Abstract
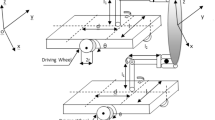
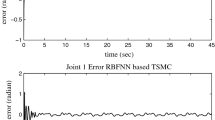
The purpose of this article is to present a fast terminal sliding mode control scheme for constrained mobile manipulators with both holonomic and non-holonomic constraints while taking uncertainties and external disturbances into account. Existing techniques cannot manage this kind of system because of the unavoidable errors in a mobile manipulator’s dynamical model. In order to improve position/force tracking performance of constrained mobile manipulators, a control scheme is presented that combines the advantages of fast terminal sliding mode control and neural networks. Without the requirement for offline training, the manipulator’s unknown dynamics are learned using a radial basis function neural network. Using an adaptive bound component, the bounds on uncertainties and neural network reconstruction error are quantified. The stability of the system and the convergence of the tracking errors are investigated using the Lyapunov theory. Analyzed simulation results indicate the proposed controller’s robust performance in a variety of circumstances.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilart, L.E., Hamelt, T., & Souerest, P. (1997). Robust path following control for wheeled robots via sliding mode techniques. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robot and systems. Innovative Robotics for Real-World Applications. IROS ’97, 3, 1389–1395.
Bloch, A., & Drakunov, S. (1995). Tracking in nonholonomic dynamic systems via sliding modes. In Proceedings of the 34th conference on decision and control. 2103–2106.
Boukens, M., & Boukabou, A. (2017). Design of an intelligent optimal neural network-based tracking controller for nonholonomic mobile robot systems. Neuro-computing, 226, 46–57.
Boukens, M., Boukabou, A., & Chadli, M. (2017). Robust adaptive neural network based trajectory tracking control approach for nonholonomic electrically driven mobile robots. Robotics and Autonomous System, 92, 30–40.
Chung, J. H., & Velinsky, S. A. (1998). Modeling and control of a mobile manipulator. Robotica, 16(6), 607–613.
Dao, Q. T., Mai, D. H., & Nguyen, D. K. (2022). Adaptive parameter integral sliding mode control of pneumatic artificial muscles in antagonistic configuration. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 33, 1116–1124.
Dong, W. (2002). On trajectory and force tracking control of constrained mobile manipulators with parameter uncertainty. Automatica, 38, 1475–1484.
Dong, X., Dongbin, Z., Jianqiang, Y., & Xiangmin, T. (2009). Trajectory tracking control of omnidirectional wheeled mobile manipulators: Robust neural network-based sliding mode approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Part B (Cybernetics), 39, 788–799.
Han, S., Ha, H., Zhao, Y., & Lee, J. (2017). Assumed model feedforward sliding mode control for a wheeled mobile robot with 3-dof manipulator. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 31(3), 1463–1475.
Hoang, N. B., & Kang, H. J. (2016). Neural network-based adaptive tracking control of mobile robots in the presence of wheel slip and external disturbance force. Neurocomputing, 188, 12–22.
Jorge, A., Chacal, B., & Ramirez, H. S. (1994). On the sliding mode control of wheeled mobile robots. IEEE, 2, 1938–1943.
Kumar, Ruchika, et al. (2019). Finite time control scheme for robot manipulators using fast terminal sliding mode control and RBFNN. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 1(7), 758–766.
Kumar, N., Panwar, V., Borm, J. H., & Chai, J. (2014). Enhancing precision performance of trajectory tracking controller for robot manipulators using RBFNN and adaptive bound. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 231, 320–328.
Lanzon, & Richards, R. J. (1999). Trajectory/force control of robot manipulators using sliding mode and adaptive control. Proceedings of the American Control Conference, 3, 1940–1944.
Lee, M. J., & Choi, Y. K. (2004). An adaptive neurocontroller using RBFN for robot manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 51(3), 711–717.
Lewis F., Jagannathan S., & Yesildirek, A. (1999). Neural network control of robot manipulators and nonlinear systems, Taylor and Francis.
