Abstract
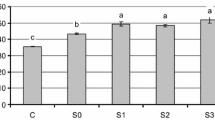
Recycling of sewage sludge (SS) as an organic amendment and a source of nutrients can be a potential option for proper disposal of organic waste. Symbiotic microbes show greater potential to carry out the bioremediation of heavy metals present in SS. A pot culture study was conducted to find the influence of SS and microbial symbionts [Rhizobium (R) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi [Funneliformis caledonius (Nicolson & Gerd.), Fc; and Glomus bagyarajii Mehrotra, Gb] on the growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). The major attributes of growth (height, fresh and dry weight and leaf number), photosynthesis (chlorophyll and carotenoid contents) and biochemical (protein and proline content) and the status of the uptake of N, P and K as well as the population of rhizospheric microbes were determined. Plants were grown in autoclaved garden soil alone (S) or garden soil amended with 20% SS with or without single or combined inoculation of symbiotic microbes in a pot experiment. SS amendment modified the properties of S by decreasing pH and increasing organic carbon in a resulting soil–sludge mixture (0.8 kg SS + 3.2 kg S). Plant sampling was done on 90 days after sowing. Highest plant growth, biochemical responses and nutrient contents were observed with SS + R + Gb treatment, whereas unamended soil without any inoculum exhibited the lowest values of the mentioned parameters. The content of proline, an indicator of stress, was found highest in C. arietinum raised in soil amended with SS. However, proline content decreased in the amended soil when inoculated with R + Gb. The nodulation and the percent root colonization were also found highest in SS-treated C. arietinum supplied with R + Gb. Overall, the study outcomes provide evidence that S mixed with appropriate amount of SS should be inoculated with combined inoculum of symbiotic microbes in order to achieve optimum growth, photosynthesis and biochemical attributes in economically important C. arietinum.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Abd-Alla MH, Yan F, Schubert S (1999) Effects of sewage sludge application on nodulation, nitrogen fixation, and plant growth of faba bean, soybean, and lupin. Angew Bot 73:69–75
Afkhami ME, Friesen ML, Stinchcombe JR (2021) Multiple mutualism effects generate synergistic selection and strengthen fitness alignment in the interaction between legumes, rhizobia and mycorrhizal fungi. Ecol Lett 24:1824–1834
Aggangan NS, Cortes AD, Reaño CE (2019) Growth response of cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) plant as affected by bamboo biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sterilized and unsterilized soil. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 22:101347
Agoro MA, Adeniji AO, Adefisoye MA, Okoh OO (2020) Heavy metals in wastewater and sewage sludge from selected municipal treatment plants in eastern cape province. South Africa Water 12:2746
Ahmad M, Zahir ZA, Nazli F, Akram F, Arshad M, Khalid M (2013) Effectiveness of halo- tolerant, auxin producing Pseudomonas and Rhizobium strains to improve osmotic stress tolerance in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). Braz J Microbiol 44:1341–1348
Allito BB, Ewusi-Mensah N, Logah V (2020) Legume-rhizobium strain specificity enhances nutrition and nitrogen fixation in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Agronomy 10:826
Amir H, Cavaloc Y, Laurent A, Pagand P, Gunkel P, Lemestre M, Médevielle V, Pain A, McCoy S (2019) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and sewage sludge enhance growth and adaptation of Metrosideros laurifolia on ultramafic soil in New Caledonia: a field experiment. Sci Total Environ 651:334–343
Antolín MC, Pascual I, García C, Polo A, Sánchez-Díaz M (2005) Growth, yield and solute content of barley in soils treated with sewage sludge under semiarid mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res 94:224–237
Antonkiewicz J, Popławska A, Kołodziej B, Ciarkowska K, Gambuś F, Bryk M, Babula J (2020) Application ofash and municipal sewage sludge as macronutrient sources in sustainable plant biomass production. J Environ Manage 264:110450
Arlo L, Beretta A, Szogi AA, del Pino A (2022) Biomass production, metal and nutrient content in sorghum plants grown on soils amended with sewage sludge. Heliyon 8:e08658
Arumugam R, Rajasekaran S, Nagarajan SM (2010) Response of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobium inoculation on growth and chlorophyll content of Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp Var. Pusa 151. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 14:113–115
Bagyaraj DJ, Reddy MSB, Nalini A (1989) Selection of an efficient inoculant VA mycorrhizal fungus for Leucaena. For Ecol Manag 27:81–85
Balacco JR, Vaidya BP, Hagmann DF, Goodey NM, Krumins JA (2022) Mycorrhizal infection can ameliorate abiotic factors in urban soils. Microb Ecol 85:100–107
