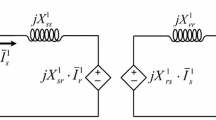
Abstract
We present an analytical model of permanent-magnet five-phase synchronous machines including the third space harmonic of the airgap induction, which is generally disregarded by most authors, despite its relevance for the estimation of the machine behavior. Firstly, we address the numerical estimation of the self and mutual inductances required by the model using the machine dimensions and winding characteristics. Afterward, we derive a model in the stator reference frame, which is subsequently simplified through complex coordinate transformations, thus resulting in a set of simpler, decoupled equations expressed in the stator reference frame. Then, to test and validate the model, it was applied to two prototype machines available in our laboratory. We designed the rotor of these two machines so that each has a different amplitude for the third harmonic of the airgap induction. Finally, to further validate the model, analytical results were compared with corresponding results obtained through finite element analyses and also through practical experiments, from which an excellent agreement emerged between the three types of results. The results obtained with the finite element method and through experiments also proved not only that the model is consistent and valid, but also that it can be used to predict the machine behavior under normal and faulty operation.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Khalik, A. S., Ahmed, S., & Massoud, A. M. (2016). Steady-state mathematical modeling of a five-phase induction machine with a combined star/pentagon stator winding connection. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 63(3), 1331–1343. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2015.2493151
Abdel-Khalik, A. S., Hamdy, R. A., Massoud, A. M., et al. (2019). Low-order space harmonic modeling of asymmetrical six-phase induction machines. IEEE Access, 7, 6866–6876. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2889044
Bianchi, N., & Bolognani, S. (1998). Magnetic models of saturated interior permanent magnet motors based on finite element analysis. In Conference record of 1998 IEEE industry applications conference. Thirty-Third IAS annual meeting (Cat. No.98CH36242) (vol. 1, pp. 27–34). https://doi.org/10.1109/IAS.1998.732255
Bo, Z., Jimin, Z., Guiqing, H., et al. (2011). Asymmetry of inductance and torque ripple of multi-unit permanent magnet synchronous motor. In 2011 International conference on electrical machines and systems (pp. 1–4). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEMS.2011.6073960
Brauer, H. J., Hennen, M. D., & De Doncker, R. W. (2011). Control for polyphase switched reluctance machines to minimize torque-ripple and decrease ohmic machine losses. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2011.2161332
Cao, B., Grainger, B. M., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Direct torque model predictive control of a five-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 36(2), 2346–2360. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2020.3011312
Chen, J., Li, J., Qu, R., et al. (2018). Magnet-frozen-permeability FEA and DC-biased measurement for machine inductance: Application on a variable-flux pm machine. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65(6), 4599–4607. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2772165
Chen, Y., Zhu, Z., & Howe, D. (2005). Calculation of d- and q-axis inductances of pm brushless ac machines accounting for skew. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 41(10), 3940–3942. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2005.854976
Chomat, M., Schreier, L., & Bendl, J. (2015). Effect of stator winding configurations on operation of converter fed five-phase induction machine. In 2015 International conference on electrical drives and power electronics (EDPE) (pp 488–496). https://doi.org/10.1109/EDPE.2015.7325343
Fu, J. R., & Lipo, T. (1993). Disturbance free operation of a multiphase current regulated motor drive with an opened phase. In Industry applications society annual meeting, 1993, conference record of the 1993 IEEE (vol. 1, pp. 637–644). https://doi.org/10.1109/IAS.1993.298884
Gieras, J. (2010). Permanent magnet motor technology: Design and applications. [Electrical and computer engineering, CRC PressINC, Boca Raton,USA. http://books.google.com.br/books?id=8b6yPQAACAAJ
Hendershot, J., Hendershot, J., & Miller, T. (2010). Design of brushless permanent-magnet machines. Motor Design Books, LLC. http://books.google.com/books?id=n833QwAACAAJ
Hussain, T., Ahmed, S., Iqbal, A., et al. (2008). Five-phase induction motor behaviour under faulted conditions. In India conference, 2008. INDICON 2008. Annual IEEE (pp. 509–513). https://doi.org/10.1109/INDCON.2008.4768776
Jacobina, C., Freitas, I., Oliveira, T., et al. (2004). Fault tolerant control of five-phase ac motor drive. In Power electronics specialists conference, 2004. PESC 04. 2004 IEEE 35th annual (vol. 5, pp. 3486–3492). https://doi.org/10.1109/PESC.2004.1355091
Kestelyn, X., & Semail, E. (2011). A vectorial approach for generation of optimal current references for multiphase permanent magnet synchronous machines in real-time. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2011.2119454
Kim, W. H., Kim, M. J., Lee, K. D., et al. (2014). Inductance calculation in IPMSM considering magnetic saturation. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 50(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2013.2277586
