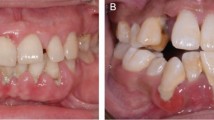
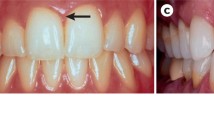
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Behçet’s disease (BD) is a recurrent, chronic inflammatory disease affected by environmental triggers. Oral aphthous ulcerations are the most common and often the first sign of the disease. Although the etiology of BD has not been clearly established, its systemic effects originate from vasculitis and involve almost all organ systems such as gastrointestinal, neural, cardiac, and pleuropulmonary systems. Periodontal disease is the chronic inflammation of the surrounding tissues of the teeth. Depending on the degree of the disease, bleeding, mobility, pain, discomfort, and tooth loss may occur. This review focused on the effect of periodontal disease on the occurrence and severity of Behçet’s disease, the shared characteristics between the two diseases, and the evaluation and discussion of possible interactions.
Recent Findings
Oral health is impaired in BD patients, and these patients seem to have high plaque accumulation and increased periodontal indices. High plaque accumulation, together with the host response, forms the basis of the etiology of periodontal diseases. It has been shown that severe periodontitis is associated with chronic inflammatory conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Many studies have reported that periodontal therapy is effective in reducing systemic pro-inflammatory mediators. Therefore, in an autoinflammatory and autoimmune disease such as BD, suppression of inflammatory pathways may be effective in the course of the disease. Indeed, periodontal treatment, dental examinations, and prophylaxis are effective on the severity of BD.
Summary
BD is a recurrent, in some cases, life-threatening disease if not treated aggressively. In these patients, the quality of life from eating to sexual life, even sleep quality, is seriously affected. In addition, this disease is difficult to treat and control. Periodontal treatment can have a significant effect in improving the quality of life by helping balance environmental triggers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behçet’s disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(17):1284–91.
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, et al. 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37715.
van der Houwen TB, van Hagen PM, van Laar JAM. Immunopathogenesis of Behçet’s disease and treatment modalities. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;52:151956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.151956.
Davatchi F, Chams-Davatchi C, Shams H, Shahram F, Nadji A, Akhlaghi M, et al. Behcet’s disease: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017;13(1):57–65.
Bonfioli AA, Orefice F. Behcet’s disease. Seminars in ophthalmology. Taylor & Francis; 2005. p. 199–206.
Davatchi F, Shahram F, Chams-Davatchi C, Shams H, Nadji A, Akhlaghi M, et al. Behcet’s disease: from East to West. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29(8):823–33.
Yazici Y, Hatemi G, Bodaghi B, Cheon JH, Suzuki N, Ambrose N, et al. Behçet syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2021;7(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00301-1.
Azizlerli G, AkdağKöse A, Sarıca R, Gül A, Tutkun İT, Kulaç M, et al. Prevalence of Behçet’s disease in Istanbul, Turkey. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42(10):803–6.
Kinane DF, Stathopoulou PG, Papapanou PN. Periodontal diseases. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017;3:17038. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.38.
Sedghi LM, Bacino M, Kapila YL. Periodontal disease: the good, the bad, and the unknown. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:766944. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.766944.
Hajishengallis G, Chavakis T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(7):426–40.
Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW. Periodontal diseases. Lancet. 2005;366(9499):1809–20.
Armitage GC. Periodontal diagnoses and classification of periodontal diseases. Periodontology 2000. 2004;34(1):9–21.
Jordan RC. Diagnosis of periodontal manifestations of systemic diseases. Periodontology 2000. 2004;34(1):217–29.
Albandar JM, Rams TE. Global epidemiology of periodontal diseases: an overview. Periodontology 2000. 2002;29(1):7–10.
Hajishengallis G. Periodontitis: from microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(1):30–44.
Mumcu G, Ergun T, Inanc N, Fresko I, Atalay T, Hayran O, et al. Oral health is impaired in Behcet’s disease and is associated with disease severity. Rheumatology. 2004;43(8):1028–33.
Yosipovitch G, Kaplan I, Calderon S, David M, Chan YH, Weinberger A. Distribution of mucosal pH on the bucca, tongue, lips and palate. A study in healthy volunteers and patients with lichen planus, Behçet’s disease and burning mouth syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2001;81(3):178–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/000155501750376258.
Seymour GJ, Gemmell E. Cytokines in periodontal disease: where to from here? Acta Odontol Scand. 2001;59(3):167–73.
Senusi A, Higgins S, Fortune F. The influence of oral health and psycho-social well-being on clinical outcomes in Behçet’s disease. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(10):1873–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-018-4117-y.
Rezidivierende HB. aphthöse, durch ein Virus verursachte Geschwüre am Mund, am Auge und and den Genitalien. Dermatol Wochenschr. 1937;105:1152–7.