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Belimov AA, Zinovkina NY, Safronova VI, Litvinsky VA, Nosikov VV, Zavalin AA, Tikhonovich IA (2019) Rhizobial ACC deaminase contributes to efficient symbiosis with pea (Pisum sativum L.) under single and combined cadmium and water deficit stress. Environ Exp Bot 167:103859
Biermann B, Linderman RG (1982) Quantifying vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae: a proposed method towards standarization. New Phytol 87:63–67
Chen Y, Yu F, Liang S, Wang Z, Liu Z, Xiong Y (2014) Utilization of solar energy in sewage sludge composting: fertilizer effect and application. Waste Manag 34:2014–2021
Ciecko Z, Kalembasa S, Wyszkowski M, Rolka E (2004) Effect of soil contamination by cadmium on potassium uptake by plants. Pol J Environ Stud 13:333–337
Clautilde M, Enama A, Robert N (2011) Effet simultané de la dilution et de la combinaison du Rhizobium et des mycorhizes sur la production foliaire et les propriétés physico-chimiques des jeunes feuilles de Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. J Appl Biosci 40:2668–2676
Dar MI, Khan FA, Green ID, Naikoo MI (2015) The transfer and fate of Pb from sewage sludge amended soil in a multi-trophic food chain: a comparison with the labile elements Cd and Zn. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16133–16142
Dar MI, Naikoo MI, Khan FA, Green IA (2018) Assessing the feasibility of sewage sludge applications for the cultivation of Brassica juncea L.: metal accumulation, growth, biochemical and yield responses. J Environ Sci Renew Resour 1:104
Dar MI, Naikoo MI, Khan FA, Rehman F, Green ID, Naushin F, Ansari AA (2017) An introduction to reactive oxygen species metabolism under changing climate in plants. reactive oxygen species and antioxidant systems in plants: role and regulation under abiotic stress. Springer, Singapore, pp 25–52
Dar MI, Naikoo MI, Rehman F, Naushin F, Khan FA (2016) Proline accumulation in plants: roles in stress tolerance and plant development. In: Iqbal N, Rahat N, Khan NA (eds) Osmolytes and plants acclimation to changing environment: emerging omics technologies. Springer, India, pp 155–166
Dhanker R, Chaudhary S, Goyal S, Garg VK (2021) Influence of urban sewage sludge amendment on agricultural soil parameters. Environ Technol Innov 23:101642
Eid EM, Shaltout KH, Alamri SA, Alrumman SA, Hussain AA, Sewelam N, Ragab GA (2021) Monitored sewage sludge application improves soil quality, enhances plant growth, and provides evidence for metal remediation by Sorghum bicolor L. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2325–2338
Elhindi KM, El-Din AS, Elgorban AM (2017) The impact of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mitigating salt-induced adverse effects in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Saudi J Biol Sci 24:170–179
Epstein E (2003) Land application of sewage sludge and biosolids. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Epstein E, Taylor JM, Chaney RL (1976) Effects of sewage sludge and sludge compost applied to soil on some soil physical and chemical properties. J Environ Qual 5:422–426
FAO (2011) Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations
Farzaneh M, Vierheilig H, Lössl A, Kaul HP (2011) Arbuscular mycorrhiza enhances nutrient uptake in chickpea. Plant Soil Environ 57:465–470
Ferrol N, Azcón-Aguilar C, Pérez-Tienda J (2019) Arbuscular mycorrhizas as key players in sustainable plant phosphorus acquisition: An overview on the mechanisms involved. Plant Sci 280:441–447
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:375–400
Gerdemann JW, Nicolson TH (1963) Spores of mycorrhizal endogone species extracted from soil by wet sieving and decanting. Trans Br Mycol Soc 46:235–246
Gontia-Mishra I, Sapre S, Sharma A, Tiwari S (2016) Amelioration of drought tolerance in wheat by the interaction of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Plant Biol 18:992–1000
Gough EC, Owen KJ, Zwart RS, Thompson JP (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi acted synergistically with Bradyrhizobium sp. to improve nodulation, nitrogen fixation, plant growth and seed yield of mung bean (Vigna radiata) but increased the population density of the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei. Plant Soil 465:1–22
Green ID, Diaz A, Tibbett M (2010) Factors affecting the concentration in seven-spotted ladybirds (Coccinella septempunctata L.) of Cd and Zn transferred through the food chain. Environ Pollut 158:135–141
Hart M, Ehret DL, Krumbein A, Leung C, Murch S, Turi C, Franken P (2015) Inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves the nutritional value of tomatoes. Mycorrhiza 25:359–376
Hasan M, Naushin F (2022) Potentials of co-inoculation of microbial organisms and sewage sludge on growth of a pulse crop and microbial population. Res J Agric Sci 13:1046–1050
Hmaeid N, Metoui O, Wali M, Zorrig W, Abdelly C (2014) Comparative effects of Rhizobacteria in promoting growth of Hordeum-maritimum L. plants under salt stress. J Plant Biol Res 3:37–50
