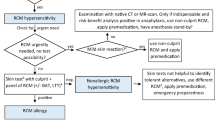
Opinion statement
Classically, hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media (ICM) have been termed pseudoallergic, allergy-like, or anaphylactoid. The origin of these terms to define ICM hypersensitivity reactions could be in relation to the use of traditional, classic, ionic ICMs. These ionic ICMs have a high osmolality, and the reactions have been considered as secondary to non-specific histamine release. Currently, ionic ICMs have been replaced by non-ionic compounds with low or iso-osmolality, which, although to a lesser extent, can also produce hypersensitivity reactions. In recent years, there has been growing evidence that some of these reactions, especially the more severe, can be triggered by an IgE-dependent mechanism. Also, in recent decades, there has been an increase in non-immediate reactions, especially in the form of maculopapular exanthems occurring up to several days after the administration of ICM. In these non-immediate reactions, the involvement of T lymphocytes has been clearly demonstrated. The finding of positive skin tests and other in vitro studies for ICMs would support a specific immunological mechanism in a percentage of ICM-induced reactions. However, although there is a body of evidence suggesting that ICMs can induce true allergy reactions, the main guidelines for contrast media management, such as those proposed by US (American College of Radiology Manual on Contrast Media) or European (European Society of Urogenital Radiology Guidelines on Contrast Media) societies, continue to consider only immediate reactions and handle them as non-allergic reactions, without any allergy testing. In ICM reactions an allergic evaluation should be mandatory, not only to study the possible mechanisms involved but also to identify the ICM involved in the reaction and to find an alternative one that could be used in future radiological explorations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Ring J, Arroyave CM, Frizler MJ, Tan EM. In vitro histamine and serotonin release by radiographic contrast media (RCM). Complement-dependent and -independent release reaction and changes in ultrastructure of human blood cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978;32:105–18.
Stellato C, de Crescenzo G, Patella V, Mastronardi P, Mazzarella B, Marone G. Human basophil/mast cell releasability. XI. Heterogeneity of the effects of contrast media on mediator release. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;97:838–50.
Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, et al. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:832–6.
Demoly P, Adkinson NF, Brockow K, Castells M, Chiriac AM, Greenberger PA, et al. International consensus on drug allergy. Allergy. 2014;69:420–37.
Wolf GL, Arenson RL, Cross AP. A prospective trial of ionic vs nonionic contrast agents in routine clinical practice: comparison of adverse effects. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989;152:939–44.
Laroche D, Aimone-Gastin I, Dubois F, Huet H, Gerard P, Vergnaud MC, et al. Mechanisms of severe, immediate reactions to iodinated contrast material. Radiology. 1998;209:183–90.
• Brockow K. Immediate and delayed reactions to radiocontrast media: is there an allergic mechanism? Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009;29:453–68. Clear review of hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media
Trcka J, Schmidt C, Seitz CS, Brocker EB, Gross GE, Trautmann A. Anaphylaxis to iodinated contrast material: nonallergic hypersensitivity or IgE-mediated allergy? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190:666–70.
Dewachter P, Laroche D, Mouton-Faivre C, Bloch-Morot E, Cercueil JP, Metge L, et al. Immediate reactions following iodinated contrast media injection: a study of 38 cases. Eur J Radiol. 2011;77:495–501.
Morales-Cabeza C, Roa-Medellin D, Torrado I, De Barrio M, Fernandez-Alvarez C, Montes-Acenero JF, et al. Immediate reactions to iodinated contrast media. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;119:553–57.
• Yoon SH, Lee SY, Kang HR, Kim JY, Hahn S, Park CM, et al. Skin tests in patients with hypersensitivity reaction to iodinated contrast media: a meta-analysis. Allergy. 2015;70:625–37. A meta-analysis that evalued skin tests in immediate and non-immediate reactions.
Dona I, Barrionuevo E, Blanca-Lopez N, Torres MJ, Fernandez TD, Mayorga C, et al. Trends in hypersensitivity drug reactions: more drugs, more response patterns, more heterogeneity. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2014;24:143–53.
•• Rosado Ingelmo A, Dona Diaz I, Cabanas Moreno R, Moya Quesada MC, Garcia-Aviles C, Garcia Nunez I, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis and management of hypersensitivity reactions to contrast media. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2016;26:144–55. Spanish guidelines providing indications for management of hypersensitivity reactions to contrast media.
Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Cornejo-Garcia JA, Lopez S, Chaves P, Rondon C, et al. Monitoring non-immediate allergic reactions to iodine contrast media. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;152:233–8.
