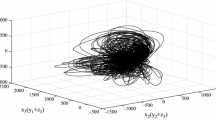
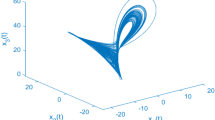
Abstract
This manuscript presents a theoretical and numerical analysis to achieve compound synchronization of four non-identical chaotic systems for different multi-switching states. Multi-switching compound synchronization is achieved for three drive systems and one response system via active backstepping technique. By using Lyapunov stability theory, asymptotically stable synchronization states are established. To elaborate the considered scheme an example of Pehlivan system, Liu system, Qi system and Lu system is discussed. The conclusions drawn from computational and analytical approaches are in excellent agreement.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shibasaki N, Uchida A, Yoshimori S, Davis P (2006) Characteristics of chaos synchronization in semiconductor lasers subject to polarization-rotated optical feedback. IEEE J Quantum Electron 42(3):342–350
Lu H, Leeuwen CV (2006) Synchronization of chaotic neural networks via output or state coupling. Chaos Solitons Fractals 30(1):166–176
Blasius B, Stone L (2000) Chaos and phase synchronization in ecological systems. Int J Bifurc Chaos 10(10):2361–2380
Li C, Liao X, Wong K (2004) Chaotic lag synchronization of coupled time-delayed systems and its applications in secure communication. Phys D 194(3–4):187–202
Moskalenko OI, Koronovskii AA, Hramov AE (2010) Generalized synchronization of chaos for secure communication: remarkable stability to noise. Phys Lett A 374(29):2925–2931
Li Z, Xu D (2004) A secure communication scheme using projective chaos synchronization. Chaos Solitons Fractals 22(2):477–481
Wu X, Li S (2012) Dynamics analysis and hybrid function projective synchronization of a new chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn 69(4):1979–1994
Haeri M, Emadzadeh AA (2007) Synchronizing different chaotic systems using active sliding mode control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 31(1):119–129
Feng G, Cao J (2013) Master-slave synchronization of chaotic systems with modified impulsive controller. Adv Differ Equ 2013:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2013-24
Al-sawalha MM, Noorani MSM (2010) Adaptive reduced-order anti-synchronization of chaotic systems with fully unknown parameters. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15(10):3022–3034
Pecora LM, Carroll TL (1990) Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys Rev Lett 64(8):821–824
Runzi L, Yinglan W, Shucheng D (2011) Combination synchronization of three classic chaotic systems using active backstepping design. Chaos 21:043114. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3655366
Lin H, Cai J, Wang J (2013) Finite-Time combination-combination synchronization for hyperchaotic systems. J Chaos 2013, Article ID 304643. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/304643
Sun J, Wang Y, Wang Y, Cui G, Shen Y (2016) Compound-combination synchronization of five chaotic systems via nonlinear control. Optik 127(8):4136–4143
Ojo KS, Njah AN, Olusula OI (2015) Compound-combination synchronization of chaos in identical and different orders chaotic system. Arch Control Sci 25(LXI):463–490
Wu A, Zhang J (2014) Compound synchronization of fourth-order memristor oscillator. Adv Differ Equ 2014:100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2014-100
Zhang B, Deng F (2014) Double-Compound Synchronization of six memristor-based Lorenz Systems. Nonlinear Dyn 77(4):1519–1530
Sun J, Yin Q, Shen Y (2014) Compound synchronization for four chaotic systems of integer order and fractional order. Europhys Lett 106(4):40005
Runzi L, Yinglan W (2012) Finite time stochastic combination synchronization of three different chaotic systems and its application in secure communication. Chaos 22:023109. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3702864
Sun J, Shen Y, Yin Q, Xu C (2013) Compound synchronization of four memristor chaotic oscillator systems and secure communication. Chaos 23:013140. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4794794
Ucar A, Lonngren KE, Bai EW (2008) Multi-switching synchronization of chaotic systems with active controllers. Chaos Solitons Fractals 38(1):254–262
Wang X, Sun P (2011) Multi-switching synchronization of chaotic system with adaptive controllers and unknown parameters. NonLinear Dyn 63(4):599–609
Ajayi AA, Ojo SK, Vincent UE, Njah NA (2014) Multiswitching synchronization of a driven hyperchaotic circuit using active backstepping. J Nonlinear Dyn 2014, Article ID 918586. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/918586
Vincent UE, Saseyi AO, McClintock PVE (2015) Multi-switching combination synchronization of chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dyn 80(1–2):845–854
Zheng S (2016) Multi-switching combination synchronization of three different chaotic systems via active nonlinear control. Optik 127(21):10247–10258
Ojo KS, Njah AN, Olusola OI, Omeike MO (2014) Generalized reduced-order hybrid combination synchronization of three Josephson junctions via backstepping technique. Nonlinear Dyn 77(3):583–595
Wu Z, Fu X (2013) Combination synchronization of three different order nonlinear systems using active backstepping design. Nonlinear Dyn 73(3):1863–1872
Pehlivan I, Uyarolu Y (2010) A new chaotic attractor from general Lorenz system family and its electronic experimental implementation. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 18(2):171–184
Liu C, Liu T, Liu L, Liu K (2004) A new chaotic attractor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 22(5):1031–1038
Qi G, Chen G, Van Wyk MA, Van Wyk BJ, Zhang Y (2008) A four wing chaotic attractor generated from a new 3-D quadratic autonomous system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 38(3):705–721
Lu J, Chen G (2002) A new chaotic attractor coined. Int J Bifurc Chaos 12(3):659–661
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Budhraja, M. & Ibraheem, A. Multi-switching compound synchronization of four different chaotic systems via active backstepping method. Int. J. Dynam. Control 6, 1126–1135 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-017-0365-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-017-0365-z