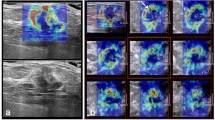
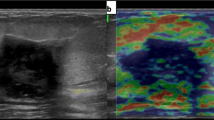
Abstract
Study aims
We sought to evaluate the diagnostic performance of quantitative elastography (shear wave elastography) and to establish the optimal cutoff value to differentiate malignant and benign breast lesions using QelaXtoTM software.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective observational study of adult women with suspicious breast lesions (BIRADS 3, 4 or 5) who underwent programmed ultrasound-guided core biopsies. Breast lesions were assessed using quantitative elastography combined with B-mode ultrasound. Histopathology was used as reference standard. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were estimated, and a ROC curve analysis was conducted. Three elastography cutoff values were considered: 36, 50 and 80 kPa.
Results
We included 143 women (mean age of 56 years) with a total of 145 breast lesions: 68 benign tumors (47.26%) and 77 malignancies (52.74%). Mean elasticity measurements of benign and malignant lesions were significantly different (24.6 kPa, SD 28.47, vs. 101.49 kPa, SD 47.38, \(p<0.0001\)). Using the 50 kPa cutoff, elastography showed a global sensitivity of 87% to discriminate malignant lesions (AUC = 0.897). Moreover, sensitivity was 90.7% when lesions were located 5–40 mm below the skin surface (optimal elastographic field of view). Our false positive rate was 17.65%, comprised mainly of fibroepithelial neoplasms, fibroadenomas and fibrosis.
Conclusions
Quantitative elastography can differentiate malignant and benign breast lesions with acceptable to excellent performance. In our sample, the QelaXtoTM software showed a lower optimal cutoff than other ultrasound systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For example, Lee et al. informed that the elastographic values for malignant masses were on average 119.0 (\(\pm 52.2\)) kPa and the benign lesions were 41.4 (\(\pm 32.1\)) kPa, whereas the elastographic values published by Chang et al. were slightly superior. The malignant masses had a medium elasticity of 153.3 (\(\pm 58.1\)) kPa and the benign, 46.1 (\(\pm 42.9\) kPa).
References
Garra BS, Cespedes EI, Ophir J et al (1997) Elastography of breast lesions: initial clinical results. Radiology 202(1):79–86
Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E et al (2006) Breast disease: clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology 239(2):341–350
Sigrist RMS, Liau J, Kaffas AE, Chammas MC, Willmann JK (2017) Ultrasound elastography: review of techniques and clinical applications. Theranostics 7(5):1303–1329
Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF et al (2013) EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: basic principles and technology. Ultraschall Med 34(2):169–184
Ricci P, Maggini E, Mancuso E et al (2014) Clinical application of breast elastography: state of the art. Eur J Radiol 83(3):429–437
Barr RG, Managuli RA (2019) A clinical study comparing the diagnostic performance of assist strain ratio against manual strain ratio in ultrasound breast elastography. Ultrasound Q 35(1):82–87
Barr RG, Zhang Z (2015) Shear-wave elastography of the breast: value of a quality measure and comparison with strain elastography. Radiology 275(1):45–53
Suvannarerg V, Chitchumnong P, Apiwat W et al (2019) Diagnostic performance of qualitative and quantitative shear wave elastography in differentiating malignant from benign breast masses, and association with the histological prognostic factors. Quant Imaging Med Surg 9(3):386–398
Athanasiou A, Tardivon A, Tanter M et al (2010) Breast lesions: quantitative elastography with supersonic shear imaging-preliminary results. Radiology 256(1):297–303
Tozaki M, Fukuma E (2011) Pattern classification of ShearWave\(^{{\rm TM}}\) elastography images for differential diagnosis between benign and malignant solid breast masses. Acta radiol 52(10):1069–1075
Chang JM, Moon WK, Cho N et al (2011) Clinical application of shear wave elastography (SWE) in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129(1):89–97
Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K et al (2010) Quantitative shear wave ultrasound elastography: initial experience in solid breast masses. Breast Cancer Res 12(6):R104
Berg WA, Cosgrove DO, Doré CJ et al (2012) Shear-wave elastography improves the specificity of breast US: the BE1 multinational study of 939 masses. Radiology 262(2):435–449
