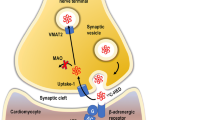
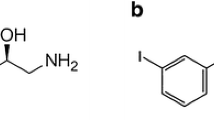
Abstract
Cardiac innervation imaging with 123I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy or 11C-meta-hydroxyephedrine positron emission tomography visualizes and quantifies the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. No other imaging modality is able to stratify this potentially important trigger for various cardiac diseases. Recent literature has focussed mostly on its prognostic ability in heart failure patients, but its use is not limited to heart failure alone. In this review, the literature regarding cardiac innervation imaging in arrhythmia and arrhythmogenic syndromes is discussed, which shows potential for further study into the prognostic and diagnostic value of innervation imaging for atrial fibrillation and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy especially.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen MJ, Zipes DP (2014) Role of the autonomic nervous system in modulating cardiac arrhythmias. Circ Res 114(6):1004–1021
Verschure DO, Veltman CE, Manrique A, Somsen GA, Koutelou M, Katsikis A et al (2014) For what endpoint does myocardial 123I-MIBG scintigraphy have the greatest prognostic value in patients with chronic heart failure? Results of a pooled individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 15(9):996–1003
Verberne HJ, Brewster LM, Somsen GA, van Eck-Smit BL (2008) Prognostic value of myocardial 123I-meta iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) parameters in patients with heart failure: a systematic review. Eur Heart J 29(9):1147–1159
Scholtens AM, Braat AJ, Tuinenburg A, Meine M, Verberne HJ (2014) Cardiac sympathetic innervation and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart Fail Rev 19(5):567–573
Flotats A, Carrio I, Agostini D, Le Guludec D, Marcassa C, Schafers M et al (2010) Proposal for standardization of 123I-meta iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) cardiac sympathetic imaging by the EANM Cardiovascular Committee and the European Council of Nuclear Cardiology. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37(9):1802–1812
Schwaiger M, Kalff V, Rosenspire K, Haka MS, Molina E, Hutchins GD et al (1990) Noninvasive evaluation of sympathetic nervous system in human heart by positron emission tomography. Circulation 82(2):457–464
Benjamin EJ, Chen PS, Bild DE, Mascette AM, Albert CM, Alonso A et al (2009) Prevention of atrial fibrillation: report from a national heart, lung, and blood institute workshop. Circulation 119(4):606–618
Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS et al (2004) Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 110(9):1042–1046
Coumel P, Attuel P, Lavallee J, Flammang D, Leclercq JF, Slama R (1978) The atrial arrhythmia syndrome of vagal origin. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss 71(6):645–656
Amar D, Zhang H, Miodownik S, Kadish AH (2003) Competing autonomic mechanisms precede the onset of postoperative atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 42(7):1262–1268
Bettoni M, Zimmermann M (2002) Autonomic tone variations before the onset of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation 105(23):2753–2759
Tomita T, Takei M, Saikawa Y, Hanaoka T, Uchikawa S, Tsutsui H et al (2003) Role of autonomic tone in the initiation and termination of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients without structural heart disease. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 14(6):559–564
Akutsu Y, Kaneko K, Kodama Y, Li HL, Suyama J, Shinozuka A et al (2011) Iodine-123 mIBG imaging for predicting the development of atrial fibrillation. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 4(1):78–86
Ovadia M, Duque KS (2012) The potential utility of (123)I-mIBG in atrial fibrillation and in the electrophysiology laboratory. Curr Cardiol Rep 14(2):200–207
Arimoto T, Tada H, Igarashi M, Sekiguchi Y, Sato A, Koyama T et al (2011) High washout rate of iodine-123-meta iodobenzylguanidine imaging predicts the outcome of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 22(12):1297–1304
Wichter T, Borggrefe M, Haverkamp W, Chen X, Breithardt G (1992) Efficacy of antiarrhythmic drugs in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular disease. Results in patients with inducible and noninducible ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 86(1):29–37
Marcus FI, McKenna WJ, Sherrill D, Basso C, Bauce B, Bluemke DA et al (2010) Diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: proposed modification of the Task Force Criteria. Eur Heart J 31(7):806–814
Takahashi N, Ishida Y, Maeno M, Hirose Y, Kawano S, Fukuoka S et al (1997) Noninvasive identification of left ventricular involvements in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia: comparison of 123I-MIBG, 201TlCl, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrafast computed tomography. Ann Nucl Med 11(3):233–241
Lerch H, Bartenstein P, Wichter T, Hindricks G, Borggrefe M, Breithardt G et al (1993) Sympathetic innervation of the left ventricle is impaired in arrhythmogenic right ventricular disease. Eur J Nucl Med 20(3):207–212
