Abstract
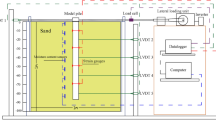
Stone columns are one of the cost-effective and efficient methods for improving the ground which strengthen the soil and reduce the settlements. The study of the behaviour of stone columns in layered soils is of great importance. In this paper, results obtained from the experiments done on the stone columns with varying thickness of clayey silt soil (lithomargic clay) at bottom and the lateritic soil at the top are discussed. The lateritic layers are varied from top for a depth of 1D to 5D where D is the stone column diameter. Experiments were performed on untreated soils alone, soil with the ordinary stone column, geogrid encased stone column with and without additional horizontal reinforcement called basal layer to geogrid encased stone column in lithomargic clay. Similar experiments were conducted using lateritic soil. By considering layered combination of these two soils, experiments were also performed on ordinary stone column, geogrid encased stone column and geogrid encased stone column with basal layer. Laboratory tests were conducted in a unit cell on the floating stone column of diameter 60 mm. The load capacity of the stone column and bulging characteristics are significantly affected with the increase in the layers of lateritic soil. The encasement of stone column enhances the stone column’s capacity and reduces the bulging. The additional horizontal reinforcement layer also showed a significant impact on the load capacity of the stone column. Experiments conducted were modelled and analysed using PLAXIS 2D software package.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambily, A.P., Gandhi, S.R.: Effect of sand pad thickness on load sharing in stone column. In: Proc. Indian Geotechnical Conference, Chennai, pp. 555–556 (2006)
Ambily, A.P., Gandhi, S.R.: Behavior of stone columns based on experimental and fem analysis. 133, 405–415 (2007)
Babu, M.R.D., Nayak, S.: A critical review of construction , Analysis and Behaviour of Stone Columns. 1, 22–22 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-012-9555-9
Bergado, D.T., Rantucci, G., Widodo, S.: Full scale load tests on granular piles and sand drains in the soft Bangkok clay. In: Proc. Intl. Conf. On In-situ Soil and Rock Reinforcement, pp. 111–118, Paris (1984)
Chauhan, V.B., Kolekar, Y.A.: Soil Testing, Soil Stability and Ground Improvement. 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61902-6
Dash, S.K., Bora, M.C.: Influence of geosynthetic encasement on the performance of stone columns floating in soft clay. Can. Geotech. J. 50, 754–765 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2012-0437
Deb, K., Basudhar, P.K., Asce, A.M., Chandra, S.: Generalized model for geosynthetic-reinforced granular fill-soft soil with stone columns. 7, 266–276 (2007)
Debnath, P., Dey, A.K.: Bearing capacity of geogrid reinforced sand over encased stone columns in soft clay. Geotext. Geomembr. 45, 653–664 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2017.08.006
Fattah, M.Y., Zabar, B.S., Hassan, H.A.: Experimental analysis of embankment on ordinary and encased stone columns. Int. J. Geomech. 16, 04015102 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000579
Hanna, A.M., Etezad, M., Ayadat, T.: Mode of failure of a group of stone columns in soft soil. Int. J. Geomech. 13, 87–96 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000175
Hughes, J.M.O., Withers, N.J.: Reinforcing of soft cohesive soils with stone columns. Gr. Eng. 7(3), 42–49 (1974)
Indian Standards (IS: 15284): Indian standard code of practice for design and construction for ground improvement-guidelines, Part 1: Stone Columns, India (2003)
Malarvizhi S.N., Ilamparuthi K.: Comparative study on the behavior of encased stone column and conventional stone column 47, 873–885 (2008)
Mckelvey, D., Sivakumar, V., Bell, A., Graham, J.: Modelling vibrated stone columns in soft clay. 137–149 (2004)
Nayak, S., Sarvade, P.G.: Effect of cement and quarry dust on shear strength and hydraulic characteristics of lithomargic clay. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 30, 419–430 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-011-9477-y
Ng, K.S.: Numerical study on bearing capacity of single stone column. 1–10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40703-018-0077-z
Shahu, J.T., Madhav, M.R., Hayashi, S.: Analysis of Soft Ground-Granular Pile-Granular Mat System, vol. 27, pp. 4–5 (2000)
Vitkar, P P, Madhav, M: Strip Footing on Weak Clay Stabilized with a Granular Trench or Pile. (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, S., Balaji, M. & Preetham, H.K. A Study on the Behaviour of Stone Columns in a Layered Soil System. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotech. 7, 85–102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-019-00090-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-019-00090-x