Abstract
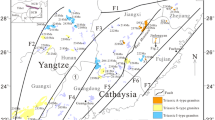
The Central Tianshan Block is one of numerous microcontinental blocks within the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB) that overlies Precambrian basement rocks. Constraining the evolution of these ancient basement rocks is central to understanding the accretionary and collisional tectonics of the CAOB, and their place within the Rodinia supercontinent. However, to date, the timing and tectonic settings in which the basement rocks in the Central Tianshan Block formed are poorly constrained, with only sparse geochemical and geochronological data from granitic rocks within the northern segment of the block. Here, we present a systematic study combining U-Pb geochronology, whole-rock geochemistry, and the Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of newly-identified granitic gneisses from the Bingdaban area of Central Tianshan Block. The analyzed samples yield a weighted mean Neoproterozoic 206Pb/238U ages of 975–911 Ma. These weakly-peraluminous granitic rocks show a common geochemical I-type granite affinity. The granitic gneisses are calc-alkaline and enriched in large ion lithophile elements (LILEs) and light rare earth elements (LREEs), but they are depleted in high field strength elements (HFSEs); these characteristics are similar to those of typical subduction-related magmatism. All samples show initial (87Sr/86Sr)(t) ratios between 0.705136 and 0.706745. Values for ƐNd(t) in the granitic gneisses are in the range from −5.7 to −1.2, which correspond to Nd model ages of 2.0–1.7 Ga, indicating a role for Mesoproterozoic to Paleoproterozoic rocks in the generation of the granitic protoliths. The documented geochemical features indicate that the protoliths for the gneisses have a similar petrogenesis and magmatic source, which may reflect partial melting of thickened crust with the addition of small amounts of mantle-derived material. The Central Tianshan Block probably constitute part of an exterior orogen that developed along the margin of the Rodinian supercontinent during the Early Neoproterozoic and underwent a transition from subduction to syn-collision compression at 975–911 Ma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexeiev D V, Biske Y S, Wang B, et al. 2015. Tectono-Stratigraphic framework and Palaeozoic evolution of the Chinese South Tianshan. Geotectonics, 49: 93–122.
Allen M B, Windley B F, Zhang C. 1993. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan, Central Asia. Tectonophysics, 220(1–4): 89–115.
Barbarin B. 1999. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments. Lithos, 46(3): 605–626.
Batchelor R A, Bowden P. 1985. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters. Chemical Geology, 48(1–4): 43–55.
Bonin B. 2007. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects. Lithos, 97(1–2): 1–29.
Chappell B W, White A J R. 1974. Two contrasting granite types. Pacific Geology, 8: 173–174.
Chappell B W, White A J R. 1992. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 83(1–2): 1–26.
Chappell B W. 1999. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos, 46(3): 535–551.
Chappell B W, White A J R. 2001. Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 48(4): 489–499.
Charvet J, Shu L S, Laurent-Charvet S, et al. 2011. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan belt, NW China. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(2): 166–184.
Chen X Y, Wang Y J, Sun L H. 2009. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the granitic gneisses from Bingdaban and Laerdundaban (Tianshan Orogen) and their geological significances. Geochimica, 38(5): 424–431. (in Chinese)
Chen Y B, Hu A Q, Zhang G X, et al. 1999. Zircon U-Pb age and its geological significance in the Duku Highway granitic gneiss in the Western Tianshan Mountains. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(21): 217–325. (in Chinese)
Coleman R G. 1989. Continental growth of northwest China. Tectonics, 8(3): 621–635.
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al. 1982. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80: 189–200.
Du L, Long X P, Yuan C, et al. 2018. Petrogenesis of Late Paleozoic diorites and A-type granites in the central Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Response to post-collisional extension triggered by slab breakoff. Lithos, 318–319: 47–59.
Foley S F, Barth M G, Jenner G A. 2000. Rutile/melt partition coefficients for trace elements and an assessment of the influence of rutile on the trace element characteristics of subduction zone magmas. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(5): 933–938.
Frost B R, Barnes C G, Collins W J, et al. 2001. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences. Journal of Petrology, 42(11): 2033–2048.
Gao J, Li M S, Xiao X C, et al. 1998. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan Orogen, northwestern China. Tectonophysics, 287(1–4): 213–231.
Gao J, Klemd R. 2003. Formation of HP-LT rocks and their tectonic implications in the western Tianshan Orogen, NW China: geochemical and age constraints. Lithos, 66(1–2): 1–22.
Gao J, Long L L, Klemd R, et al. 2009. Tectonic evolution of the South Tianshan orogen and adjacent regions, NW China: geochemical and age constraints of granitoid rocks. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1221–1238.
