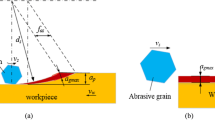
Abstract
Grinding with cubic boron nitride (CBN) superabrasive is a widely used method of machining superalloy in aerospace industries. However, there are some issues, such as poor grinding quality and severe tool wear, in grinding of powder metallurgy superalloy FGH96. In addition, abrasive wheel wear is the significant factor that hinders the further application of CBN abrasive wheels. In this case, the experiment of grinding FGH96 with single CBN abrasive grain using different parameters was carried out. The wear characteristics of CBN abrasive grain were analyzed by experiment and simulation. The material removal behavior affected by CBN abrasive wear was also studied by discussing the pile-up ratio during grinding process. It shows that morphological characteristics of CBN abrasive grain and grinding infeed direction affect the CBN abrasive wear seriously by simulation analysis. Attrition wear, micro break, and macro fracture had an important impact on material removal characteristics. Besides, compared with the single cutting edge, higher pile-up ratio was obtained by multiple cutting edges, which reduced the removal efficiency of the material. Therefore, weakening multiple cutting edge grinding on abrasive grains in the industrial production, such as applying suitable dressing strategy, is an available method to improve the grinding quality and efficiency.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai M, Gong YD, Sun Y et al (2019) Experimental study on grinding surface properties of nickel-based single crystal superalloy DD5. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 101:71–85
Miao Q, Ding WF, Kuang WJ et al (2020) Comparison on grindability and surface integrity in creep feed grinding of GH4169, K403, DZ408 and DD6 nickel-based superalloys. J Manuf Process 49:175–186
Ge YC, Zhu ZW, Ma Z et al (2018) Tool design and experimental study on electrochemical turning of nickel-based cast superalloy. J Electrochem Soc 165(5):E162–E170
Qian N, Ding WF, Zhu YJ (2018) Comparative investigation on grindability of K4125 and Inconel 718 nickel-based superalloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97(5):1649–1661
Jamshidi H, Budak E (2020) An analytical grinding force model based on individual grit interaction. J Mater Process Technol 283:116700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116700
Duan P, Zhang P, Li J et al (2019) Intermediate temperature brittleness in a directionally solidified nickel-based superalloy M4706. Mater Sci Eng A 759:530–536
Zhao ZC, Qian N, Ding WF et al (2020) Profile grinding of DZ125 nickel-based superalloy: grinding heat, temperature field, and surface quality. J Mater Process Technol 57:10–22
Shu DL, Tian SG, Tian N et al (2017) Thermodynamic analysis of carbide precipitation and effect of its configuration on creep properties of FGH95 powder nickel-based superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A 700:152–161
Huang XH, Zou F, Ming WW et al (2020) Wear mechanisms and effects of monolithic Sialon ceramic tools in side milling of superalloy FGH96. Ceram Int 46(17):26813–26822
Wang ZM, Wang HN, Li X et al (2020) Surface integrity of powder metallurgy superalloy FGH96 affected by grinding with electroplated CBN wheel. Procedia CIRP 87:204–209
Xu DD, Liao ZR, Axinte D et al (2020) Investigation of surface integrity in laser-assisted machining of nickel based superalloy. Mater Des 194:108851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108851
Zhang BY, Zeng YN, Pang XQ et al (2022) Feasibility analysis and process characteristics of selective laser ablation assisted milling Inconel 718. Adv Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-021-00384-9
Thakur A, Gangopadhyay S (2016) State-of-the-art in surface integrity in machining of nickel-based super alloys. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 100:25–54
Shi Y, Wang ZH, Xu SZ et al (2019) Study on the grindability of nano-vitrified bond CBN grinding wheel for nickel-based alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100(5):1913–1921
Dai CW, Ding WF, Zhu YJ et al (2018) Grinding temperature and power consumption in high speed grinding of Inconel 718 nickel-based superalloy with a vitrified CBN wheel. Precis Eng 52:192–200
Ichida Y (2001) Creep feed profile grinding of Ni-based superalloys with ultrafine-polycrystalline cBN abrasive grits. Precis Eng 25(4):274–283
Herman D, Krzos J (2009) Influence of vitrified bond structure on radial wear of cBN grinding wheels. J Mater Process Technol 209(14):5377–5386
Zhang SQ, Yang ZX, Jiang RS et al (2021) Effect of creep feed grinding on surface integrity and fatigue life of Ni3Al based superalloy IC10. Chin J Aeronaut 34(1):438–448
Yu T, Bastawros AF, Chandra A (2017) Experimental and modeling characterization of wear and life expectancy of electroplated CBN grinding wheels. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 121:70–80
Zhu YJ, Ding WF, Yu TY et al (2017) Investigation on stress distribution and wear behavior of brazed polycrystalline cubic boron nitride superabrasive grains: numerical simulation and experimental study. Wear 376:1234–1244