Hu J, Lin X, Wang J, Dai J, Cui X, Chen R, Zhang J (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus enhances crop yield and P-uptake of maize (Zea mays L.): a field case study on a sandy loam soil as affected by long-term P-deficiency fertilization. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2460–2465
Hussain A, Ali A, Noorka IR (2012) Effect of phosphorus with and without Rhizobium inoculation on nitrogen and phosphorus concentration and uptake by mungbean (Vigna radiata L.). J Agric Res 50:49–57
Igiehon ON, Babalola OO (2021) Rhizobium and mycorrhizal fungal species improved soybean yield under drought stress conditions. Curr Microbiol 78:1615–1627
Jackson ML (1958) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Jahan U, Kafeel U, Naikoo MI, Kaifiyan M, Hasan M, Khan FA (2023) Trophic transfer, bioaccumulation, and detoxification of lead and zinc via sewage sludge applied soil-barley-aphid-ladybird food chain. Water Air Soil Poll 234:508
Jahromi F, Aroca R, Porcel R, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2008) Influence of salinity on the in vitro development of Glomus intraradices and on the in vivo physiological and molecular responses of mycorrhizal lettuce plants. Microb Ecol 55:45–53
Kalam SU, Naushin F, Bagyaraj DJ, Khan FA (2019) Role of AM fungi in the uptake and accumulation of Cd and Ni by Luffa aegyptiaca. Water Air Soil Poll 230:1–8
Kala TC, Christi RM, Bai NR (2011) Effect of Rhizobium inoculation on the growth and yield of horsegram (Dolichos biflorus Linn). Plant Arch 11:97–99
Kenneth E, Pallet KE, Young J (2000) Carotenoids. In: Alscher RG, Hess JL (eds) Antioxidants in Higher Plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 60
Khaitov B, Kurbonov A, Abdiev A, Adilov M (2016) Effect of chickpea in association with Rhizobium to crop productivity and soil fertility. Eurasian J Soil Sci 5:105–112
Kordrostami M, Rabiei B, Kumleh HH (2017) Biochemical, physiological and molecular evaluation of rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance at the seedling stage. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:529–544
Krishna KR, Dart DT (1984) Effect of mycorrhizal inoculation and soluble phosphorus fertilizer on growth and phosphorus uptake of pearl millet. Plant Soil 81:274–275
Lakshmipathy R, Balakrishna AN, Bagyaraj DJ, Ashwin R (2019) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for sustainable agriculture. J Soil Biol Ecol 39:132–140
Larimer AL, Clay K, Bever JD (2014) Synergism and context dependency of interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia with a prairie legume. Ecology 95:1045–1054
Lata K, Sharma TK, Dassani S (2021) Effect of mycorrhiza and Rhizobium inoculation on the growth and yield of mung (Vigna radiata) plant. Plant Arch 21:1847–1850
Lesueur D, Deaker R, Herrmann L, Bräu L, Jansa J (2016) The production and potential of biofertilizers to improve crop yields. bioformulations: for sustainable agriculture. Springer, New Delhi, pp 71–92
Lindner RC (1944) Rapid analytical methods for some of the more common inorganic constituents of plant tissue. Plant Physiol 19:76–89
Lone R, Alaklabi A, Malik JA, Koul KK (2020) Mycorrhizal influence on storage metabolites and mineral nutrition in seed propagated potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plant. J Plant Nutr 43:2164–2175
Lone R, Shuab R, Khan S, Ahmad J, Koul KK (2018) Influence of mycorrhizal inoculation on carrot growth, metabolites and nutrition. J Plant Nutr 41:432–444
Lone R, Shuab R, Sharma V, Kumar V, Mir R, Koul KK (2015) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and development of potato (Solanum tuberosum) plant. Asian J Crop Sci 7:233–243
Lowry OH, Rosenberg NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. The J Biol Chem 193:265–257
Mackinney G (1941) Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem 140:315–319
Maji D, Misra P, Singh S, Kalra A (2017) Humic acid rich vermicompost promotes plant growth by improving microbial community structure of soil as well as root nodulation and mycorrhizal colonization in the roots of Pisum sativum. Appl Soil Ecol 110:97–108
Matse DT, Huang CH, Huang YM, Yen MY (2020) Effects of coinoculation of Rhizobium with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on the nitrogen fixation and nutrient uptake of Trifolium repens in low phosphorus soil. J Plant Nutr 43:739–752
Mazen A, Faheed FA, Ahmed AF (2010) Study of potential impacts of using sewage sludge in the amendment of desert reclaimed soil on wheat and jews. Braz Arch Biol Technol 53:917–930
Murtaza G, Ehsanullah ZA, Hussain S, Rasool T, Shehzad H (2014) The influence of Rhizobium seed inoculation and different levels of phosphorus application on growth, yield and quality of mashbean (Vigra mungo L.). Int J Mod Agric 3:92–96
Özyazici MA (2013) Effects of sewage sludge on the yield of plants in the rotation system of wheat-white head cabbage-tomato. Eurasian J Soil Sci 2:35–44