Kanny G, Pichler W, Morisset M, Franck P, Marie B, Kohler C, et al. T cell-mediated reactions to iodinated contrast media: evaluation by skin and lymphocyte activation tests. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:179–85.
Vernassiere C, Trechot P, Commun N, Schmutz JL, Barbaud A. Low negative predictive value of skin tests in investigating delayed reactions to radio-contrast media. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;50:359–66.
• Torres MJ, Gomez F, Dona I, Rosado A, Mayorga C, Garcia I, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of patients with nonimmediate cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media. Allergy. 2012;67:929–35. Study showing diagnostic value of skin tests and drug provocation test in non-immedite reactions.
Caimmi S, Benyahia B, Suau D, Bousquet-Rouanet L, Caimmi D, Bousquet PJ, et al. Clinical value of negative skin tests to iodinated contrast media. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010;40:805–10.
• Brockow K, Romano A, Aberer W, Bircher AJ, Barbaud A, Bonadonna P, et al. Skin testing in patients with hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media—a European multicenter study. Allergy. 2009;64:234–41. A European study showing diagnostic value in inmediate and non-immediate reactions to iodinated contrast media.
• Hasdenteufel F, Waton J, Cordebar V, Studer M, Collignon O, Luyasu S, et al. Delayed hypersensitivity reactions caused by iodixanol: an assessment of cross-reactivity in 22 patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:1356–7. A study that evalue cross-reactivity between iodinated contrast media in non-immediate reactions.
Stejskal V, Nilsson R, Grepe A. Immunologic basis for adverse reactions to radiographic contrast media. Acta Radiol. 1990;31:605–12.
Keller M, Lerch M, Britschgi M, Tache V, Gerber BO, Luthi M, et al. Processing-dependent and -independent pathways for recognition of iodinated contrast media by specific human T cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010;40:257–68.
Lerch M, Keller M, Britschgi M, Kanny G, Tache V, Schmid DA, et al. Cross-reactivity patterns of T cells specific for iodinated contrast media. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1529–36.
Radiology ESoU. ESUR Guidelines on contrast media Available from http://www.esur.org.
ACR Manual on Contrast Media Available from: http://www.acr.org. 2017.].
Rawlins MD. Mechanisms of adverse drug reactions. In: Davies DMFR, de Glanville H, editors. Davies’s Textbook of Adverse Drug Reactions. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1991.
Katayama H. Adverse reactions to contrast media. What are the risk factors? Invest Radiol. 1990;25(Suppl 1):S16–7.
Palmer FJ. The RACR survey of intravenous contrast media reactions. Final report. Australas Radiol. 1988;32:426–8.
Caro JJ, Trindade E, McGregor M. The risks of death and of severe nonfatal reactions with high- vs low-osmolality contrast media: a meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;156:825–32.
Gomi T, Nagamoto M, Hasegawa M, Katoh A, Sugiyama M, Murata N, et al. Are there any differences in acute adverse reactions among five low-osmolar non-ionic iodinated contrast media? Eur Radiol. 2010;20:1631–5.
Chen QL, Zhao XY, Wang XM, Lv N, Zhu LL, Xu HM, et al. Retrospective analysis of non-laboratory-based adverse drug reactions induced by intravenous radiocontrast agents in a Joint Commission International-accredited academic medical center hospital in China. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:565–73.
Kim TH, Yoon SH, Lee SY, Choi YH, Park CM, Kang HR, et al. Biphasic and protracted anaphylaxis to iodinated contrast media. Eur Radiol. 2017;27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5052-0.
Kim SR, Lee JH, Park KH, Park HJ, Park JW. Varied incidence of immediate adverse reactions to low-osmolar non-ionic iodide radiocontrast media used in computed tomography. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017;47:106–12.
Gueant-Rodriguez RM, Romano A, Barbaud A, Brockow K, Gueant JL. Hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:3359–72.
Szebeni J. Hypersensitivity reactions to radiocontrast media: the role of complement activation. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004;4:25–30.
• Lerondeau B, Trechot P, Waton J, Poreaux C, Luc A, Schmutz JL, et al. Analysis of cross-reactivity among radiocontrast media in 97 hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:633–5 e4. This large study analyze cross-reactivity and propose three subgroups of iodinated contrast media with cross-reactivity.
Salas M, Gomez F, Fernandez TD, Dona I, Aranda A, Ariza A, et al. Diagnosis of immediate hypersensitivity reactions to radiocontrast media. Allergy. 2013;68:1203–6.
Prieto-Garcia A, Tomas M, Pineda R, Tornero P, Herrero T, Fuentes V, et al. Skin test-positive immediate hypersensitivity reaction to iodinated contrast media: the role of controlled challenge testing. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013;23:183–9.
