Abstract
Purpose
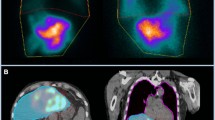
Yttrium 90-labeled intra-arterial liver therapy is an effective treatment for patients with unresectable primary or metastatic liver malignancy. Optimal radioisotope dose calculation is dependent upon lung shunt fraction (LSF) which is typically estimated by planar scintigraphy. The goal of this systematic review was to compare LSF using 2D planar scintigraphy and 3D SPECT/CT. A secondary outcome was to assess the impact on lung dosimetry.
Methods
PubMed, SCOPUS and Web of Science database were searched for studies in English language related to lung shunt fraction quantification utilizing technetium 99m-labeled macroaggregated albumin (99mTc-MAA) planar scintigraphy and SPECT/CT, published between January 2010 and November 2020. The review was conducted using the PRISMA statement and QUADAS-2 criteria.
Results
A total of 8 studies (one prospective, 4 retrospective studies and 3 abstracts from national conferences) with a sample size of 552 were included in this review. There were 456 patients (82.6%) with hepatocellular carcinoma and 95 patients (17.4%) with hepatic metastasis. A wider range of LSF percentages was noted in planar scintigraphy methodology (range 1.2–33.3%) when compared to SPECT/CT (range 0.4–21.7%). The median LSF percentages were 6.7 and 2.9% using planar scintigraphy and SPECT/CT, respectively.
Conclusion
The current clinical assessment of LSF is substantially overestimated by 2D planar scintigraphy when compared to 3D SPECT/CT. However, unclearness of blinding between the index test and reference standard was an area of quality concern. Hence, further randomized or prospective studies are needed to strengthen the role of SPECT/CT in lung shunt fraction estimation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik L et al (2011) Radioembolization results in longer time-to-progression and reduced toxicity compared with chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 140(2):497–507
Hendlisz A, Van den Eynde M, Peeters M et al (2010) Phase III trial comparing protracted intravenous fluorouracil infusion alone or with yttrium-90 resin microspheres radioembolization for liver-limited metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to standard chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 28:3687–3694
Riaz A, Gates VL, Atassi B et al (2011) Radiation segmentectomy: a novel approach to increase safety and efficacy of radioembolization. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(1):163–171
Jia Z, Wang W (2018) Yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable metastatic neuroendocrine liver tumor: a systematic review. Eur J Radiol 100:23–29
Kritzinger J, Klass D, Ho S et al (2013) Hepatic embolotherapy in interventional oncology: technology, techniques, and applications. Clin Radiol 68:1–15
https://www.sirtex.com/media/169247/ssl-us-14-sir-spheres-microspheres-ifu-us.pdf. Accessed Sept 2020
https://www.bostonscientific.com/en-US/products/cancer-therapies/therasphere-y90-glass-microspheres/therasphere-y90-microspheres-brief-summary.html. Accessed Sept 2020
Whiting PF, Rutjes AWS, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB et al (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536
Dittmann H, Kopp D, Kupferschlaeger J, Feil D, Groezinger G, Syha R, Weissinger M, la Fougère C (2018) A prospective study of quantitative SPECT/CT for evaluation of lung shunt fraction before SIRT of liver tumors. J Nucl Med 59(9):1366–1372
Elsayed M, Cheng B, Xing M, Sethi I, Brandon D, Schuster DM, Bercu Z, Galt J, Barron B, Kokabi N (2020) Comparison of Tc-99m MAA planar versus SPECT/CT imaging for lung shunt fraction evaluation prior to Y-90 radioembolization: are we overestimating lung shunt fraction? Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 44(2):254–260
Lopez B, Mahvash A, Lam MGEH, Kappadath SC (2019) Calculation of lung mean dose and quantification of error for 90Y-microsphere radioembolization using 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT and diagnostic chest CT. Med Phys 46(9):3929–3940
Allred JD, Niedbala J, Mikell JK, Owen D, Frey KA, Dewaraja YK (2018) The value of 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT for lung shunt estimation in 90Y radioembolization: a phantom and patient study. EJNMMI Res 8(1):50
Kao YH, Magsombol BM, Toh Y, Tay KH, Chow PKh, Goh AS, Ng DC (2014) Personalized predictive lung dosimetry by technetium-99m macroaggregated albumin SPECT/CT for yttrium-90 radioembolization. EJNMMI Res 29(4):33
Georgiou M, Kuker R, Portelance L, Studenski M, Lorenzo A (2018) Comparison of 2D planar versus 3D SPECT/CT lung shunt fraction calculation from 99mTc MAA pre-90Y imaging for hepatic microsphere radioembolization. J Nucl Med 59(supplement 1):601
