Abstract
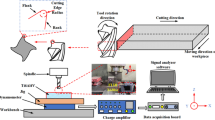
It is consolidated that the machining of titanium alloys poses obstacles due to their low machinability, which can cause surface problems in the machined components and compromise their performance in different applications. In order to generate better surface finishes, published works focus mainly on the correct choice of cutting conditions, regardless of the cutting tool, which has a considerable influence on surface roughness. Bearing this in mind, the present paper aims to determine the effect of the geometry (clearance angle and corner radius) of uncoated cemented tungsten carbide cutting inserts on several roughness parameters obtained after turning Ti–15Mo alloy. According to the obtained results, a relevant geometric contribution of the corner radius, whose increase reduced the roughness values, became clear. Material deformation due to bigger corner radii or distinct clearance angles did not significantly influence the roughness parameters. A flat profile, with wide valleys and narrow peaks, was observed in all conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peters M, Hemptenmacher J, Kumpfert J, Leyens C (2003) Structure and properties of titanium and titanium alloys. In: Leyens C, Peters M (eds) Titanium and titanium alloys: fundamentals and applications. Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim, pp 1–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/3527602119.ch1
Koizumi H, Takeuchi Y, Imai H, Kawai T, Yoneyama T (2019) Application of titanium and titanium alloys to fixed dental prostheses. J Prosthod Res 63:266–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpor.2019.04.011
Boyer RR, Briggs RD (2005) The use of β titanium alloys in the aerospace industry. J Mater Eng Perform 14:681–685. https://doi.org/10.1361/105994905x75448
Zlatin N, Field M (1973) Procedures and precautions in machining titanium alloys. In: Jaffee RI, Burte HM (eds) Titanium science and technology. Springer, Boston, pp 489–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-1346-6_37
Che-Haron CH (2001) Tool life and surface integrity in turning titanium alloy. J Mater Process Technol 118:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/s09240136(01)00926-8
Martins JRS, Nogueira RA, Araújo RO, Donato TAG, Arana-Chavez VE, Claro APRA, Moraes JCS, Buzalaf MAR, Grandini CR (2011) Preparation and characterization of Ti–15Mo alloy used as biomaterial. Mater Res 14:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392011005000013
Gunawarman NM, Akahori T, Souma T, Ikeda M, Toda H, Terashima K (2005) Fatigue characteristics of low cost β titanium alloys for healthcare and medical applications. Mater Trans 46:1570–1577. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.46.1570
Niinomi M, Kuroda D, Fukunaga KI, Morinaga M, Kato Y, Yashiro T, Suzuki A (1999) Corrosion wear fracture of new β type biomedical titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 263:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01167-8
Niinomi M (2003) Recent research and development in titanium alloys for biomedical applications and healthcare goods. Sci Technol Adv Mater 4:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stam.2003.09.002
Key JA (1929) Bone atrophy and absorption. Int J Orthod Oral Surg Radiog 15:949–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0099-6963(29)90381-1
Bagno A, Bello CDJ (2004) Surface treatments and roughness properties of Ti-based biomaterials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:935–949. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:jmsm.000004279.28493.7f
Rich A, Harris AK (1981) Anomalous preferences of cultured macrophages for hydrophobic and roughened substrata. J Cell Sci 50:1–7
Thomas KA, Cook SD (1985) An evaluation of variables influencing implant fixation by direct bone apposition. J Bio Mater Res 19:875–901. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820190802
Sarraf M, Ghomi ER, Alipour S, Ramakrishna S, Sukiman NL (2022) A state-of-the-art review of the fabrication and characteristics of titanium and its alloys for biomedical applications. Bio-Des Manuf 5:371–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-021-00170-3
Albrektsson T, Branemark P-I, Hansson H-A, Kasemo B, Larsson K, Lundström I, McQueen DH, Skalak R (1983) The interface zone of inorganic implants in vivo: titanium implants in bone. Ann Bio Eng 11:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02363944
Conchra D, Simpson J, Weber HP, Buser D (1994) Attachment and growth of periodontal cells on smooth and rough titanium. Int J Oral Maxillofac Imp 9:289–297