Pinnobphun P, Buranapraditkun S, Kampitak T, Hirankarn N, Klaewsongkram J. The diagnostic value of basophil activation test in patients with an immediate hypersensitivity reaction to radiocontrast media. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011;106:387–93.
Chirumbolo S. Basophil activation test (BAT) in the diagnosis of immediate hypersensitivity reactions to radiocontrast media. Allergy. 2013;68:1627–8.
Mita H, Tadokoro K, Akiyama K. Detection of IgE antibody to a radiocontrast medium. Allergy. 1998;53:1133–40.
Alam R, Anantharaman R. Use of IABP in contrast media-induced anaphylactic shock: the ultimate lifesaver. BMJ Case Rep 2013; 2013. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-008838.
Palmiere C, Reggiani Bonetti L. Risk factors in fatal cases of anaphylaxis due to contrast media: a forensic evaluation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014;164:280–8.
Jansman FG, Kieft H, Harting JW. Fatal anaphylactoid reaction following ioversol administration. Pharm World Sci. 2007;29:584–6.
Bohm I. Kounis syndrome in a patient with allergy to iodinated contrast media. Int J Cardiol. 2011;151:102–3.
Park JM, Cho J, Chung SP, Kim MJ. Kounis syndrome captured by coronary angiography computed tomography. Am J Emerg Med. 2010;28:640 e5–8.
Brown SG. Clinical features and severity grading of anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:371–6.
Ring J, Messmer K. Incidence and severity of anaphylactoid reactions to colloid volume substitutes. Lancet. 1977;1:466–9.
Epskamp C, Snels DG, Yo GL, Zuetenhorst HJ, Hamberg P. Bullous fixed drug eruption in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma induced by iodinated contrast during pazopanib treatment. Eur J Dermatol. 2016;26:207–8.
Cha SH, Kim HS, Lee JY, Kim HO, Park YM. Fixed drug eruption due to iopromide (Ultravist(R)). Ann Dermatol. 2011;23(Suppl 1):S33–5.
Belgodere X, Wolkenstein P, Pastor MJ. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by iopamidol. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2004;131:831–2.
Poliak N, Elias M, Cianferoni A, Treat J. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: the first pediatric case caused by a contrast agent. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;105:242–3.
Brockow K, Christiansen C, Kanny G, Clement O, Barbaud A, Bircher A, et al. Management of hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media. Allergy. 2005;60:150–8.
Brockow K, Romano A, Blanca M, Ring J, Pichler W, Demoly P. General considerations for skin test procedures in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2002;57:45–51.
Kvedariene V, Martins P, Rouanet L, Demoly P. Diagnosis of iodinated contrast media hypersensitivity: results of a 6-year period. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006;36:1072–7.
Gracia Bara MT, Moreno E, Laffond E, Munoz FJ, Macias E, Davila I. Selection of contrast media in patients with delayed reactions should be based on challenge test results. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:554–5. author reply 5–6
•• Mayorga C, Celik G, Rouzaire P, Whitaker P, Bonadonna P, Rodrigues-Cernadas J, et al. In vitro tests for drug hypersensitivity reactions: an ENDA/EAACI Drug Allergy Interest Group position paper. Allergy. 2016;71:1103–34. A European position paper providing data and recommendations regarding in vitro methods for drug hypersensitivity reactions.
Ebo DG, Leysen J, Mayorga C, Rozieres A, Knol EF, Terreehorst I. The in vitro diagnosis of drug allergy: status and perspectives. Allergy. 2011;66:1275–86.
Bohm I, Speck U, Schild HH. Pilot study on basophil activation induced by contrast medium. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2011;25:267–76.
Javaloyes G, Goikoetxea MJ, Sanz ML, Cabrera-Freitag P, Gastaminza G. Basophil activation test in the diagnosis of gadobutrol anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012;108:286–7.
Philipse E, Sabato V, Bridts C, De Clerck L, Ebo D. Basophil activation in the diagnosis of life-threatening hypersensitivity reaction to iodinated contrast media: a case report. Acta Clin Belg. 2013;68:140–2.
Mayorga C, Dona I, Perez-Inestrosa E, Fernandez TD, Torres MJ. The value of in vitro tests to diminish drug challenges. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061222.
Antunez C, Barbaud A, Gomez E, Audonnet S, Lopez S, Gueant-Rodriguez RM, et al. Recognition of iodixanol by dendritic cells increases the cellular response in delayed allergic reactions to contrast media. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011;41:657–64.