Klingshirn, E. (1983). High phase order induction motors—part I-description and theoretical considerations. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems PAS, 102(1), 47–53. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAS.1983.317996
Klingshirn, E. (1983). High phase order induction motors—part II-experimental results. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems PAS, 102(1), 54–59. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAS.1983.317997
Lee, J. Y., Lee, S. H., Lee, G. H., et al. (2006). Determination of parameters considering magnetic nonlinearity in an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 42(4), 1303–1306. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2006.871951
Levi, E. (2008). Multiphase electric machines for variable-speed applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 55(5), 1893–1909. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2008.918488
Levi, E., Bojoi, R., Profumo, F., et al. (2007). Multiphase induction motor drives—a technology status review. IET Electric Power Applications, 1(4), 489–516. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-epa:20060342
Li, Z., Huang, X., Wu, L., et al. (2019). Open-circuit field prediction of interior permanent-magnet motor using hybrid field model accounting for saturation. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 55(7), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2019.2907023
Long, L., Sun, T., & Liang, J. (2020). Five phase permanent magnet synchronous motor decoupled model with dual frame frequency adaptive flux observer. Energy Reports, 6, 1403–1408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.11.010
Meessen, K. J., Thelin, P., Soulard, J., et al. (2008). Inductance calculations of permanent-magnet synchronous machines including flux change and self- and cross-saturations. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 44(10), 2324–2331. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2008.2001419
Miller, T. (1989). Brushless permanent-magnet and reluctance motor drives. Monographs in electrical and electronic engineering. Clarendon Press.
Nanoty, A., & Chudasama, A. (2011). Design of multiphase induction motor for electric ship propulsion. In Electric ship technologies symposium (ESTS), 2011 IEEE (pp. 283 –287). https://doi.org/10.1109/ESTS.2011.5770882
Parsa, L., & Toliyat, H. (2004). Fault-tolerant five-phase permanent magnet motor drives. In Conference record of the 2004 IEEE industry applications conference, 2004. 39th IAS Annual Meeting (vol. 2, pp. 1048–1054). https://doi.org/10.1109/IAS.2004.1348542
Parsa, L., & Toliyat, H. (2005). Five-phase permanent-magnet motor drives. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 41(1), 30–37. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2004.841021
Parsa, L., Toliyat, H. A., & Goodarzi, A. (2007). Five-phase interior permanent-magnet motors with low torque pulsation. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 43(1), 40–46. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2006.887235
Pavithran, K., Parimelalagan, R., & Krishnamurthy, M. (1988). Studies on inverter-fed five-phase induction motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 3(2), 224–235. https://doi.org/10.1109/63.4353
Pereira, L. (1997). Comparison between the dc machine and the auto-commutated synchronous machine. PhD thesis, University of Kaiserslautern (in German).
Pereira, L. A., Scharlau, C., Pereira, L. F. A., et al. (2006). General model of a five-phase induction machine allowing for harmonics in the air gap field. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 21(4), 891–899.
Pereira, L. A., Haffner, S., Pereira, L. F. A., et al. (2013a). Performance comparison of five phase and three phase induction machines under steady state including losses and saturation. In Industrial electronics society, IECON 2013—39th annual conference of the IEEE (pp. 3036–3041). https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2013.6699613
Pereira, L. A., Haffner, S., Pereira, L. F. A., et al. (2013b). Torque capability of high phase induction machines with sinusoidal and trapezoidal airgap field under steady state. In IECON 2013—39th Annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society (pp. 3183–3188). https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2013.6699637
Pereira, L. A., Haffner, S., Pereira, L. F. A., et al. (2015). Parameterized model and performance of five-phase induction machines including losses and saturation. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 26(3), 255–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-015-0169-3
Pyrhonen, J., Jokinen, T., & Hrabovcova, V. (2013). Design of electrical machines. John Wiley Sons.
Richter, R. (1963). Elektrische Maschinen—Zweiter Band—Synchronmaschine und Einankerumformer. Birkhäuser Verlag.
Richter, R. (1967). Elektrische Maschinen-Erster Band–Allgemeine Berechnungselemente-Die Gleichstrommaschine. Birkhäuser Verlag.
Sadeghi, S., & Parsa, L. (2011). Multiobjective design optimization of five-phase Halbach array permanent-magnet machine. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 47(6), 1658–1666. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2106217
Sahu, S., Nayak, B., & Dash, R. N. (2021). Modeling and vector control of five phase surface permanent magnet synchronous motor. In 2021 Innovations in Energy Management and Renewable Resources(52042) (pp. 1–4). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMRE52042.2021.9387021
Scharlau, C., Pereira, L. F. A., Pereira, L. A., et al. (2008). Performance of a five-phase induction machine with optimized air gap field under open loop \(v\)/\(f\) control. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 23(4), 1046–1056.