Davatchi F, Shahram F, Chams-Davatchi C, Shams H, Nadji A, Akhlaghi M, et al. How to deal with Behcet’s disease in daily practice. Int J Rheum Dis. 2010;13(2):105–16.
Disease ITftRotICfBs, Davatchi F, Assaad-Khalil S, Calamia K, Crook J, Sadeghi-Abdollahi B, et al. The International Criteria for Behçet’s Disease (ICBD): a collaborative study of 27 countries on the sensitivity and specificity of the new criteria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28(3):338–47.
Davatchi F. Behcet’s disease. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014;17(4):355–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12378.
Park UC, Kim TW, Yu HG. Immunopathogenesis of ocular Behçet’s disease. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:653539. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/653539.
Morton LT, Situnayake D, Wallace GR. Genetics of Behçet’s disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(1):39–44.
Kalayciyan A, Zouboulis C. An update on Behçet’s disease. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21(1):1–10.
D’aiuto F, Parkar M, Brett P, Ready D, Tonetti M. Gene polymorphisms in pro-inflammatory cytokines are associated with systemic inflammation in patients with severe periodontal infections. Cytokine. 2004;28(1):29–34.
Remmers EF, Cosan F, Kirino Y, Ombrello MJ, Abaci N, Satorius C, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MHC class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behcet’s disease. Nat Genet. 2010;42(8):698–702.
Akman A, Ekinci NC, Kacaroglu H, Yavuzer U, Alpsoy E, Yegin O. Relationship between periodontal findings and specific polymorphisms of interleukin-1α and-1β in Turkish patients with Behçet’s disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 2008;300(1):19–26.
Schäfer AS, van der Velden U, Laine ML, Loos BG. Genetic susceptibility to periodontal disease: new insights and challenges. In Lang NP, Lindhe J, editors, Clinical periodontology and implant dentistry. - Volume 1: basic concepts. Chichester: Wiley Blackwell. 2015;290–310.
Loos BG, Van Dyke TE. The role of inflammation and genetics in periodontal disease. Periodontology 2000. 2020;83(1):26–39.
Mumcu G, Ergun T, Elbir Y, Eksioglu-Demiralp E, Yavuz S, Atalay T, et al. Clinical and immunological effects of azithromycin in Behcet’s disease. J Oral Pathol Med. 2005;34(1):13–6.
Yurdakul S, Yazici H. Behçet’s syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008;22(5):793–809.
Galeone M, Colucci R, D’Erme AM, Moretti S, Lotti T. Potential infectious etiology of Behçet’s disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012;2012:595380. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/595380.
Mumcu G, Inanc N, Yavuz S, Direskeneli H. The role of infectious agents in the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and treatment strategies in Behçet’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25(4 Suppl 45):S27-33.
Tanaka T, Yamakawa N, Koike N, Suzuki J, Mizuno F, Usui M. Behçet’s disease and antibody titers to various heat-shock protein 60s. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 1999;7(2):69–74.
Perazzio SF, Andrade LE, De Souza AW. Understanding Behçet’s disease in the context of innate immunity activation. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 586558.
Türsen U. Pathophysiology of the Behçet’s disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012;2012:493015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/493015.
Nakae K, Agata T, Maeda K, Masuda K, Hashimoto T, Inaba G, editors. Behcet’s disease, pathogenic mechanism and clinical future: case control studies on Behcet’s disease. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press; 1981.
Çelenligil-Nazliel H, Kansu E, Ebersole JL. Periodontal findings and systemic antibody responses to oral microorganisms in Behçet’s disease. J Periodontol. 1999;70(12):1449–56.
Löe H, Theilade E, Jensen SB. Experimental gingivitis in man. J Periodontol. 1965;36(3):177–87.
Akman A, Kacaroglu H, Donmez L, Bacanli A, Alpsoy E. Relationship between periodontal findings and Behcet’s disease: a controlled study. J Clin Periodontol. 2007;34(6):485–91.
Arabaci T, Kara C, Çiçek Y. Relationship between periodontal parameters and Behçet’s disease and evaluation of different treatments for oral recurrent aphthous stomatitis. J Periodontal Res. 2009;44(6):718–25.
Habibagahi Z, Khorshidi H, Hekmati S. Periodontal health status among patients with Behçet’s disease. Scientifica. 2016;2016:7506041. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7506041.
Bokhari SAH, Khan AA, Butt AK, Hanif M, Izhar M, Tatakis DN, et al. Periodontitis in coronary heart disease patients: strong association between bleeding on probing and systemic biomarkers. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41(11):1048–54.
Tonetti MS, Greenwell H, Kornman KS. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45:S149–61.
Lang NP, Adler R, Joss A, Nyman S. Absence of bleeding on probing an indicator of periodontal stability. J Clin Periodontol. 1990;17(10):714–21.
Lehner T. The role of heat shock protein, microbial and autoimmune agents in the aetiology of Behget’s disease. Int Rev Immunol. 1997;14(1):21–32.