Lincks J, Boyan BD, Blanchard CR, Lohmann CH, Liu Y, Cochran DL, Dean D, Schwartz Z (1998) Response of MG63 osteoblast-like cells to titanium and titanium alloy is dependent on surface roughness and composition. Biomater Silver Jubilee Compend. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-008045154-1.50019-8
Albrektsson T, Wenneberg A (2004) Oral implant surfaces: part 1—Review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int J Prosthodont 17:536–543
Wenneberg A, Albrektsson T (2009) Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Imp Res 20:172–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01775.x
Taborelli M, Jobin M, François P, Vaudaux P, Tonetti M, Szmukler-Moncler S, Simpson JP, Descouts P (1997) Influence of surface treatments developed for oral implants on the physical and biological properties of titanium. (I) Surface characterization. Clin Oral Imp Res 8:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.1997.080307.x
Castellani R, de Ruijter A, Renggli H, Jansen J (1999) Response of rat bone marrow cells to differently roughened titanium discs. Clin Oral Imp Res 10:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.1999.100504.x
Che-Haron CH, Jawaid A (2005) The effect of machining on surface integrity of titanium alloy Ti–6%Al–4%V. J Mater Process Technol 166:188–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.08.012
Ribeiro M, Moreira M, Ferreira JR (2003) Optimization of titanium alloy (6Al-4V) machining. J Mater Process Technol 143–144:458–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00457-6
Akkus H, Yaka H (2021) Optimization of cutting parameters in turning of titanium alloy (grade 5) by analyzing surface roughness, tool wear and energy consumption. Exp Tech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-021-00525-6
An QL, Fu YC, Xu JH (2011) Experimental study on turning of TC9 titanium alloy with cold water mist jet cooling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51:549–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2011.03.005
Davis R, Singh A, Jackson MJ, Coelho RT, Prakash D, Charalambous CP, Ahmed W, Silva LRR, Lawrence AA (2022) A comprehensive review on metallic implant biomaterials and their subtractive manufacturing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 120:1473–1530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08770-8
Oliaei SNB, Karpat Y (2016) Investigating the influence of built-up edge on forces and surface roughness in micro scale orthogonal machining of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. J Mater Process Technol 235:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.04.01
Bai J, Bai Q, Tong Z (2018) Experimental and multiscale numerical investigation of wear mechanism and cutting performance of polycrystalline diamond tools in micro-end milling of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 74:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.03.007
García-Martínez E, Miguel V, Martínez-Martínez A, Coello J, Naranjo JA, Manjabacas MC (2022) Optimization of the dry turning process of Ti48Al2Cr2Nb aluminide based on the cutting tool configuration. Mater 15:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041472
Xavior MA, Vinayagamoorthy R (2014) Fuzzy inference system for prediction during precision turning of Ti–6Al–4V. Proc Eng 97:308–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.254
Shah D, Bhavsar S (2020) Effect of tool nose radius and machining parameters on cutting force, cutting temperature and surface roughness—an experimental study of Ti–6Al–4V (ELI). Mater Today: Proc 22:1977–1986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.163
Shah DR, Pancholi N, Gajera H, Patel B (2022) Investigation of cutting temperature, cutting force and surface roughness using multi-objective optimization for turning of Ti–6Al–4 V (ELI). Mater Today Proc 50:1379–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.285
ISO 16610-21 (2011) Geometrical product specifications (GPS)—filtration—part 21: linear profile filters: Gaussian filters
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES) [Grant number: Finance Code 001]; and the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) [Grant numbers: 2015/15622-2, 2017/12309-7, 2017/12304-5, and 2018/24614-1].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Technical Editor: Adriano Fagali de Souza.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paris, D., Rubio, J.C.C., Cruz, D.C. et al. An analysis of the surface roughness of Ti–15Mo alloy machined with uncoated cemented tungsten carbide cutting inserts with different geometries. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 44, 309 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-022-03619-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-022-03619-3