Poon-iad N, Teyateeti A, Chaudakshetrin P (2019) Selective internal radiotherapy dose calculation: a pilot study to compare lung shunt fraction on planar and SPECT/CT imaging. International Symposium on Standards, Applications and Quality Assurance in Medical Radiation Dosimetry (18–21 June 2019), IAEA, Vienna
Gill H, Bian J, Gabriel M, Molvar C, Wagner R, Halama J (2019) 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT imaging for quantitative assessment of lung shunt fraction prior to 90Y transarterial radioembolization. J Nucl Med 60(supplement 1):265
Ho S, Lau WY, Leung TW, Chan M, Johnson PJ, Li AK (1997) Clinical evaluation of the partition model for estimating radiation doses from yttrium-90 microspheres in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Eur J Nucl Med 24:293–298
Dezarn WA, Cessna JT, DeWerd LA et al (2011) American Association of Physicists in Medicine. Recommendations of the American Association of Physicists in Medicine on dosimetry, imaging, and quality assurance procedures for 90Y microsphere brachytherapy in the treatment of hepatic malignancies. Med Phys 38(8):4824–4845
Lewandowski RJ, Gabr A, Abouchaleh N, Ali R, Al Asadi A, Mora RA et al (2018) Radiation segmentectomy: potential curative therapy for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 287(3):1050–1058
Gabr A, Kulik L, Mouli S, Riaz A, Ali R, Desai K et al (2020) Liver transplantation following yttrium-90 radioembolization: 15-year experience in 207-patient cohort. Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31318
Vouche M, Habib A, Ward TJ, Kim E, Kulik L, Ganger D et al (2014) Unresectable solitary hepatocellular carcinoma not amenable to radiofrequency ablation: multicenter radiology-pathology correlation and survival of radiation segmentectomy. Hepatology. 60(1):192–201. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27057
Zaharakis A, Leveque F, Backiel J, Tursi G, Palestro C, Nichols K (2014) SPECT/CT for estimating hepatopulmonary shunting in selective internal radiotherapy: a phantom study. J Nucl Med 55(supplement 1):1496
Gaba RC, Zivin SP, Dikopf MS, Parvinian A, Casadaban LC, Lu Y, Bui JT (2014) Characteristics of primary and secondary hepatic malignancies associated with hepatopulmonary shunting. Radiology 271(2):602–612
Ludwig JM, Ambinder EM, Ghodadra A, Xing M, Prajapati HJ, Kim HS (2016) Lung shunt fraction prior to yttrium-90 radioembolization predicts survival in patients with neuroendocrine liver metastases: single-center prospective analysis. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 39(7):1007–1014
Yu N, Srinivas SM, Difilippo FP et al (2013) Lung dose calculation with SPECT/CT for 90yttrium radioembolization of liver cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:834–839
Peters SMB, van der Werf NR, Segbers M, van Velden FHP, Wierts R, Blokland KJAK, Konijnenberg MW, Lazarenko SV, Visser EP, Gotthardt M (2019) Towards standardization of absolute SPECT/CT quantification: a multi-center and multi-vendor phantom study. EJNMMI Phys 6(1):29
Buck AK, Nekolla S, Ziegler S, Beer A, Krause BJ, Herrmann K, Scheidhauer K, Wester HJ, Rummeny EJ, Schwaiger M, Drzezga A (2008) SPECT/CT. J Nucl Med 49:1305–1319
Roach PJ, Schembri GP, Ho Shon IA et al (2006) SPECT/CT imaging using a spiral CT scanner for anatomical localization: impact on diagnostic accuracy and reporter confidence in clinical practice. Nucl Med Commun 27:977–987
Salem R, Parikh P, Atassi B et al (2008) Incidence of radiation pneumonitis after hepatic intra-arterial radiotherapy with yttrium-90 microspheres assuming uniform lung distribution. Am J Clin Oncol 31:431–438
Van de Wiele C, Maes A, Brugman E, D’Asseler Y, De Spiegeleer B, Mees G, Stellamans K (2012) SIRT of liver metastases: physiological and pathophysiological considerations. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:1646–1655
Elschot M, Nijsen JF, Lam MG et al (2014) 99mTc-MAA overestimates the absorbed dose to the lungs in radioembolization: a quantitative evaluation in patients treated with 166Ho-microspheres. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41:1965–1975
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and idea: HG; methodology: HG and JH; literature search and data analysis: HG and JH; writing—original draft preparation: HG; writing—review and editing: JH.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, H., Hiller, J. Systematic review of lung shunt fraction quantification comparing SPECT/CT and planar scintigraphy for yttrium 90 radioembolization planning. Clin Transl Imaging 9, 181–188 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-021-00417-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-021-00417-0