato MC, Criscimanna A, Mattina A, Vetro C, Galluzzo A, D’Acquisto G, Giordano C (2007) Metabolic parameters and adipokine profile during GH replacement therapy in children with GH deficiency. Eur J Endocrinol 156(3):353–360
Bergman RN, Finegood DT, Ader M (1985) Assessment of insulin sensitivity in vivo. Endocr Rev 6(1):45–86
Gungor N, Saad R, Janosky J, Arslanian S (2004) Validation of surrogate estimates of insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in children and adolescents. J Pediatr 144(1):47–55
Uwaifo GI, Fallon EM, Chin J, Elberg J, Parikh SJ, Yanovski JA (2002) Indices of insulin action, disposal, and secretion derived from fasting samples and clamps in normal glucose-tolerant black and white children. Diabetes Care 25(11):2081–2087
Schwartz B, Jacobs DR Jr, Moran A, Steinberger J, Hong CP, Sinaiko AR (2008) Measurement of insulin sensitivity in children: comparison between the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp and surrogate measures. Diabetes Care 31(4):783–788
Rosenfalck AM, Fisker S, Hilsted J, Dinesen B, Vølund A, Jørgensen JO, Christiansen JS, Madsbad S (1999) The effect of the deterioration of insulin sensitivity on beta-cell function in growth-hormone-deficient adults following 4-month growth hormone replacement therapy. Growth Horm IGF Res 9(2):96–105
Giannini C, Weiss R, Cali A, Bonadonna R, Santoro N, Pierpont B, Shaw M, Caprio S (2012) Evidence for early defects in insulin sensitivity and secretion before the onset of glucose dysregulation in obese youths: a longitudinal study. Diabetes 61(3):606–614
Sjaarda LG, Bacha F, Lee S, Tfayli H, Andreatta E, Arslanian S (2012) Oral disposition index in obese youth from normal to prediabetes to diabetes: relationship to clamp disposition index. J Pediatr. 161(1):51–57
Xiang AH, Wang C, Peters RK, Trigo E, Kjos SL, Buchanan TA (2006) Coordinate changes in plasma glucose and pancreatic beta-cell function in Latino women at high risk for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 55(4):1074–1079
Tripathy D, Eriksson KF, Orho-Melander M, Fredriksson J, Ahlqvist G, Groop L (2004) Parallel manifestation of insulin resistance and beta cell decompensation is compatible with a common defect in Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 47(5):782–793
Burns SF, Bacha F, Lee SJ, Tfayli H, Gungor N, Arslanian SA (2011) Declining β-cell function relative to insulin sensitivity with escalating OGTT 2-h g.lucose concentrations in the nondiabetic through the diabetic range in overweight youth. Diabetes Care 34(9):2033–2040
Jensen RB, Thankamony A, O’Connell SM, Salgin B, Kirk J, Donaldson M, Ivarsson SA, Söder O, Roche E, Hoey H, Dunger DB, Juul A, NESGAS Group (2013) Baseline IGF-I levels determine insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity during the first year on growth hormone therapy in children born small for gestational age. Results from a North European Multicentre Study (NESGAS). Horm Res Paediatr 80(1):38–46
Rabinovitch A, Quigley C, Rechler MM (1983) Growth hormone stimulates islet B-cell replication in neonatal rat pancreatic monolayer cultures. Diabetes 32(4):307–312
Formby B, Ullrich A, Coussens L, Walker L, Peterson CM (1988) Growth hormone stimulates insulin gene expression in cultured human fetal pancreatic islets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 66(5):1075–1079
Sørensen K, Aksglaede L, Munch-Andersen T, Aachmann-Andersen NJ, Leffers H, Helge JW, Hilsted L, Juul A (2009) Impact of the growth hormone receptor exon 3 deletion gene polymorphism on glucose metabolism, lipids, and insulin-like growth factor-I levels during puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(8):2966–2969
Prodam F, Savastio S, Genoni G, Babu D, Giordano M, Ricotti R, Aimaretti G, Bona G, Bellone S (2014) Effects of growth hormone (GH) therapy withdrawal on glucose metabolism in not confirmed GH deficient adolescents at final height. PLoS One 30. 9(1):e87157
Giavoli C, Ferrante E, Profka E, Olgiati L, Bergamaschi S, Ronchi CL, Verrua E, Filopanti M, Passeri E, Montefusco L, Lania AG, Corbetta S, Arosio M, Ambrosi B, Spada A, Beck-Peccoz P (2010) Influence of the d3GH receptor polymorphism on the metabolic and biochemical phenotype of GH-deficient adults at baseline and during short- and long-term recombinant human GH replacement therapy. Eur J Endocrinol 163(3):361–368
Arafat AM, Möhlig M, Weickert MO, Schöfl C, Spranger J, Pfeiffer AF (2010) Improved insulin sensitivity, preserved beta cell function and improved whole-body glucose metabolism after low-dose growth hormone replacement therapy in adults with severe growth hormone deficiency: a pilot study. Diabetologia 53(7):1304–1313
van der Kaay D, Bakker B, van der Hulst F, Mul D, Mulder J, Schroor E, van Elswijk D, Rowaan I, Willeboer M, de Ridder M, Hokken-Koelega A (2010) Randomized GH trial with two different dosages in combination with a GnRH analogue in short small for gestational age children: effects on metabolic profile and serum GH, IGF1, and IGFBP3 levels. Eur J Endocrinol. 162(5):887–895
Acknowledgments
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciresi, A., Amato, M.C. & Giordano, C. Reduction in insulin sensitivity and inadequate β-cell capacity to counteract the increase in insulin resistance in children with idiopathic growth hormone deficiency during 12 months of growth hormone treatment. J Endocrinol Invest 38, 351–359 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0184-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0184-4