Abstract
In many application problems such as the electromagnetics, the unknowns are usually defined at the edges to satisfy the continuity requirement. This paper develops the first positivity-preserving edge-centred finite volume scheme for diffusion problems on general unstructured polygonal meshes. The edge-centred unknowns are primary and have associated finite volume equations. The cell-vertex and cell-centred unknowns are treated as auxiliary ones and are interpolated by the primary unknowns, making the final scheme purely edge-centred. The scheme has a fixed stencil due to the fixed decomposition of the co-normal, which makes the scheme very easy to implement. The positivity-preserving property is rigorously proved. Numerical experiments indicate that the scheme has second-order accuracy and positivity for heterogeneous and anisotropic problems on highly distorted meshes.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Aavatsmark I, Barkve T, Bøe O, Mannseth T (1998) Discretization on unstructured grids for inhomogeneous, anisotropic media. I. Derivation of the methods. SIAM J Sci Comput 19(5):1700–1716
Brezzi F, Lipnikov K, Simoncini V (2005) A family of mimetic finite difference methods on polygonal and polyhedral meshes. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 15(10):1533–1551
Camier J, Hermeline F (2016) A monotone nonlinear finite volume method for approximating diffusion operators on general meshes. Int J Numer Methods Eng 107:496–519
Contreras F, Lyra P, Souza M, Carvalho D (2016) A cell-centered multipoint flux approximation method with a diamond stencil coupled with a higher order finite volume method for the simulation of oil-water displacements in heterogeneous and anisotropic petroleum reservoirs. Comput Fluids 127:1–16
Coudière Y, Vila J-P, Villedieu P (1999) Convergence rate of a finite volume scheme for a two-dimensional convection-diffusion problem. M2AN Math Model Numer Anal 33(3):493–516
Droniou J (2014) Finite volume schemes for diffusion equations: introduction to and review of modern methods. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 24(8):1575–1619
Gao Z, Wu J (2015) A second-order positivity-preserving finite volume scheme for diffusion equations on general meshes. SIAM J Sci Comput 37(1):A420–A438
Giacomini M, Sevilla R (2020) A second-order face-centred finite volume method on general meshes with automatic mesh adaptation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 121(23):5227–5255
Goldston RJ (2020) Introduction to plasma physics. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Le Potier C (2005) Schéma volumes finis monotones pour des opérateurs de diffusion fortement anisotropes sur des maillages de triangles non structurés. C R Acad Sci Paris Ser I(341):787–792
Lipnikov K, Shashkov M, Svyatskiy D, Vassilevski Y (2007) Monotone finite volume schemes for diffusion equations on unstructured triangular and shape-regular polygonal meshes. J Comput Phys 227(1):492–512
Lipnikov K, Svyatskiy D, Vassilevski Y (2009) Interpolation-free monotone finite volume method for diffusion equations on polygonal meshes. J Comput Phys 228(3):703–716
Lipnikov K, Svyatskiy D, Vassilevski Y (2012) Minimal stencil finite volume scheme with the discrete maximum principle. Russ J Numer Anal Math Model 27(4):369–385
Lipnikov K, Manzini G, Shashkov M (2014) Mimetic finite difference method. J Comput Phys 257:1163–1227
Liu Z, Miao S, Zhang Z (2023) A family of edge-centered finite volume schemes for heterogeneous and anisotropic diffusion problems on unstructured meshes. Comput Math Appl 146:165–175
Markowich P, Ringhofer C, Schmeiser C (1990) Semiconductor equations. Springer Vienna, Vienna
Miao S, Wu J (2022) A nonlinear correction scheme for the heterogeneous and anisotropic diffusion problems on polygonal meshes. J Comput Phys 448:110729
Potier CL (2020) A second order in space combination of methods verifying a maximum principle for the discretization of diffusion operators. C R Math Acad Sci Paris 358(1):89–95
Schneider M, Gläser D, Flemisch B, Helmig R (2018) Comparison of finite-volume schemes for diffusion problems. Oil Gas Sci Technol - Rev IFP Energies nouvelles 73:82
Sevilla R, Giacomini M, Huerta A (2018) A face-centred finite volume method for second-order elliptic problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 115(8):986–1014
Sevilla R, Giacomini M, Huerta A (2019) A locking-free face-centred finite volume (FCFV) method for linear elastostatics. Comput Struct 212:43–57
Su S, Dong Q, Wu J (2018) A decoupled and positivity-preserving discrete duality finite volume scheme for anisotropic diffusion problems on general polygonal meshes. J Comput Phys 372:773–798
Su S, Dong Q, Wu J (2019) A vertex-centered and positivity-preserving scheme for anisotropic diffusion equations on general polyhedral meshes. Math Methods Appl Sci 42(1):59–84
Terekhov K, Mallison B, Tchelepi H (2017) Cell-centered nonlinear finite-volume methods for the heterogeneous anisotropic diffusion problem. J Comput Phys 330:245–267
Vieira L, Giacomini M, Sevilla R, Huerta A (2020) A second-order face-centred finite volume method for elliptic problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 358(112655):23
Vila-Pérez J, Giacomini M, Sevilla R, Huerta A (2022) A non-oscillatory face-centred finite volume method for compressible flows. Comput Fluids 235:105272
Wang Y, Yang T, Chang L (2022) An edge-centered scheme for anisotropic diffusion problems with discontinuities on distorted quadrilateral meshes. J Comput Sci 64:101832
Yuan G, Sheng Z (2008) Monotone finite volume schemes for diffusion equations on polygonal meshes. J Comput Phys 227(12):6288–6312
Zhang X, Su S, Wu J (2017) A vertex-centered and positivity-preserving scheme for anisotropic diffusion problems on arbitrary polygonal grids. J Comput Phys 344:419–436
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for the carefully readings and valuable suggestions. This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12201020, 12288101), the State-funded Postdoctoral Fellowship Program (GZB20230028), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation grants (2023M740103), the foundation of LCP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Lemma 1
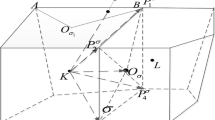
For arbitrary two triangles \(\triangle \varvec{x}_E\varvec{x}_P\varvec{x}_K\) and \(\triangle \varvec{x}_F\varvec{x}_P\varvec{x}_K\) with the common edge \(\sigma \) (see Fig. 2), \(\varvec{n}_{E,\sigma }\) is the unit outer vector normal to the edge \(\sigma \) outward to the triangle \(\triangle \varvec{x}_E\varvec{x}_P\varvec{x}_K\). \(\Lambda \) is a positive definite tensor. For the decomposition (3) and (7), we have
where \(d_{E,\sigma }\) (resp. \(d_{F,\sigma }\)) denotes the distance from the vertex \({\varvec{x}}_{E}\) (resp. \({\varvec{x}}_{F}\)) to the edge \({\varvec{x}}_K{\varvec{x}}_P\).
Proof
The geometrical relations gives
Combined this with (4), we have
where the identity \({\mathcal {R}({\varvec{x}}_P{\varvec{x}}_K)}=-|{\varvec{x}}_K{\varvec{x}}_P|{\varvec{n}}_{E,\sigma }\) is used in second equality. Similarly, we obtain
Recalling that \({\varvec{n}}_{E,\sigma }=-{\varvec{n}}_{F,\sigma }\) and \(\Lambda \) is positive definite, we immediately obtain (27). \(\square \)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, S., Su, S. A positivity-preserving edge-centred finite volume scheme for heterogeneous and anisotropic diffusion problems on polygonal meshes. Comp. Appl. Math. 43, 196 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-024-02716-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-024-02716-4