Abstract
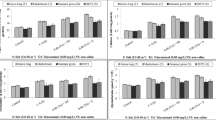
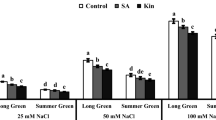
The exposure of plants to high salinity and drought stresses significantly and negatively affected growth, photosynthesis, biochemistry as well as the texture and quality of cucumber fruits. The objective of this study was to determine whether cucumber grown at an increased salinity level or drought stress responds positively to the supply of Si. Two cucumber cultivars (Cucumis sativus L.) were grown under salinity stress and drought stress which were imposed through addition of 150 mM NaCl to the soil and through supply of half of the water required for normal irrigation like that of the control, respectively. Si was supplied as K2SiO3 at 2.25 mM. Its application reduced deterioration through maintenance of membrane integrity, reduction in lipid peroxidation and increased reactive oxygen scavenging. It helped plants to take up and retain water and thus improve water status of the upper parts of the plants. Moreover, it improved photosynthesis and increased chlorophyll content to allow a constant supply of assimilates to the growing tissues. Application of Si increased firmness of the mature cucumber fruits and leaves, this way producing a rougher texture and fruit senescence was delayed. Improvement in cucumber water status and enhancement of antioxidant activities indicate a metabolic and physiological role of Si, which results in a higher nutritional and commercial value of the crop.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarie S, Hanaoka N, Ueno O, Miyazaki A, Kubota F, Agata W, Kaufman PB (1998) Effects of silicon on tolerance to water deficit and heat stress in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) monitored by electrolyte leakage. Plant Prod Sci 1:96–103
Ahmad R, Zaheer SH, Ismail S (1992) Role of silicon in salt tolerance of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Sci 85:43–50
Al-Aghabary K, Zhu ZJ, Shi QH (2004) Influence of silicon supply on chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence and antioxidative enzyme activities in tomato plants under salt stress. J Plant Nutr 27:2101–2115
Alexieva V, Sergiev I, Mapelli S, Karanov E (2001) The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 24:1337–1344
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis, 15th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Bradbury M, Ahmad R (1990) The effect of silicon on the growth of Prosopis juliflora growing in saline soil. Plant Soil 125:71–78
Epstein E (1999) Silicon. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:641–664
Gong H, Chen K (2012) The regulatory role of silicon on water relations, photosynthetic gas exchange and carboxylation activities of wheat leaves in field drought conditions. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1589–1594
Hammond KE, Evans DE, Hodson MJ (1995) Aluminum/silicon interactions in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. Plant Soil 173:89–95
Hashemi A, Abdolzadeh A, Sadeghipour HR (2010) Beneficial effects of silicon nutrition in alleviating salinity stress in hydroponically grown canola (Brassica napus L.). Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56:244–253
Iwasaki K, Meier P, Fecht M, Horst WJ (2002) Effects of silicon supply on apoplastic manganese concentrations in leaves and their relation to manganese tolerance in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp). Plant Soil 238:281–288
Janz D, Lautner S, Wildhagen H, Behnke K, Schnitzler JP, Rennenberg H, Fromm J, Polle A (2012) Salt stress induces the formation of a novel type of “pressure wood” in two Populus species. New Phytol 194:129–141
Khan NA (2006) NaCl-inhibited chlorophyll synthesis and associated changes in ethylene evolution and antioxidative enzyme activities in wheat. Biol Plant 47:437–440
Li R, Shi F, Fukuda K, Yang Y (2010) Effects of salt and alkali stresses on germination, growth, photosynthesis and ion accumulation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56:725–733
Liang YC (1998) Effects of Si on leaf ultrastructure, chlorophyll content and photosynthetic activity in barley under salt stress. Pedosphere 8:289–296
Liang YC, Shen QR, Shen ZG, Ma TS (1996) Effects of silicon on salinity tolerance of two barley cultivars. J Plant Nutr 19:173–183
Ma JF, Yamaji N (2006) Silicon uptake and accumulation in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci 11:392–397
Matoh T, Kairusmee P, Takahashi E (1986) Salt-induced damage to rice plants and alleviation on effects of silicate. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 32:295–304
Ouzounidou G, Papadopoulou P, Giannakoula A, Ilias I (2008) Plant growth regulators treatments modulate growth, physiology and quality characteristics of Cucumis melo L. plants. Pak J Bot 40:1185–1193
Ouzounidou G, Paschalidis C, Petropoulos D, Koriki A, Zamanidis P, Petridis A (2013a) Interaction of soil moisture and excess of boron and nitrogen on lettuce growth and quality. Hort Sci 40:119–125
Ouzounidou G, Papadopoulou K, Asfi M, Mirtziou I, Gaitis F (2013b) Efficacy of different chemicals on shelf-life extension of parsley stored at two temperatures. Int J Food Sci Technol 48:1610–1617
Ouzounidou G, Ilias IF, Giannakoula A, Theocharidou I (2014) Effect of water stress and NaCl triggered changes on yield, physiology, biochemistry of broad bean (Vicia faba L.) plants and on quality of harvested pods. Biologia 69:1010–1017
Rafi MM, Epstein E (1997) Silicon deprivation causes physical abnormalities in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Plant Physiol 151:497–501
Savvas D, Giotis D, Chatzieustratiou E, Bakea M, Patakioutas G (2009) Silicon supply in soilless cultivations of zucchini alleviates stress induced by salinity and powdery mildew infections. Environ Exp Bot 65:11–17
Shalata A, Tal M (1998) The effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in the leaf of the cultivated tomato and its wild salt-tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii. Physiol Plant 104:167–174
Solatni Z, Shekari F, Jamshidi K, Fotovat R, Azimkhani R (2012) The effect of silicon on germination and some growth characteristics of salt-stressed canola seedling. Int J Agron Agric Res 2:12–21
Von Caemmerer S, Farquhar GD (1981) Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and gas exchange of leaves. Planta 153:376–387
Wang WB, Kim YH, Lee HS, Kim KY, Dengand XP, Kwak SS (2009) Analysis of antioxidant enzyme activity during germination of alfalfa under salt and drought stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:570–577
Yin L, Wang S, Li J, Tanaka K, Oka M (2013) Application of silicon improves salt tolerance through ameliorating osmotic and ionic stresses in the seedling of Sorgum bicolor. Acta Physiol Plant 35:3099–3107
Yoshida S, Navasero SA, Ramirez EA (1969) Effect of silica and nitrogen supply on some leaf character of rice plant. Plant Soil 31:48–56
Zhu Z, Wei G, Li J, Qian Q, Yu J (2004) Silicon alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzymes activity in leaves of salt-stressed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Sci 167:527–533
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouzounidou, G., Giannakoula, A., Ilias, I. et al. Alleviation of drought and salinity stresses on growth, physiology, biochemistry and quality of two Cucumis sativus L. cultivars by Si application. Braz. J. Bot 39, 531–539 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-016-0274-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-016-0274-y