Wang HN, Li X, Wang ZM et al (2020) Influence of electroplated CBN wheel wear on grinding surface morphology of powder metallurgy superalloy FGH96. Materials 13(4):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13041005
Bazan A, Kawalec A, Rydzak T et al (2020) Variation of grain height characteristics of electroplated CBN grinding-wheel active surfaces associated with their wear. Metals 10(11):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10111479
Bazan A, Kawalec A, Rydzak T et al (2020) Determination of selected texture features on a single-layer grinding wheel active surface for tracking their changes as a result of wear. Materials 14(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010006
Butler DL, Blunt LA, See BK et al (2002) The characterisation of grinding wheels using 3D surface measurement techniques. J Mater Process Technol 127(2):234–237
Xie J, Xu J, Tang Y et al (2008) 3D graphical evaluation of micron-scale protrusion topography of diamond grinding wheel. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48(11):1254–1260
Zhao ZC, Fu YC, Xu JH et al (2016) Behavior and quantitative characterization of CBN wheel wear in high-speed grinding of nickel-based superalloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(9):3545–3555
Li BK, Yin JF, Zhu YJ et al (2021) Grain wear evolution of cubic boron nitride abrasives during single grain grinding of powder metallurgy superalloy FGH96. Ceram Int 47(2):2508–2516
Ghosh A, Chattopadhyay AK (2007) Experimental investigation on performance of touch-dressed single-layer brazed cBN wheels. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(7/8):1206–1213
Zhang C, Shin YC (2003) Wear of diamond dresser in laser assisted truing and dressing of vitrified CBN wheels. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(1):41–49
Zhang M, Li F, Yuan Z et al (2013) Effect of heat treatment on the micro-indentation behavior of powder metallurgy nickel based superalloy FGH96. Mater Des 49:705–715
Chen SY, Wei DS, Wang JL et al (2019) Experimental and modeling investigation of the creep-fatigue interactive deformation behavior of PM super alloy FGH96 at evaluated temperature. Mater Sci Eng A 749:106–117
Wang FW, Chen YL, Gao Y et al (2021) Peridynamic simulation to fracture mechanism of CBN grain in the honing wheel dressing process. Micromachines 12(10):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12101186
Dai JB, Su HH, Hu H et al (2017) The influence of grain geometry and wear conditions on the material removal mechanism in silicon carbide grinding with single grain. Ceram Int 43(15):11973–11980
Zhu YJ, Ding WF, Rao ZW et al (2019) Effect of grinding wheel speed on self-sharpening ability of PCBN grain during grinding of nickel-based superalloys with a constant undeformed chip thickness. Wear 426/427:1573–1583
Ghosh S, Chattopadhyay AB, Paul S (2008) Modelling of specific energy requirement during high-efficiency deep grinding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48(11):1242–1253
Xiao GD, Zhao B, Ding WF et al (2021) On the grinding performance of metal-bonded aggregated cBN grinding wheels based on open-pore structures. Ceram Int 47(14):19709–19715
Dai CW, Ding WF, Xu JH et al (2017) Influence of grain wear on material removal behavior during grinding nickel-based superalloy with a single diamond grain. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 113:49–58
Fang SQ (2020) Morphological study of a cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting tool and characterization of its wear scenarios in abrasive machining process. Ceram Int 46(11):19491–19498
Li BK, Miao Q, Li M et al (2020) An investigation on machined surface quality and tool wear during creep feed grinding of powder metallurgy nickel-based superalloy FGH96 with alumina abrasive wheels. Adv Manuf 8:160–176
Öpöz TT, Chen X (2012) Experimental investigation of material removal mechanism in single grit grinding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 63:32–40
Shi Z, Malkin S (2006) Wear of electroplated CBN grinding wheels. J Manuf Sci Eng 128(1):110–118
Linke BS (2015) Review on grinding tool wear with regard to sustainability. J Manuf Sci Eng 137(6):060801. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4029399
Öpöz TT, Chen X (2015) Experimental study on single grit grinding of Inconel 718. Proc I Mech E Part B J Eng Manuf 229(5):713–726
Yang M, Li CH, Zhang YB et al (2019) Predictive model for minimum chip thickness and size effect in single diamond grain grinding of zirconia ceramics under different lubricating conditions. Ceram Int 45(12):14908–14920
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 92160301, 52175415), Major Special Projects of Aero-engine and Gas Turbine (Grant No. 2017-VII-0002-0095), and Funding for Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation in NUAA (Grant No. BCXJ19-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, BK., Zhao, B., Ding, WF. et al. CBN grain wear and its effects on material removal during grinding of FGH96 powder metallurgy superalloy. Adv. Manuf. 11, 21–38 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-022-00412-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-022-00412-2