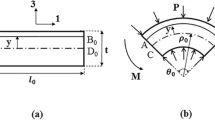
Abstract
Variations in in-plane mixed-mode fracture toughness versus changes in thickness of shear CT (CTS) specimens and loading direction and effects of yield strength of different aluminum alloys have been investigated by experimental testing and numerical analysis. Several samples were made by Al2024-O, Al6061-T6 and Al7075-T6 alloys. Based on the results, increasing the thickness reduces the mixed-mode fracture toughness and near to the critical thickness, this reduction is lesser. Increase in mixed-mode loading angle for brittle materials has not significant effects on the toughness while in softer materials by changing the angle from 15° to 60°, the amount is halved. Near the mode I fracture conditions, there is no meaningful relationship between the yield strength and fracture toughness but with an increase in the second mode effects, these parameters will be proportional. The mixed-mode toughness of the alloys with different thicknesses can be calculated numerically with a precise accuracy by applying failure load in the analysis.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barsom JM, Rolfe ST (1999) Fracture and fatigue control in structures: applications of fracture mechanics. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Seitl S, Hutar P, Garcıa TE, Fernandez-Canteli A (2013) Experimental and numerical analysis of in- and out- of plane constraint effects on fracture parameters: aluminium alloy 2024. Appl Comput Mech 7:53–64
Li J, Zhang X-B, Recho N (2004) J–Mp based criteria for bifurcation assessment of a crack in elastic–plastic materials under mixed mode I–II loading. Eng Fract Mech 71(3):329–343
Kamat SV, Hirth JP (1996) Mixed mode I/II fracture toughness of 2034 aluminum alloys. Acta Mater 44(1):201–208
Pirondi A, Donne CD (2001) Characterisation of ductile mixed-mode fracture with the crack-tip displacement vector. Eng Fract Mech 68(12):1385–1402
Brown EN, Rae PJ, Liu C (2007) Mixed-mode-I/II fracture of polytetrafluoroethylene. Mater Sci Eng A 468–470:253–258
Zhang S, Guo W, Li H, Deng Y (2011) Experimental investigation of three-dimensional mixed-mode fracture of a titanium alloy at room and elevated temperatures. Sci China Technol Sci 54(10):2760
Guo W, Dong H, Yang Z (2008) Experimental investigation of thickness effects on mixed-mode I/II fracture of an aluminum alloy. Cornel University. arXiv:0807.1577v2
Hallbäck N, Jönsson N (1996) T-stress evaluations of mixed mode I/II fracture specimens and T-effects on mixed mode failure of aluminium. Int J Fract 76(2):141–168
Hallbäck N (1997) Mixed-mode I/II fracture behaviour of a high strength steel. Int J Fract 87(4):363–388
Hallbäck N, Nilsson F (1994) Mixed-mode I/II fracture behaviour of an aluminium alloy. J Mech Phys Solids 42:1345–1374
Pearce GM, Tao C, Quek YHE, Chowdhury NT (2018) A modified Arcan test for mixed-mode loading of bolted joints in composite structures. Compos Struct 187:203–211
Fagerholt E, Dørum C, Børvik T, Laukli HI, Hopperstad OS (2010) Experimental and numerical investigation of fracture in a cast aluminium alloy. Int J Solids Struct 47(24):3352–3365
Aliha MRM, Bahmani A (2017) Rock fracture toughness study under mixed mode I/III loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(7):1739–1751
Matvienko YG, Chernyatin AS, Razumovsky IA, Shi HJ, Wang ZX (2013) The effect of thickness on components of the non-singular T-stress under mixed mode loading. In: 13th international conference on fracture, Beijing, China
Mu MY, Wang GZ, Tu ST, Xuan FZ (2016) Three-dimensional analyses of in-plane and out-of-plane crack-tip constraint characterization for fracture specimens. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 39(12):1461–1476
Aliha MRM, Saghafi H (2013) The effects of thickness and Poisson’s ratio on 3D mixed-mode fracture. Eng Fract Mech 98:15–28
Miao X-T, Yu Q, Zhou C-Y, Li J, Wang Y-Z, He X-H (2018) Experimental and numerical investigation on fracture behavior of CTS specimen under I–II mixed mode loading. Eur J Mech A Solids 72:235–244
Khan K, Al-Shayea NA (2000) Effect of specimen geometry and testing method on mixed mode I ± II fracture toughness of a limestone rock from Saudi Arabia. Rock Mech Rock Eng 33(3):179–206
Nasrnia A, Aboutalebi FH (2018) Experimental investigation and numerical simulations of U-notch specimens under mixed mode loading by the conventional and extended finite element methods. Arch Appl Mech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-018-1381-y
Seifi R, Kazemi MA (2018) An investigation on the effects of equal channel angular pressing on the mixed-mode fracture toughness and mechanical properties of 6063 aluminium alloy. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 41(8):1758–1770
Barhli SM, Mostafavi M, Cinar AF (2017) J-Integral calculation by finite element processing of measured full-field surface displacements. Exp Mech 57:997–1009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in preparing of this paper.
Additional information
Technical Editor: Paulo de Tarso Rocha de Mendonça, Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seifi, R., Bahri, M. Mixed-mode fracture toughness versus thickness and yield strength in aluminum alloys. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41, 463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1964-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1964-8