Gao J, Wang X S, Klemd R, et al. 2015. Record of assembly and breakup of Rodinia in the Southwestern Altaids: Evidence from Neoproterozoic magmatism in the Chinese Western Tianshan Orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 173–193.
Gao Z J, Peng C W. 1985. The Precambrian of Tianshan, Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geology, 3(2): 14–25. (in Chinese)
Goldstein S L, O’Nions R K, Hamilton P J. 1984. A Sm-Nd isotopic study of atmospheric dusts and particulates from major river systems. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 70(2): 221–236.
Han B F, He G Q, Wang X C, et al. 2011. Late Carboniferous collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan-Yili terranes in the western segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and implications for the Northern Xinjiang, western China. Earth-Science Reviews, 109(3–4): 74–93.
He Z Y, Zhang Z M, Zong K Q, et al. 2012. Neoproterozoic granulites from the northeastern margin of the Tarim Craton: Petrology, zircon U-Pb ages and implications for the Rodinia assembly. Precambrian Research, 212–213: 21–33.
He Z Y, Zhang Z M, Zong K Q, et al. 2014. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic studies of the Xingxingxia Complex from Eastern Tianshan (NW China): Significance to the reconstruction and tectonics of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Lithos, 190–191: 485–499.
He Z Y, Klemd R, Zhang Z M, et al. 2015. Mesoproterozoic continental arc magmatism and crustal growth in the eastern Central Tianshan Arc Terrane of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Geochronological and geochemical evidence. Lithos, 236–237: 74–89.
Hu A Q, Zhang G X, Zhang Q F, et al. 1998. Constraints on the age of basement and crustal growth in Tianshan Orogen by Nd isotopic composition. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 41(6): 648–657.
Hu A Q, Jahn B M, Zhang G X, et al. 2000. Crustal evolution and Phanerozoic crustal growth in northern Xinjiang: Nd isotopic evidence. Part I. Isotopic characterization of basement rocks. Tectonophysics, 328(1–2): 15–51.
Hu A Q, Wei G J, Deng W F, et al. 2006. 1.4 Ga SHRIMP U-Pb age for zircons of granodiorite and its geological significance from the eastern segment of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, China. Geochimica, 35(4): 333–345. (in Chinese)
Hu A Q, Jian W G, Zhang J B, et al. 2008. SHRIMP U-Pb ages for zircons of the amphibolites and tectonic evolution significance from the Wenquan domain in the West Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(12): 2731–2740. (in Chinese)
Hu A Q, Wei G J, Jahn B M, et al. 2010. Formation of the 0.9 Ga Neoproterozoic granitoids in the Tianshan Orogen, NW China: Constraints from the SHRIMP zircon age determination and its tectonic significance. Geochimica, 39(3): 197–212. (in Chinese)
Huang B T, He Z Y, Zong K Q, et al. 2014. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of Neoproterozoic granitic gneisses from the Alatage area, Xinjiang: constraints on the Precambrian crustal evolution in the Central Tianshan Block. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(3): 287–296.
Huang B T, He Z Y, Zhang Z M, et al. 2015a. Early Neoproterozoic granitic gneisses in the Chinese Eastern Tianshan: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 339–352.
Huang Z Y, Long X P, Kröner A, et al. 2015b. Neoproterozoic granitic gneisses in the Chinese Central Tianshan Block: Implications for tectonic affinity and Precambrian crustal evolution. Precambrian Research, 269: 73–89.
Huang Z Y, Long X P, Wang X C, et al. 2017. Precambrian evolution of the Chinese Central Tianshan Block: Constraints on its tectonic affinity to the Tarim Craton and responses to supercontinental cycles. Precambrian Research, 295: 24–37.
Jacobsen S B, Wasserburg G J. 1980. Sm-Nd isotopic evolution of chondrites. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 50(1): 139–155.
Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B. 2000. Massive granitoid generation in Central Asia: Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Episodes, 23(2): 82–92.
Keto L S, Jacobsen S B. 1987. Nd and Sr isotopic variations of Early Paleozoic oceans. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 84(1): 27–41.
Klemd R, John T, Scherer E E, et al. 2011. Changes in dip of subducted slabs at depth: Petrological and geochronological evidence from HP-UHP rocks (Tianshan, NW-China). Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 310(1–2): 9–20.
Kröner A, Alexeiev D V, Hegner E, et al. 2007. Accretionary growth and crust formation in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and comparison with the Arabian-Nubian shield. Memoir of the Geological Society of America, 200: 181–209.
