Abstract
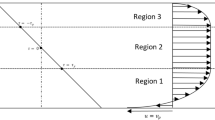
A mesoscale modeling of magneto-rheological damper is performed by using dissipative particle dynamics method. Bounce-back and periodic boundary conditions are used, and the model is validated by Couette flow, Poiseuille flow and flow through a micro-tube. Shear stress and damping behavior are probed with considering hysteresis condition. Three electrical coils are placed inside MR damper, control damping force by applying magnetic strength distribution as step function pattern. Results show that by increasing both of average strength of magnetic field and shear rate, shear stress increases. The effects of different parameters such as frequency and amplitude of piston velocity, magnetic field strength, diameter of magnetic particles and strength of dissipative forces on damping force and hysteresis condition are investigated by using Bouc–Wen model. Results show by increasing frequency and decreasing amplitude and magnetic field strength, hysteresis range and strength of damping force reduce. Sensitivity analysis performed on MR fluid parameters reveals that the weight of magnetic particles and the dissipative force have the most effect on strength of damping force so that, by increasing dissipative force, damping force increases linearly, but enhancement in the weight of magnetic particles leads to damping force firstly increases and then reduces.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
BASF Co. (2009) Badische Anilin- und Soda-Fabrik. www.basf.com
Schurter K, Roschke PN (2001) Fuzzy modeling of a magneto rheological damper using ANFIS. Proc IEEE Fuzzy Conf 2:22–27
Butz T, Stryk O (2002) Modelling and simulation of electro and magneto rheological fluid dampers. Z Angew Math Mech 82:3–20
Chooi O (2008) Design, modelling and testing of magneto rheological (MR) dampers using analytical flow solutions. Comp Struct 86:473–482
Dominguez A, Sedaghati R, Stiharu I (2008) Modeling and application of MR dampers in semi-adaptive structures. Comp Struct 86:407–415
Bai X, Wang D, Fu H (2013) Principle, modeling, and testing of an annular-radial-duct magneto rheological damper. Sens Actuator Phys 201:302–309
Mazlan S, Iryani I, Kikuchi T, Zamuzuri H (2014) Design of magneto rheological damper with a combination of shear and squeeze modes. Mater Des 54:87–95
Sternberg A, Zemp R, Carlos J (2014) Multiphysics behavior of a magneto rheological damper and experimental validation. Eng Struct 69:194–205
Attia EM, Elsodany NM, El-Gamal HA, Elgohary MA (2017) Theoretical and experimental study of magneto rheological fluid disc brake. Alex Eng J 56:189–200
Kumbhar BK, Patil SR, Sawant SM (2015) Synthesis and characterization of magneto-rheological (MR) fluids for MR brake application. Eng Sci Technol J 18:432–438
Huang J, Zhang JQ, Yang Y, Wei YQ (2002) Analysis and design of a cylindrical magneto-rheological fluid brake. Comput Struct 129:559–562
Wang HY, Ni YQ, Ko JM, Spencer BF (2005) Magneto-rheological tuned liquid column dampers (MR-TLCDs) for vibration mitigation of tall buildings: modelling and analysis of open-loop control. Comput Struct 83:2023–2034
Fujitani J, Shiozaki Y, Hiwatashi T, Hata K, Tomura T, Sodeyama H, Soda S (2010) A research and development of smart building structures by magneto-rheological damper. Adv Build Technol 1:473–480
Wang JY, Ni YQ, Ko JM, Spencer BF (2011) Semi-active TLCDS using magneto-rheological fluids for vibration mitigation of tall buildings. Adv Build Technol 2:537–544
Jain VK, Ranjan P, Suri VK, Komanduri R (2010) Chemo-mechanical magneto-rheological finishing (CMMRF) of silicon for microelectronics applications. Manuf Technol 59:323–328
Shimada K, Wu Y, Matsuo Y, Yamamoto K (2005) Float polishing technique using new tool consisting of micro magnetic clusters. J Mater Process Technol 162:690–695
Khatri N, Mishra V, Sharma R, Garg H, Karar V (2017) Improving the surface finish of diamond turned silicon with magneto-rheological finishing. Mater Today Proc 4:10158–10162
Sadiq A, Shunmugam MS (2010) A novel method to improve finish on non-magnetic surfaces in magneto-rheological abrasive honing. Process Tribol 43:1122–1126
Wu Y, Shimada K, Wong YC (2003) Effect of magnetic cluster and magnetic field on polishing using magnetic compound fluid (MCF). J Magn Magn Mater 262:242–247
Allen MP, Tildesley DJ (1987) Computer simulation of liquids, vol 2. Oxford Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 32–35
Rapaport DC (1995) The art of molecular dynamics simulation, vol 3. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 54–57
Haile JM (1992) Molecular dynamics simulation, elementary methods, vol 1. Wiley, New York, pp 23–32
Satoh A (2003) Introduction to molecular-micro simulation of colloidal dispersions, vol 3. Elsevier, Amesterdam, pp 45–55
Hoogerbrugge PJ, Koelman JMVA (1992) Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics. Europhys Lett 19:155–160
Koelman JMVA, Hoogerbrugge PJ (1993) Dynamic simulations of hard-sphere suspensions under steady shear. Europhys Lett 21:363–368
Espanol P (1995) Hydrodynamics from dissipative particle dynamics. Phys Rev 52:1734–1742
Marsh CA, Backx G, Ernst MH (1997) Static and dynamic properties of dissipative particle dynamics. Phys Rev 56:1676–1691
Bird GA (1994) Molecular gas dynamics and the direct simulation of gas flows, vol 2. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 32–35
Sapinski B, Filus J (2003) Analysis of parametric models of MR linear damper. Dept Process Control Univ Min Metall 3:26–33
Li WH, Yao GZ, Chen G, Yeo SH, Yap FF (2000) Testing and steady state modeling of a linear MR damper under sinusoidal loading. Nanyang Technol Univ 3:32–36
Wen YK (1976) Method for random vibration of hysteretic systems. ASCE J Eng Mech Div 102:249–263
Spencer BF, Dyke SJ, Sain MK, Carlson JD (1996) Phenomenological model of a magneto-rheological damper. ASCE J Eng Mech 12:23–26
Revenga M, Zuniga N, Espanol P (1998) Dissipative particle dynamics with energy conservation, heat conduction. Int J Mod Phys 9:1319–1328
Duong-Kong D, Phan-Tien N, Fan X (2004) An implementation of no-slip boundary conditions in DPD. J Comput Mech 35:24–29
Phan-Thien N (2013) Understanding viscoelasticity, vol 2. Springer, FL, pp 113–117
Engin T, Evrensel C, Gordaninejad F (2005) Numerical simulation of laminar flow of water-based magneto-rheological fluids in micro tubes with wall roughness effect. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 32:1016–1025
Irving JH, Kirkwood JG (1950) Calculation of stress in molecular dynamic models. J Chem Phys 18:817–829
Yanga Z, Wangb H, Hanc X, Fangd W (2011) Damping force of MR damper analysis and experimental. Int Conf Electron Mech Eng Inf Technol 32:32–44
Carlson DJ (2004) MR technology workshop. Lord Corp 1:22–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghafarian Eidgahi Moghadam, M., Shahmardan, M.M. & Norouzi, M. Magneto-rheological damper modeling by using dissipative particle dynamics method. Comp. Part. Mech. 7, 567–592 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-019-00280-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-019-00280-x