Schreier, L., Bendl, J., & Chomat, M. (2013). Comparison of five-phase induction machine operation with various stator-winding arrangements. In IECON 2013—39th Annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society (pp 2685–2690). https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2013.6699555
Schreier, L., Bendl, J., & Chomat, M. (2017). Operation of five-phase induction motor after loss of one phase of feeding source. Electrical Engineering, 99(1), 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0370-9
Sneessens, C., Labbe, T., Baudart, F., et al. (2009). Modelling and torque control of a five-phase permanent-magnet synchronous motor using tooth-concentrated winding technology. In 2009 8th International symposium on advanced electromechanical motion systems and electric drives joint symposium (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/ELECTROMOTION.2009.5259107
Sun, T., Kwon, S. O., & Lee, S. H., et al. (2008). Investigation and comparison of inductance calculation methods in interior permanent magnet synchronous motors. In 2008 International conference on electrical machines and systems (pp. 3131–3136).
Tani, A., Mengoni, M., Zarri, L., et al. (2012). Control of multiphase induction motors with an odd number of phases under open-circuit phase faults. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 27(2), 565–577. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2011.2140334
Tao, T., Zhao, W., Du, Y., et al. (2020). Simplified fault-tolerant model predictive control for a five-phase permanent-magnet motor with reduced computation burden. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 35(4), 3850–3858. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2019.2934578
Toliyat, H. (1998). Analysis and simulation of five-phase variable-speed induction motor drives under asymmetrical connections. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 13(4), 748–756. https://doi.org/10.1109/63.704150
Toliyat, H., Lipo, T., & White, J. (1991). Analysis of a concentrated winding induction machine for adjustable speed drive applications. I. motor analysis. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 6(4), 679–683. https://doi.org/10.1109/60.103641
Toliyat, H., Lipo, T., & White, J. (1991). Analysis of a concentrated winding induction machine for adjustable speed drive applications. II. motor design and performance. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 6(4), 684–692. https://doi.org/10.1109/60.103642
Walker, J., Dorrell, D., & Cossar, C. (2005). Flux-linkage calculation in permanent-magnet motors using the frozen permeabilities method. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 41(10), 3946–3948. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2005.854973
Wang, P., Zheng, P., Sui, Y., et al. (2014). Design and analytical inductance calculations of five-phase fault-tolerant permanent-magnet machine. In 2014 17th International conference on electrical machines and systems (ICEMS), (pp. 1639–1642). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEMS.2014.7013740
Ward, E., & Härer, H. (1969). Preliminary investigation of an invertor-fed 5-phase induction motor. In Proceedings of the institution of electrical engineers, IET (pp. 980–984).
White, D. C. S., & Woodson, H. H. (1968). Electromechanical energy conversion. The MIT Press.
Wu, S., Shi, T., Chen, Z., et al. (2022). Analytical modeling of equivalent air-gap length and inductance calculation of interior permanent magnet motors. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(2), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2021.3131526
Zhang, Z. (2021). A robust non-permanent magnet five-phase synchronous reluctance traction motor. In 2021 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC) (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITEC51675.2021.9490116
Zheng, P., Sui, Y., Zhao, J., et al. (2011). Investigation of a novel five-phase modular permanent-magnet in-wheel motor. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 47(10), 4084–4087. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2150207
Zhu, Z., & Howe, D. (1997). Winding inductances of brushless machines with surface-mounted magnets. In 1997 IEEE International electric machines and drives conference record (pp. WB2/2.1–WB2/2.3). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMDC.1997.604305
Acknowledgements
This study was financed in part by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001. This study was also supported by Foundation for Research Support of the State of Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS), (Program Pesquisador Gaúcho—2022) under the grant number 21/2551-0002155-1. Finally, the authors also thank the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for the financial support under grants numbers 306126/2019-2, 404491/2021-9, and 305036/2022-0, and WEG Equipamentos Elétricos (Jaraguá do Sul, Brazil) for the technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A: Main Dimensions of the Prototype Machines
The main dimensions of the two prototype machines of 1.5 KW designed and currently available in our laboratory at UFRGS can be seen in Figs 19 and 20, in which Fig. 19 illustrates the stator dimensions and details of the stator slots, while Fig. 20 details the rotor dimensions. Note also that both machines have been used to test and validate the proposed model.
Appendix B: Iron and Permanent Magnet Characteristics
In Fig. 21, we present the main magnetic characteristic (induction B versus magnetic field H) of the iron parts of the two prototypes used in this paper for numerical and experimental validation of the proposed analytical model. In addition, Fig. 22 shows the demagnetization curve of permanent magnets (N38UH) at a temperature of \(22\,^\circ \)C, where the remanent induction and the coercive force are in red.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, L.A., Branco, G.G.C., Nicol, G. et al. Model of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Including the Third Harmonic of the Airgap Induction. J Control Autom Electr Syst 35, 191–211 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-023-01056-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-023-01056-8