Lewis, F. W., Jagannathan, S., & Yesildirak, A. (1998). Neural network control of robot manipulators and non-linear systems. CRC Press.
Li, J. F., & Xiang, F. H. (2021). RBF network adaptive sliding mode control of ball and plate system based on reaching law. Arabian Journal of Science and Engineering, 47, 9393–9404.
Li, Z., Gu, J., Ming, A., Xu, C., & Shimojo, M. (2006). Intelligent compliant force/motion control of nonholonomic mobile manipulator working on the nonrigid surface. Neural Computing and Applications, 15, 204–216.
Li, Z., Ge, S. S., & Ming, A. (2007a). Adaptive robust motion/force control of holonomic-constrainted nonholonomic mobile manipulator. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 37(3), 607–616.
Li, Z., Yang, C., Luo, J., Wang, Z., & Ming, A. (2007b). Robust motion /force control of nonholonomic mobile manipulator using hybrid joints. Advanced Robotics, 21(11), 1231–1252.
Mai, T., & Wang, Y. (2014). Adaptive force/motion control system based on recurrent fuzzy wavelet CMAC neural networks for condenser cleaning crawler-type mobile manipulator robot. IEEE Transaction on Control Systems Technology, 22(5), 1973–1982.
Matraji, I., Al-Durra, Haryono, A., Al-Wahedi, K., & Abou-Khousa, M. (2018). Trajectory tracking control of skid-steered mobile robot based on adaptive second order sliding mode control. Control Engineering Practice, 72, 167–176.
Mohamed, B., Damak, T., & Jallouli, M. (2011). Robust adaptive control for mobile manipulators. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 8(1), 8–13.
Panwar, V. (2016). Wavelet neural network-based H\(\infty \) trajectory tracking for robot manipulators using fast terminal sliding mode control. Robotica, 35(7), 1488–1503.
Park, J., & Sandberg, J. W. (1991). Universal approximation using radial basis function networks. Neural Computing, 3, 246–257.
Pavlov, V., & Timofeyev, A. (1976). Construction and stabilization of programmed movements of a mobile robot-manipulator. Eng. Cybernet, 14, 70–79.
Rani, M., Kumar, N., & Singh, H. P. (2018). Efficient position/force control of constrained mobile manipulators. International Journal of Dynamic and Control, 6, 1629–1638.
Ruchika, Kumar, N., & Dinanath. (2019). Non-singular terminal sliding mode control of robot manipulators with \(H_\infty \) trajectory tracking performance. Arabian Journal of Science and Engineering, 44, 9057–9065.
Singh, H. P., & Sukavanam, N. (2012). Intelligent robust adaptive trajectory and force tracking controller for holonomic constrained nonholonomic mobile manipulators. Advance Science Letters, 16(1), 313–321.
Slotine, J. J. E. (1985). The robust control of robot manipulators. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 4(2), 49–64.
Su, C., & Stepanenko. (1994). Robust motion/force control of mechanical systems with classical nonholonomic constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 39(3), 609–614.
Tang, Y. (1998). Terminal sliding mode control for rigid robots. Automatica, 34, 51–56.
Wu, X., Wang, Y., & Dang, X. (2014). Robust adaptive sliding-mode control of condenser-cleaning mobile manipulator using fuzzy wavelet neural network. Fuzzy Sets and Systems , 235, 62–82.
Yanfeng, G., Hua, Z., & Yanhui, Y. (2011). Back-stepping and neural network control of a mobile robot for curved weld seam tracking. Advanced in Control Engineering and Information Science, 15, 38–44.
Yang, J. M., & Kim, J. W. (1999). Sliding mode control for trajectory tracking of nonholonomic wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 15(3), 578–587.
Yao, Q. (2021). Synchronization of second-order chaotic systems with uncertainties and disturbances using fixed-time adaptive sliding mode control. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 142, 1–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruchika, Kumar, N. Force/position Control of Constrained Mobile Manipulators with Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control and Neural Network. J Control Autom Electr Syst 34, 1145–1158 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-023-01032-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-023-01032-2