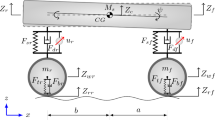
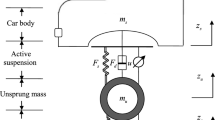
Abstract
In this paper, a new adaptive sliding mode controller using an enhanced disturbance observer is proposed for active suspension. For acquiring the knowledge of the states, the use of sensors is avoided to reduce the designing cost. Instead of it, an ensemble Kalman filter is used for estimating the states. Chattering in the traditional sliding mode control method is minimized by introducing a continuous term in switching function. An enhanced nonlinear disturbance observer is designed to ensure the robustness of the proposed controller. Through rigorous analysis, the stability is proved using the Lyapunov method. To demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed controller, it is subjected to different road profiles in simulation and experimental setups.





































Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SMD:
-
Sprung mass displacement
- SMV:
-
Sprung mass velocity
- SMA:
-
Sprung mass acceleration
- UMD:
-
Unsprung mass displacement
- UMV:
-
Unsprung mass velocity
- RSD:
-
Relative suspension deflection
- RTD:
-
Relative tyre force
- SMC:
-
Sliding mode control
- ENKF:
-
Ensemble Kalman filter
- ENDO:
-
Enhanced nonlinear disturbance observer
References
Garrido H, Curadelli O, Ambrosini D (2018) On the assumed inherent stability of semi-active control systems. Eng Struct 159:286–298
Funde J, Wani K, Dhote ND, Patil SA (2019) Performance analysis of semi-active suspension system based on suspension working space and dynamic tire deflection. In: Innovative design, analysis and development practices in aerospace and automotive engineering (I-DAD), vol 2019. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–15
Zhang X-L, Zhang T, Nie J, Chen L (2018) A semiactive skyhook-inertance control strategy based on continuously adjustable inerter. Shock Vib 2018:1–8
Sun W, Pan H, Gao H (2016) Filter-based adaptive vibration control for active vehicle suspensions with electrohydraulic actuators. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 65(6):4619–4626
Choi HD, Ahn CK, Lim MT, Song MK (2016) Dynamic output-feedback h8 control for active half-vehicle suspension systems with time-varying input delay. Int J Control Autom Syst 14(1):59–68
Rizvi SMH, Abid M, Khan AQ, Satti SG, Latif J (2018) H8 control of 8 degrees of freedom vehicle active suspension system. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 30(2):161–169
Erol B, Delibaşı A (2018) Proportional-integral-derivative type h8 controller for quarter car active suspension system. J Vib Control 24(10):1951–1966
Jing H, Wang R, Li C, Bao J (2019) Robust finite-frequency h8 control of full-car active suspension. J Sound Vib 441:221–239
Zhang H, Zheng X, Yan H, Peng C, Wang Z, Chen Q (2017) Codesign of event-triggered and distributed h infintity filtering for active semi-vehicle suspension systems. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 22(2):1047–1058
Pan H, Jin X, Sun W, Gao H (2017) A bioinspired dynamics-based adaptive tracking control for nonlinear suspension systems. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 26(5):903–914
Wu Z, Jing H, Gao X, Bian J, Li F, Allen R (2015) Vibration isolation by exploring bio-inspired structural nonlinearity. Bioinspir Biomim 10(5):056015
Ebrahimi F, Hashemabadi D, Habibi M, Safarpour H (2020) Thermal buckling and forced vibration characteristics of a porous GNP reinforced nanocomposite cylindrical shell. Microsyst Technol 26(2):461–473
SafarPour H, Mohammadi K, Ghadiri M, Rajabpour A (2017) Influence of various temperature distributions on critical speed and vibrational characteristics of rotating cylindrical microshells with modified lengthscale parametery. Eur Phys J Plus 132(6):281
Chen S-A, Wang J-C, Yao M, Kim Y-B (2017) Improved optimal sliding mode control for a non-linear vehicle active suspension system. J Sound Vib 395:1–25
Wang H, Mustafa GI, Tian Y (2018) Model-free fractional-order sliding mode control for an active vehicle suspension system. Adv Eng Softw 115:452–461
Liu Y, Zeng Q, Liu L, Tong S (2018) An Adaptive Neural Network Controller for Active Suspension Systems With Hydraulic Actuator. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2018.2875187
Liu S, Zhou H, Luo X, Xiao J (2016) Adaptive sliding fault tolerant control for nonlinear uncertain active suspension systems. J Frankl Inst 353(1):180–199
Rath JJ, Defoort M, Karimi HR, Veluvolu KC (2017) Output feedback active suspension control with higher order terminal sliding mode. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(2):1392–1403
Ozer HO, Hacioglu Y, Yagiz N (2018) High order sliding mode control with estimation for vehicle active suspensions. Trans Inst Meas Control 40(5):1457–1470
Lin B, Su X, Li X (2019) Fuzzy sliding mode control for active suspension system with proportional differential sliding mode observer. Asian J Control 21(1):264–276
Pang H, Liu F, Xu Z (2018) Variable universe fuzzy control for vehicle semi-active suspension system with mr damper combining fuzzy neural network and particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 306:130–140
Huang Y, Na J, Wu X, Gao G (2018) Approximation-free control for vehicle active suspensions with hydraulic actuator. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(9):7258–7267
Deshpande VS, Mohan B, Shendge P, Phadke S (2014) Disturbance observer based sliding mode control of active suspension systems. J Sound Vib 333(11):2281–2296
Ning D, Sun S, Zhang F, Du H, Li W, Zhang B (2017) Disturbance observer based takagi-sugeno fuzzy control for an active seat suspension. Mech Syst Signal Process 93:515–530
Lee K-T, Dai M-J, Chuang C-C (2018) Temperature-compensated model for lithium-ion polymer batteries with extended kalman filter state-of-charge estimation for an implantable charger. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(1):589–596
Fan R, Liu Y, Huang R, Diao R, Wang S (2018) Precise fault location on transmission lines using ensemble kalman filter. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 33(6):3252–3255
Pan H, Sun W, Gao H, Yu J (2015) Finite-time stabilization for vehicle active suspension systems with hard constraints. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 16(5):2663–2672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meetei, L.V., Das, D.K. Enhanced nonlinear disturbance observer based sliding mode control design for a fully active suspension system. Int. J. Dynam. Control 9, 971–984 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-020-00682-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-020-00682-3