Kröner A, Alexeiev D V, Hegner E, et al. 2012. Zircon and muscovite ages, geochemistry, and Nd-Hf isotopes for the Aktyuz metamorphic terrane: Evidence for an Early Ordovician collisional belt in the northern Tianshan of Kyrgyzstan. Gondwana Research, 21(4): 901–927.
Kröner A, Alexeiev D V, Rojas-Agramonte Y, et al. 2013. Mesoproterozoic (Grenville-age) terranes in the Kyrgyz North Tianshan: Zircon ages and Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin and evolution of basement blocks in the southern Central Asian Orogen. Gondwana Research, 23(1): 272–295.
Kröner A, Kovach V, Belousova E, et al. 2014. Reassessment of continental growth during the accretionary history of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 25(1): 103–125.
Li Z X, Bogdanova S V, Collins A S, et al. 2008. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia: A synthesis. Precambrian Research, 160(1–2): 179–210.
Liu X J, Zhang Z G, Xu J F, et al. 2020. The youngest Permian Ocean in Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from Geochronology and Geochemistry of Bingdaban Ophiolitic Melange in Central Tianshan, northwestern China. Geological Journal, 55(3): 2062–2079.
Long L L, Gao J, Klemd R, et al. 2011. Geochemical and geochronological studies of granitoid rocks from the Western Tianshan Orogen: Implications for continental growth in the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Lithos, 126(3–4): 321–340.
Lü Z, Zhang L, Du J, et al. 2008. Coesite inclusions in garnet from eclogitic rocks in western Tianshan, northwest China: Convincing proof of UHP metamorphism. American Mineralogist, 93(11–12): 1845–1850.
Ludwig K R. 2003. User’s manual for a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel (Isoplot/Ex version 3.0). Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 4: 1–71.
Ma X X, Shu L S, Santosh M, et al. 2013. Paleoproterozoic collisional orogeny in Central Tianshan: Assembling the Tarim Block within the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 228: 1–19.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5): 635–643.
Meert J G, Torsvik T H. 2003. The making and unmaking of a supercontinent: Rodinia revisited. Tectonophysics, 375(1–4): 261–288.
Meng Y, Tang S L, Wang K, et al. 2018. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and tectonic implications of Neoproterozoic granite from south of Dabaishitou, East Tianshan. Earth Science, 43(12): 4427–4442. (in Chinese)
Middlemost E A K. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3–4): 215–224.
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956–983.
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. 1976. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63–81.
Peng M X, Zhong C G, Zuo Q H, et al. 2012. The ages of the gneissic granite from Kawabulag area in the Eastern Tianshan and their geological significances. Xinjiang Geology, 30: 12–18. (in Chinese)
Peucat J J, Vidal P, Bernard-Griffiths J, et al. 1989. Sr, Nd and Pb isotopic systematics in the Archaean low- to high-grade transition zone of southern India: Synaccretion vs. post-accretion Granulites. Journal of Geology, 97(5): 537–549.
Rojas-Agramonte Y, Kroner A, Demoux A, et al. 2011. Detrital and xenocrystic zircon ages from Neoproterozoic to Palaeozoic arc terranes of Mongolia: Significance for the origin of crustal fragments in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 19(3): 751–763.
Rudnick R L. 1995. Making continental crust. Nature, 378(6557): 571–578.
Safonova I, Biske G, Romer R L, et al. 2016. Middle Paleozoic mafic magmatism and ocean plate stratigraphy of the South Tianshan, Kyrgyzstan. Gondwana Research, 30: 236–256.
Sengör A M C, Natal’in B A, Burtman V S. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435): 299–307.
Sengör A M C, Natal’in B A. 1996. Turkic-type orogeny and its role in the making of the continental crust. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 24(1): 263–337.
Shi W X, Liao Q A, Hu Y Q, et al. 2010. Characteristics of Mesoproterozoic granites and their geological significances from Middle Tianshan Block, East Tianshan district, NW China. Geological Science and Technology Information, 29(1): 29–37. (in Chinese)
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1): 313–345.
Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. 1985. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution. Journal of Geology, 94(4): 57–72.
Tretyakov A A, Degtyarev K E, Shatagin K N, et al. 2015. Neoproterozic anorogenic rhyolite-granite volcanoplutonic association of the Aktau-Mointy sialic massif (Central Kazakhstan): Age, source, and paleotectonic position. Petrology, 23(1): 22–44.
Wang B, Chen Y, Zhan S, et al. 2007a. Primary Carboniferous and Permian paleomagnetic results from the Yili Block (NW China) and their implications on the geodynamic evolution of Chinese Tianshan Belt. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 263(3–4): 288–308.