Coit P, Mumcu G, Ture-Ozdemir F, Unal AU, Alpar U, Bostanci N, et al. Sequencing of 16S rRNA reveals a distinct salivary microbiome signature in Behcet’s disease. Clin Immunol. 2016;169:28–35.
Calgüneri M, Ertenli I, Kiraz S, Erman M, Celik I. Effect of prophylactic benzathine penicillin on mucocutaneous symptoms of Behçet’s disease. Dermatology. 1996;192(2):125–8.
Karacayli U, Mumcu G, Simsek I, Pay S, Kose O, Erdem H, et al. The close association between dental and periodontal treatments and oral ulcer course in behcet’s disease: a prospective clinical study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38(5):410–5.
Mizushima Y, Matsuda T, Hoshi K, Ohno S. Induction of Behçet’s disease symptoms after dental treatment and streptococcal antigen skin test. J Rheumatol. 1988;15(6):1029–30.
İris M, Özçıkmak E, Aksoy A, Alibaz-Öner F, İnanç N, Ergun T, et al. The assessment of contributing factors to oral ulcer presence in Behçet’s disease: dietary and non-dietary factors. Eur J Rheumatol. 2018;5(4):240.
Morikawa S, Ouchi T, Asoda S, Horie N, Tsunoda K, Kawana H, et al. Treatment of severe generalized chronic periodontitis in a patient with Behçet’s disease: a case report. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(5):2037–45.
Lee Y, Lee S, Choi J, Lee J, Chae H, Kim J, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and mortality of Adamantiades-Behçet’s disease in Korea: a nationwide, population-based study (2006–2015). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(6):999–1003.
Wakabayashi T, Morimura Y, Miyamoto Y, Okada AA. Changing patterns of intraocular inflammatory disease in Japan. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2003;11(4):277–86.
Yoshida A, Kawashima H, Motoyama Y, Shibui H, Kaburaki T, Shimizu K, et al. Comparison of patients with Behçet’s disease in the 1980s and 1990s. Ophthalmology. 2004;111(4):810–5.
Yalçındağ FN, Özdal PC, Özyazgan Y, Batıoğlu F, Tugal-Tutkun I, Group BS. Demographic and clinical characteristics of uveitis in Turkey: the first national registry report. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2018;26(1):17–26.
Kazokoglu H, Onal S, Tugal-Tutkun I, Mirza E, Akova Y, Özyazgan Y, et al. Demographic and clinical features of uveitis in tertiary centers in Turkey. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2008;15(5):285–93.
Mumcu G, Öner FA, Ergun SAT, Direskeneli RH. Decreasing incidence and severity of Behçet’s disease: a changing trend inepidemiological spectrum possibly associated with oral health. Turk J Med Sci. 2020;50(10):1587–90.
Yay M, Çelik Z, Aksoy A, Alibaz-Öner F, Inanç N, Ergun T, et al. Oral health is a mediator for disease severity in patients with Behçet’s disease: a multiple mediation analysis study. J Oral Rehabil. 2019;46(4):349–54.
Volle G, Fraison JB, Gobert D, Goulenok T, Dhote R, Fain O, et al. Dietary and nondietary triggers of oral ulcer recurrences in Behçet’s disease. Arthritis Care Res. 2017;69(9):1429–36.
Mumcu G, Inanc N, Ergun T, Ikiz K, Gunes M, Islek U, et al. Oral health related quality of life is affected by disease activity in Behçet’s disease. Oral Dis. 2006;12(2):145–51.
Schenkein HA, Papapanou PN, Genco R, Sanz M. Mechanisms underlying the association between periodontitis and atherosclerotic disease. Periodontology 2000. 2020;83(1):90–106.
Genco RJ, Van Dyke TE. Reducing the risk of CVD in patients with periodontitis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010;7(9):479–80.
D’Aiuto F, Orlandi M, Gunsolley JC. Evidence that periodontal treatment improves biomarkers and CVD outcomes. J Periodontol. 2013;84:S85–105.
H. Bokhari SA, Khan AA, Butt AK, Azhar M, Hanif M, Izhar M, et al. Non-surgical periodontal therapy reduces coronary heart disease risk markers: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(11):1065–74.
Paraskevas S, Huizinga JD, Loos BG. A systematic review and meta-analyses on C-reactive protein in relation to periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35(4):277–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2007.01173.x.
de Oliveira C, Watt R, Hamer M. Toothbrushing, inflammation, and risk of cardiovascular disease: results from Scottish Health Survey. BMJ. 2010;340:c2451. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c2451.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
No animal or human subjects by the authors were used in this study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aydındoğan, S., Velioğlu, E.M. & Hakkı, S.S. Behçet’s Disease and Periodontal Disease. Curr Oral Health Rep 10, 52–58 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40496-023-00332-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40496-023-00332-5