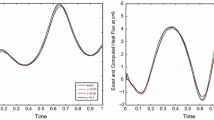
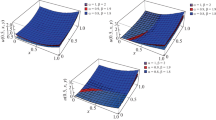
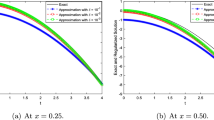
Abstract
In this study, we propose an effective approach for the numerically solution of a class of one-dimensional nonlinear inverse time fractional heat conduction problems. The boundary heat fluxes are considered as unknown functions of the boundary temperatures. A numerical method based on the finite difference and mollification approaches is developed to determine the unknown boundary functions. The stability and convergence of the numerical method are proved. Four test problems are conducted to illustrate the ability of the numerical algorithm.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkowitz B, Scher H, Silliman SE (2000) Anomalous transport in laboratory-scale, heterogeneous porusmedia. Water Resour Res 36:149–158
Chechkin AV, Gorenflo R, Sokolov IM, Gonchar VY (2003) Distributed order time fractional diffusion equation. Fract Calc Appl Anal 6:259–279
Chechkin AV, Gorenflo R, Sokolov IM (2005) Fractional diffusion in inhomogeneous media. J Phys A Math Gen 38:679–684
Cheng J, Nakagawa J, Yamamoto M, Yamazaki T (2009) Uniqueness in an inverse problem for a onedimensional fractional diffusion equation. Inverse Probl 25:115002
Dehghana M, Yousefi SA, Rashedi K (2013) Ritz–Galerkin method for solving an inverse heat conduction problem with a nonlinear source term via Bernstein multi-scaling functions and cubic B-spline functions. Inverse Probl Sci Eng 21(3):500–523
Garshasbi M, Dastour H (2015) Estimation of unknown boundary functions in an inverse heat conduction problem using a mollified marching scheme. Numer Algorithms 68:769–790
Garshasbi M, Dastour H (2016) A mollified marching solution of an inverse ablation-type moving boundary problem. Comput Appl Math 35:6–73
Garshasbi M, Reihani P, Dastour H (2012) A stable numerical solution of a class of semi-linear Cauchy problems. J Adv Res Dyn Control Syst 4:56–67
Giona M, Gerbelli S, Roman HE (1992) Fractional diffusion equation and relaxation in complex viscoelastic materials. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 191:449–453
Hatano Y, Hatano N (1998) Dispersive transport of ions in column experiments: an explanation of long-tailed profiles. Water Resour Res 34:1027–33
Jalalvand M, Jazbi B, Mokhtarzadeh MR (2013) A finite difference method for the smooth solution of linear Volterra integral equations. Int J Non-linear Anal Appl 4(2):1–10
Jin BB, Rundell W (2012) An inverse problem for a one dimensional time fractional diffusion problem. Inverse Probl 28:075010
Lin Y, Xu C (2007) Finite difference-spectral approximation for the time-fractional diffusion equation. J Comput Phys 225:1533–1552
Luchko Y (2009) Maximum principle for the generalized time-fractional diffusion equation. J Math Anal Appl 351:218–223
Luchko Y (2011) Maximum principle and its application for the time-fractional diffusion equations. Fract Calc Appl Anal 14:110–124
Mainadri F (1996) The fundamental solutions for the fractional diffusion-wave equation. Appl Math Lett 9:23–28
Metzler R, Klafter J (2000) The random walks guide to anomalous diffusion: a fractional dynamics approach. Phys Rep 339(1):1–77
Murio DA (2002) Mollification and space marching. In: Woodbury K (ed) Inverse engineering handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Murio DA (2006) On the stable numerical evaluation of Caputo fractional derivatives. Comput Math Appl 51:1539–1550
Murio DA (2007) Implicit finite difference approximation for time fractional diffusion equations. Comput Math Appl 56:1138–1145
Murio DA (2008) Time fractional IHCP with Caputo fractional derivatives. Comput Math Appl 56:2371–2381
Murio DA, Mejia CE (2008) Generalized time fractional IHCP with Caputo fractional derivatives. J Phys 135:1–8
Nigmatullin RR (1986) The realization of the generalized transfer equation in a medium with fractal geometry. Phys Stat Solidi B 133:425–30
Podlubny I (1999) Fractional differential equations. Academic Press, San Diego
Povstenko Y (2015) Linear fractional diffusion-wave equation for scientists and engineers. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Roman HE, Alemany PA (1994) Continuous-time random walks and the fractional diffusion equation. J Phys A Math Gen 27:3407–3410
Safarzade A, Heidari H (2019) Finite time mix synchronization of delay fractional-order chaotic systems. Glob Anal Discr Math 3(1):33–52
Sakamoto K, Yamamoto M (2011) Initial value/boundary value problems for fractional diffusion-wave equations and applications to some inverse problems. J Math Anal Appl 382(1):426–447
Sakamoto K, Yamamoto M (2010) Initial value/boundary value problems for fractional diffusion-wave equations and applications to some inverse problems. In: Preprint UTMS, 2010–2014
Shidfar A, Karamali GR, Damirchi J, Reihani P (2006) An inverse heat conduction problem with a nonlinear source term. Nonlinear Anal Theory Methods Appl 65:615–621
Sokolov IM, Klafter J, Blumen A (2002) Fractional kinetics. Phys Today 55:48–54
Wei T, Zhang ZQ (2013) Reconstruction of a time-dependent source term in a time-fractional diffusion equation. Eng Anal Bound Elem 37:23–31
Zhang Y, Xu X (2011) Inverse source problem for a fractional diffusion equation. Inverse Probl 27:035010
Zhou L, Selim HM (2003) Application of the fractional advection–dispersion equations in porous media. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67(4):1079–1084
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the referees for their valuable comments which helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by José Tenreiro Machado.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toubaei, S., Garshasbi, M. & Reihani, P. Boundary functions determination in an inverse time fractional heat conduction problem. Comp. Appl. Math. 38, 190 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-019-0944-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-019-0944-z