Phillips JM, Hayman DS (1970) Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans Br Mycol Soc 55:158–160
Raklami A, Bechtaoui N, Tahiri AI, Anli M, Meddich A, Oufdou K (2019) Use of rhizobacteria and mycorrhizae consortium in the open field as a strategy for improving crop nutrition, productivity and soil fertility. Front Microbiol 10:1106
Roy F, Boye JI, Simpson BK (2010) Bioactive proteins and peptides in pulse crops: pea, chickpea and lentil. Food Res Int 43:432–442
Seleiman MF, Santanen A, Kleemola J, Stoddard FL, Mäkelä PS (2013) Improved sustainability of feedstock production with sludge and interacting mycorrhiza. Chemosphere 91:1236–1242
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2009) Use of sewage sludge as fertilizer supplement for Abelmoschus esculentus plants: physiological, biochemical and growth responses. Int J Environ Waste Manag 3:91–106
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2010a) Variations in heavy metal accumulation, growth and yield of rice plants grown at different sewage sludge amendment rates. Ecotox Environ Safe 73:632–641
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2010b) Effect of different sewage sludge applications on growth and yield of Vigna radiata L. field crop: metal uptake by plant. Ecol Eng 36:969–972
Singh S, Sinha S (2005) Accumulation of metals and its effects in Brassica Juncea (L.) Czern. (cv. Rohini) grown on various amendments of tannery waste. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:118–127
Singh Z, Singh G (2018) Role of Rhizobium in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) production-a review. Agric Rev 39:31–39
Skowrońska M, Bielińska EJ, Szymański K, Futa B, Antonkiewicz J, Kołodziej B (2020) An integrated assessment of the long-term impact of municipal sewage sludge on the chemical and biological properties of soil. CATENA 189:104484
Subba Rao NS (1972) Rhizobia and nodulation. Curr Sci 41:1–42
Sundaram MD, Arangarasan V (1995) Effect of inoculation of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the yield and quality attributes in tomato. In: Adholeya A, Singh S (eds) Mycorrhizae: biofertilizer for the future. TERI Publication, New Delhi, pp 394–396
Swain A, Singh S, Mohapatra K, Abhik P (2020) Effect of sewage sludge application on yield, nutrients uptake and nutrient use efficiency of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Ann Plant Soil Res 22:305–309
Tanwar A, Singh A, Aggarwal A, Jangra E, Pichardo ST (2021) Evaluation of municipal sewage sludge for arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculum production. Eur J Soil Sci 10:343–353
Togay N, Togay Y, Dogan Y (2008) Effects of municipal sewage sludge doses on the yield, some yield components and heavy metal concentration of dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Afr J Biotechnol 7:3026–3030
Verma A, Verma AP (1995) Effect of tannery effluents on seed germination and chlorophyll content in Phaseolus radiatus L. J Indian Pollut Contam 11:63–66
Veselaj E, Sallaku G, Balliu A (2018) Tripartite relationships in legume crops are plant-microorganism-specific and strongly influenced by salinity. Agriculture 8:117
Wahid F, Fahad S, Danish S, Adnan M, Yue Z, Saud S, Siddiqui MH, Brtnicky M, Hammerschmiedt T, Datta R (2020) Sustainable management with mycorrhizae and phosphate solubilizing bacteria for enhanced phosphorus uptake in calcareous soils. Agriculture 10:334
Wu FY, Bi YL, Wong MH (2009) Dual inoculation with an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and Rhizobium to facilitate the growth of alfalfa on coal mine substrates. J Plant Nutr 32:755–771
Xie MM, Zou YN, Wu QS, Zhang ZZ, Kuča K (2020) Single or dual inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia regulates plant growth and nitrogen acquisition in white clover. Plant Soil Environ 66:287–294
Zarik L, Meddich A, Hijri M, Hafidi M, Ouhammou A, Ouahmane L, Duponnois R, Boumezzough A (2016) Use of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to improve the drought tolerance of Cupressus atlantica G. C R Biol 339:185–196
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Department of Botany, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, for providing essential laboratory equipment and encouragement throughout the course of investigation.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [MH], [FN] and [HS]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [MH] and [FN]. DJB revised the manuscript to the present form. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests/competing interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, M., Naushin, F., Shaher, H. et al. Influence of sewage sludge, Rhizobium and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nutrient uptake, growth, photosynthetic and biochemical attributes in Cicer arietinum L.. Braz. J. Bot 46, 1161–1176 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-023-00934-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-023-00934-4