Lee SH, Chang JM, Kim WH et al (2014) Added value of shear-wave elastography for evaluation of breast masses detected with screening US imaging. Radiology 273(1):61–69
Au FWF, Ghai S, Moshonov H et al (2014) Diagnostic performance of quantitative shear wave elastography in the evaluation of solid breast masses: determination of the most discriminatory parameter. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203(3):W328–36
Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K et al (2012) Differentiating benign from malignant solid breast masses: value of shear wave elastography according to lesion stiffness combined with greyscale ultrasound according to BI-RADS classification. Br J Cancer 107(2):224–229
Erdoğan H, Durmaz MS, Özbakır B et al (2020) Experience of using shear wave elastography in evaluation of testicular stiffness in cases of male infertility. J Ultrasound. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00430-5
Kara T, Ateş F, Durmaz MS et al (2020) Assessment of thyroid gland elasticity with shear-wave elastography in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis patients. J Ultrasound. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00437-y
Paternostro R, Reiberger T, Bucsics T (2019) Elastography-based screening for esophageal varices in patients with advanced chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 25(3):308–329. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i3.308
Ozgokce M, Batur M, Alpaslan M et al (2019) A comparative evaluation of cataract classifications based on shear-wave elastography and B-mode ultrasound findings. J Ultrasound 22(4):447–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-019-00400-6
Gheonea IA, Stoica Z, Bondari S (2011) Differential diagnosis of breast lesions using ultrasound elastography. Indian J Radiol Imaging 21(4):301–305
Liu B, Zheng Y, Huang G et al (2016) Breast lesions: quantitative diagnosis using ultrasound shear wave elastography—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med Biol 42(4):835–847
Luo J, Cao Y, Nian W et al (2018) Benefit of shear-wave elastography in the differential diagnosis of breast lesion: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Med Ultrason 1(1):43–49
Xue Y, Yao S, Li X, Zhang H (2017) Value of shear wave elastography in discriminating malignant and benign breast lesions: a meta-analysis. Medicine 96(42):e7412
American College of Radiology (2013) ACR BI-RADS Atlas: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Mammography, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Follow-up and Outcome Monitoring, Data Dictionary
Kim MY, Choi N, Yang JH, Yoo YB, Park KS (2015) False positive or negative results of shear-wave elastography in differentiating benign from malignant breast masses: analysis of clinical and ultrasonographic characteristics. Acta Radiol 56(10):1155–1162
Yoon JH, Jung HK, Lee JT, Ko KH (2013) Shear-wave elastography in the diagnosis of solid breast masses: what leads to false-negative or false-positive results? Eur Radiol 23(9):2432–2440
Alikhassi A, Azizi F, Ensani F (2020) Imaging features of granulomatous mastitis in 36 patients with new sonographic signs. J Ultrasound 23(1):61–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-019-00392-3
Carlino G, Rinaldi P, Giuliani M et al (2019) Ultrasound-guided preoperative localization of breast lesions: a good choice. J Ultrasound 22(1):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-018-0335-0
Funding
This Study was founded by the Radiology Department of the Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
This study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 and its late amendments. The study protocol was approved by the institutional Ethics Committee, with IRB approval number 3797.
Informed consent
As we worked with de-identified retrospective data, informed consent was waived for this retrospective study.
Consent for publication
All authors expressed explicit consent for the publication of this manuscript.
Code availability
Data-analysis code is available upon request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pesce, K., Binder, F., Chico, M.J. et al. Diagnostic performance of shear wave elastography in discriminating malignant and benign breast lesions. J Ultrasound 23, 575–583 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00481-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00481-8