Nyfeler B, Pichler WJ. The lymphocyte transformation test for the diagnosis of drug allergy: sensitivity and specificity. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997;27:175–81.
Zawodniak A, Lochmatter P, Yerly D, Kawabata T, Lerch M, Yawalkar N, et al. In vitro detection of cytotoxic T and NK cells in peripheral blood of patients with various drug-induced skin diseases. Allergy. 2010;65:376–84.
Sese L, Gaouar H, Autegarden JE, Alari A, Amsler E, Vial-Dupuy A, et al. Immediate hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast media: diagnostic accuracy of skin tests and intravenous provocation test with low dose. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016;46:472–8.
Aberer W, Bircher A, Romano A, Blanca M, Campi P, Fernandez J, et al. Drug provocation testing in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity reactions: general considerations. Allergy. 2003:854–63.
Della-Torre E, Berti A, Yacoub MR, Guglielmi B, Tombetti E, Sabbadini MG, et al. Proposal of a skin tests based approach for the prevention of recurrent hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;47:77–85.
Park HJ, Park JW, Yang MS, Kim MY, Kim SH, Jang GC, et al. Re-exposure to low osmolar iodinated contrast media in patients with prior moderate-to-severe hypersensitivity reactions: a multicentre retrospective cohort study. Eur Radiol. 2017;27:2886–93.
Abe S, Fukuda H, Tobe K, Ibukuro K. Protective effect against repeat adverse reactions to iodinated contrast medium: premedication vs. changing the contrast medium. Eur Radiol. 2016;26:2148–54.
Schatz M, Patterson R, O’Rourke J, Nickelsen J, Northup C. The administration of radiographic contrast media to patients with a history of a previous reaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975;55:358–66.
Zweiman B, Mishkin MM, Hildreth EA. An approach to the performance of contrast studies in contrast material-reactive persons. Ann Intern Med. 1975;83:159–62.
Ring J, Rothenberger KH, Clauss W. Prevention of anaphylactoid reactions after radiographic contrast media infusion by combined histamine H1- and H2-receptor antagonists: results of a prospective controlled trial. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;78:9–14.
Marshall GD Jr, Lieberman PL. Comparison of three pretreatment protocols to prevent anaphylactoid reactions to radiocontrast media. Ann Allergy. 1991;67:70–4.
Greenberger PA, Patterson R, Tapio CM. Prophylaxis against repeated radiocontrast media reactions in 857 cases. Adverse experience with cimetidine and safety of beta-adrenergic antagonists. Arch Intern Med. 1985;145:2197–200.
Lee SY, Yang MS, Choi YH, Park CM, Park HW, Cho SH, et al. Stratified premedication strategy for the prevention of contrast media hypersensitivity in high-risk patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;118:339–44. e1
Jung JW, Choi YH, Park CM, Park HW, Cho SH, Kang HR. Outcomes of corticosteroid prophylaxis for hypersensitivity reactions to low osmolar contrast media in high-risk patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016;117:304–9. e1
Kim SH, Lee SH, Lee SM, Kang HR, Park HW, Kim SS, et al. Outcomes of premedication for non-ionic radio-contrast media hypersensitivity reactions in Korea. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80:363–7.
Freed KS, Leder RA, Alexander C, DeLong DM, Kliewer MA. Breakthrough adverse reactions to low-osmolar contrast media after steroid premedication. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:1389–92.
Romano A, Artesani MC, Andriolo M, Viola M, Pettinato R, Vecchioli-Scaldazza A. Effective prophylactic protocol in delayed hypersensitivity to contrast media: report of a case involving lymphocyte transformation studies with different compounds. Radiology. 2002;225:466–70.
Rosado A, Canto G, Veleiro B, Rodriguez J. Toxic epidermal necrolysis after repeated injections of iohexol. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:262–3.
Funding
The present study has been supported by the Institute of Health “Carlos III” of the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (grants cofunded by European Regional Development Fund (ERDF): RETICs ARADyAL (RD16/0006/0001; RD16/0006/0033; RD16/0006/0019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Esther Moreno declares that she has no conflict of interest. M. Teresa Gracia-Bara declares the she has no conflict of interest. Cristobalina Mayorga declares the she has no conflict of interest. Milagros Lázaro declares the she has no conflict of interest. M. Valle Campanón declares the she has no conflict of interest. Ignacio Dávila declares the he has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Drug Allergy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno, E., Gracia-Bara, M.T., Mayorga, C. et al. Hypersensitivity Reactions to Iodinated Contrast Media: Is it a True Allergy?. Curr Treat Options Allergy 5, 103–117 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40521-018-0154-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40521-018-0154-8