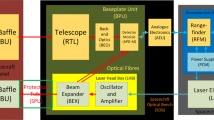
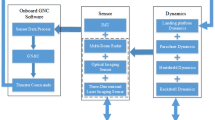
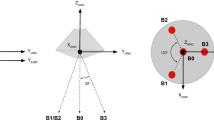
Abstract
The 1st Brazilian deep space mission, ASTER, will carry onboard a laser altimeter to assist in the investigation of the triple asteroid system 2001-SN263. The instrument was named ALR and its development is now in progress. A series of studies was conducted with a view to the creation of the instrument control software. These studies involved the modeling of the instrument and its operation and resulted in the creation of a package of computer programs to simulate the operation of a pulsed laser altimeter with operating principle based on the measurement of the time of flight of the travelling pulse. The software Simulator was called \({ALR{\_}Sim}^{\textregistered }\), and the results obtained with its use represent what should be expected as return signal when laser pulses are fired toward a target, reflect on it and return to be detected by the instrument. The program was successfully tested with regard to some of the most common situations expected. It constitutes now the main workbench dedicated to the creation and testing of control software to embark in the ALR. In addition, the Simulator constitutes also an important tool to assist the creation of software to be used on Earth, in the processing and analysis of the data received from the instrument. The main focus of this work is the special case which involves the modeling of a surface with crater, along with the simulation of the instrument operation above this type of terrain. The approach used here was the comparison of the return signal obtained from the crater with the expected return signal in case of a flat and homogeneous surface. This method proved to be useful in the extraction of details of the terrain with crater and is recommended for the analysis of the return signal of any surface.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe S et al (2006) Mass and local topography measurements of Itokawa by Hayabusa. Science 312:1344. doi:10.1126/science.1126272
Araujo RAN, Winter OC, Prado AFBA (2015) Stable retrograde orbits around the triple system 2001 SN263. Mon Not R Astron Soc MNRAS 449:4404–4414. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv592
Chapman CR (1995) Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous: Eros as the key to the S-type conundrum. In: Proceedings of XXVI lunar planetary science conference, pp 229–230
Cole DT (1998) NEAR laser rangefinder: a tool for the mapping and topologic study of asteroid 433 Eros. Johns Hopkins APL Techn Digest 19(2):142–157
de Brum AGV, Rodrigues AP (2013) Topographic profile of a target with use of laser pulses. A survey directed to the Brazilian deep space mission ASTER. J Phys: Conf Ser 465(01):2003. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/465/1/012003
de Brum AGV, Hetem A Jr, Rego IS, Francisco CPF, Fenili A, Madeira F, da Cruz FC, Assafin M (2011) Preliminary development plan of the ALR, the laser rangefinder for the ASTER deep space mission to the 2001 SN263 asteroid. J Aerosp Technol Manag JATM 3:331–338. doi:10.5028/jatm.2011.03033611
de Brum AGV, da Cruz FC, Hetem A Jr, Rodrigues AP (2014) ALR—a laser altimeter for the first Brazilian deep space mission. Modeling and simulation of the instrument and its operation. J Comput Appl Math. 1:1. doi:10.1007/s40314-014-0145-8
ESA (2014) European Space Agency Science and Technology web site. http://sci.esa.int/rosetta/ Acessed Nov 2014
Fujiwara A et al (2006) The rubble-pile asteroid Itokawa as observed by Hayabusa. Sci 312(5778): 1330–1334
Macau EEN, Winter OC, Velho HFC, Sukanov AA, de Brum AGV, Ferreira JL, Hetem Jr. A, Sandonato GM, Sfair R (2011) The aster mission: exploring for the first time a triple system asteroid. In: Proceedings of the 62nd international astronautical congress, 2011, vol 1, Cape Town
Perna D et al (2014) The triple near-Earth asteroid (153591) 2001 SN263: an ultra-blue, primitive target for the Aster space mission. Astron Astrophys A&A 568:L6. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201424447
Shan J, Toth CK (2009) Topographic laser ranging and scanning: principles and processing. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Steinvall O (2000) Effects of target shape and reflection on laser radar cross sections. Appl Opt 39(24):4381–4391
Sukhanov AA, Velho HFC, Macau EEN, Winter OC (2010) The Aster project: flight to a near-Earth asteroid. Cosm Res 48:433–450
Vaz Tolentino Observatório Lunar (2014) http://www.vaztolentino.com.br/imagens/6667-As-crateras-ARISTOTELES-e-EUDOXUS. Acessed Aug 2014
Yano H et al (2006) Touchdown of the Hayabusa spacecraft at the Muses Sea on Itokawa. Science 312(5778):1350–1353. doi:10.1126/science.1126164
Yano H et al (2012) Planetary Protection of Hayabusa-2 mission, a sample return from 1999 JU3, C-type NEO. Presentation for the NASA planetary protection subcommittee. http://science.nasa.gov/media/medialibrary/2012/05/04/Hayabusa-2_-_Hajime_Yano.pdf. Accessed Feb 2013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Elbert E. N. Macau, Antônio Fernando Bertachini de Almeida Prado and Cristiano Fiorilo de Melo.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Brum, A.G.V., da Cruz, F.C. & Hetem, A. Laser altimeter for the deep space mission aster modeling and simulation of the instrument operation above a surface with crater. Comp. Appl. Math. 35, 739–751 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-016-0322-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-016-0322-z
Keywords
- Deep space mission ASTER
- Asteroid 2001-SN263
- ALR-laser altimeter
- Pulsed laser rangefinder
- Modeling and simulation
- ALR_Sim simulator