Wichter T, Hindricks G, Lerch H, Bartenstein P, Borggrefe M, Schober O et al (1994) Regional myocardial sympathetic dysinnervation in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. An analysis using 123I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy. Circulation 89(2):667–683
Wichter T, Schafers M, Rhodes CG, Borggrefe M, Lerch H, Lammertsma AA et al (2000) Abnormalities of cardiac sympathetic innervation in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy : quantitative assessment of presynaptic norepinephrine reuptake and postsynaptic beta-adrenergic receptor density with positron emission tomography. Circulation 101(13):1552–1558
Paul M, Wichter T, Kies P, Gerss J, Wollmann C, Rahbar K et al (2011) Cardiac sympathetic dysfunction in genotyped patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy and risk of recurrent ventricular tachyarrhythmias. J Nucl Med 52(10):1559–1565
Mizusawa Y, Horie M, Wilde AA (2014) Genetic and clinical advances in congenital long QT syndrome. Circ J 78(12):2827–2833
Noda T, Takaki H, Kurita T, Suyama K, Nagaya N, Taguchi A et al (2002) Gene-specific response of dynamic ventricular repolarization to sympathetic stimulation in LQT1, LQT2 and LQT3 forms of congenital long QT syndrome. Eur Heart J 23(12):975–983
Antzelevitch C (2002) Sympathetic modulation of the long QT syndrome. Eur Heart J 23(16):1246–1252
Calkins H, Lehmann MH, Allman K, Wieland D, Schwaiger M (1993) Scintigraphic pattern of regional cardiac sympathetic innervation in patients with familial long QT syndrome using positron emission tomography. Circulation 87(5):1616–1621
Mazzadi AN, Andre-Fouet X, Duisit J, Gebuhrer V, Costes N, Chevalier P et al (2003) Cardiac retention of [11C]HED in genotyped long QT patients: a potential amplifier role for severity of the disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285(3):H1286–H1293
Momose M, Kobayashi H, Kasanuki H, Kusakabe K, Tamaki A, Onishi S et al (1998) Evaluation of regional cardiac sympathetic innervation in congenital long QT syndrome using 123I-MIBG scintigraphy. Nucl Med Commun 19(10):943–951
Gohl K, Feistel H, Weikl A, Bachmann K, Wolf F (1991) Congenital myocardial sympathetic dysinnervation (CMSD)—a structural defect of idiopathic long QT syndrome. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 14(10):1544–1553
Muller KD, Jakob H, Neuzner J, Grebe SF, Schlepper M, Pitschner HF (1993) 123I-meta iodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy in the detection of irregular regional sympathetic innervation in long QT syndrome. Eur Heart J 14(3):316–325
Takigawa M, Noda T, Shimizu W, Miyamoto K, Okamura H, Satomi K et al (2008) Seasonal and circadian distributions of ventricular fibrillation in patients with Brugada syndrome. Heart Rhythm 5(11):1523–1527
Brugada P, Brugada J (1992) Right bundle branch block, persistent ST segment elevation and sudden cardiac death: a distinct clinical and electrocardiographic syndrome. A multicenter report. J Am Coll Cardiol 20(6):1391–1396
Miyazaki T, Mitamura H, Miyoshi S, Soejima K, Aizawa Y, Ogawa S (1996) Autonomic and antiarrhythmic drug modulation of ST segment elevation in patients with Brugada syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 27(5):1061–1070
Nakamura M, Isobe M, Imamura H (1998) Incessant ventricular fibrillation attacks in a patient with Brugada syndrome. Int J Cardiol 64(2):205–206
Kawasaki T, Kaminaga T, Hirota D, Mitani H, Furui S (2001) I-123 meta iodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy in a patient with Brugada syndrome. Clin Nucl Med 26(12):1058–1059
Oyama N, Oyama N, Yokoshiki H, Satoh K, Katoh N, Hayashi T et al (2002) Iodine-123-meta iodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy of total cardiac adrenergic denervation in Brugada syndrome. Jpn Heart J 43(2):183–186
Wichter T, Matheja P, Eckardt L, Kies P, Schäfers K, Schulze-Bahr E et al (2002) Cardiac autonomic dysfunction in Brugada syndrome. Circulation 105(6):702–706
Gill JS, Hunter GJ, Gane G, Camm AJ (1993) Heterogeneity of the human myocardial sympathetic innervation: in vivo demonstration by iodine 123-labeled meta-iodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy. Am Heart J 126(2):390–398
Furuhashi M, Uno K, Tsuchihashi K (2002) Myocardial iodine-123-meta iodobenzylguanidine (123I-MIBG) imaging in Brugada syndrome. Circulation 106(13):e59–e60 (author reply e59–e60)
Kies P, Wichter T, Schäfers M, Paul M, Schäfers KP, Eckardt L, Stegger L, Schulze-Bahr E, Rimoldi O, Breithardt G, Schober O, Camici PG (2004) Abnormal myocardial presynaptic norepinephrine recycling in patients with Brugada syndrome. Circulation 110(19):3017–3022
Kostopoulou A, Koutelou M, Theodorakis G, Theodorakos A, Livanis E, Maounis T et al (2010) Disorders of the autonomic nervous system in patients with Brugada syndrome: a pilot study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 21(7):773–780
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
A.M. Scholtens and H.J. Verberne declare no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholtens, A.M., Verberne, H.J. Innervation imaging in arrhythmia and arrhythmogenic disease. Clin Transl Imaging 3, 373–378 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-015-0136-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-015-0136-9