Wang B, Shu L S, Cluzel D, et al. 2007b. Geochemical constraints on Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Yili Block (Xinjiang, NW China): Implication for the tectonic evolution of Western Tianshan. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29(1): 148–159.
Wang B, Shu L S, Faure M, et al. 2011. Paleozoic tectonics of the southern Chinese Tianshan: Insights from structural, chronological and geochemical studies of the Heiyingshan ophiolitic mélange (NW China). Tectonophysics, 497(1–4): 85–104.
Wang B, Liu H S, Shu L S, et al. 2014. Early Neoproterozoic crustal evolution in northern Yili Block: Insights from migmatite, orthogneiss and leucogranite of the Wenquan metamorphic complex in the NW Chinese Tianshan. Precambrian Research, 242: 58–81.
Wang G H, Wang Z Z, Yan C M. 2019. A survey of the genesis classification and geochemical diagram discrimination of granite. Yunnan Geology, 38(1): 28–37. (in Chinese)
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. 1987. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 95(4): 407–419.
Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K, et al. 2004. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the continental growth of central Asia. American Journal of Science, 304(4): 370–395.
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Yong Y, et al. 2008a. Early Paleozoic to Devonian multiple-accretionary model for the Qilian Shan, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3–4): 323–333.
Xiao W J, Han C M, Yuan C, et al. 2008b. Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of central Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(2–4): 102–117.
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Yuan C, et al. 2009a. Paleozoic multiple subduction-accretion processes of the southern Altaids. American Journal of Science, 309(3): 221–270.
Xiao W J, Windley B, Huang B, et al. 2009b. End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids: implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1189–1217.
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Allen M B, et al. 2013. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan orogenic collage. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1316–1341.
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Sun S, et al. 2015. A tale of amalgamation of three Permo-Triassic Collage Systems in Central Asia: Oroclines, Sutures, and Terminal Accretion. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43(1): 477–507.
Xiong F H, Hou M C, Cawood P A, et al. 2019. Neoproterozoic I-type and highly fractionated A-type granites in the Yili Block, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Precambrian Research, 328: 235–249.
Yang T N, Li J Y, Sun G H, et al. 2008. Mesoproterozoic continental arc type granite in the Central Tianshan Mountalins: Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating and geochemical analyses. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 82(1): 117–125.
Yin J Y, Chen W, Xiao W J, et al. 2017. Geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic significance of the latest Devonian-early Carboniferous I-type granites in the Central Tianshan, NW China. Gondwana Research, 47: 188–199.
Zhang D Y, Zhang Z C, Encarnación J, et al. 2012. Petrogenesis of the Kekesai composite intrusion, western Tianshan, NW China: Implications for tectonic evolution during late Paleozoic time. Lithos, 146–147: 65–79.
Zhang Z Z, Gu L X, Yang H, et al. 2005. Characteristics and genesis of the Pingdingshan mega-augen gneissic granite in the eastern Tianshan Mountain areas. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 879–908. (in Chinese)
Zhong L L, Wang B, Alexeiev D V, et al. 2017. Paleozoic multi-stage accretionary evolution of the SW Chinese Tianshan: New constraints from plutonic complex in the Nalati Range. Gondwana Research, 45: 254–274.
Zhu W B, Charvet J, Xiao W J, et al. 2011. Continental accretion and intra-continental deformation of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42(5): 769–773.
Zhu X Y, Wang B, Cluzel D, et al. 2019. Early Neoproterozoic gneissic granitoids in the southern Yili Block (NW China): Constraints on microcontinent provenance and assembly in the SW Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Precambrian Research, 325: 111–131.
Zhu Y F, Zhou J, Zeng Y. 2007. The Tianger (Bingdaban) shear zone hosted gold deposit, west Tianshan, NW China: Petrographic and geochemical characteristics. Ore Geology Reviews, 32(1–2): 337–365.
Acknowledgements
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (92055208, 41772059, 42174080), the CAS “Light of West China” Program (2018-XBYJRC-003), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars, China (2018GXNSFFA281009), the Guangxi Science Innovation Base Construction Foundation (GuikeZY21195031), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation for Innovation Research Team Program (GXNSFGA380004), and the Fifth Bagui Scholar Innovation Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. We are grateful for editor’s excellent editorial handling and constructive comments from two anonymous reviewers, which substantially improved the final presentation of the manuscript. This is a contribution to International Geoscience Programme (IGCP) 662 and Guangxi Key Mineral Resources Deep Exploration Talent Highland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Liu, X., Xiao, W. et al. Neoproterozoic I-type granites in the Central Tianshan Block (NW China): geochronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications. J. Arid Land 14, 82–101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-021-0071-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-021-0071-8