Abstract
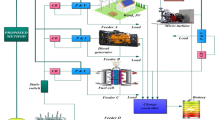
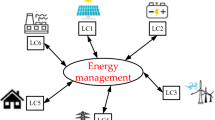
This paper presents an efficient hybrid approach-based energy management strategy for grid-connected microgrid (MG) system. The proposed hybrid technique is the combination of both random forest (RF) and cuttlefish algorithm (CFA) named as RFCFA. The proposed hybrid technique is utilized to decrease the electricity cost and increase the power flow between the source and load side. The MG system is tracked by the RF technique. The CFA is optimized based on the MG with the predicted load demand. MG employs two energy management strategies to reduce the impact of renewable energy prediction errors. The first strategy seeks at minimizing electricity costs during MG’s operation. And the second strategy is aimed at balancing the power flow and reducing forecast error effects. In the grid-connected MG system, the objective function of the proposed technique is characterized with the inclusion of fuel cost, grid power variation, operation and maintenance cost. Battery energy storage systems (BESSs) can stabilize the output power and allow renewable power system units to operate at stable rate of output power. The proposed hybrid technique is executed in the working platform of MATLAB/Simulink, and the execution is evaluated using existing techniques such as GA, CFA and RBFNBBMO.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, N., Miyatake, M., & Al-Othman, A. (2008). Power fluctuations suppression of stand-alone hybrid generation combining solar photovoltaic/wind turbine and fuel cell systems. Energy Conversion and Management,49(10), 2711–2719.
Babaei, M., & Beheshti, M. T. (2018). Demand side management of a stand-alone hybrid power grid by using fuzzy type-2 logic control. In The smart grid conference, Sanandaj, Iran (pp. 1–6).
Bajpai, P., & Dash, V. (2012). Hybrid renewable energy systems for power generation in stand-alone applications: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,16(5), 2926–2939.
Cooper, K., Hanlon, R., & Budelmann, B. (1990). Physiological color change in squid iridophores. Cell and Tissue Research,259(1), 15–24.
Dali, M., Belhadj, J., & Roboam, X. (2010). Hybrid solar–wind system with battery storage operating in grid-connected and standalone mode: Control and energy management—Experimental investigation. Energy,35(6), 2587–2595.
Deshmukh, M., & Deshmukh, S. (2008). Modeling of hybrid renewable energy systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,12(1), 235–249.
Dursun, E., & Kilic, O. (2012). Comparative evaluation of different power management strategies of a stand-alone PV/Wind/PEMFC hybrid power system. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,34(1), 81–89.
Eesa, A. S., Brifcani, A. M. A., & Orman, Z. (2013). Cuttlefish algorithm-a novel bio-inspired optimization algorithm. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research,4(9), 1978–1986.
Elsied, M., Oukaour, A., Gualous, H., & Lo Brutto, O. (2016). Optimal economic and environment operation of micro-grid power systems. Energy Conversion and Management,122, 182–194.
Feczko, E., Balba, N., Miranda-Dominguez, O., Cordova, M., Karalunas, S., Irwin, L., et al. (2018). Subtyping cognitive profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorder using a Functional Random Forest algorithm. NeuroImage,172, 674–688.
Figueiredo, J., & Martins, J. (2010). Energy production system management—Renewable energy power supply integration with building automation system. Energy Conversion and Management,51(6), 1120–1126.
Florey, E. (1969). Ultrastructure and function of cephalopod chromatophores. American Zoologist,9(2), 429–442.
Froesch, D., & Messenger, J. (2009). On leucophores and the chromatic unit of Octopus vulgaris. Journal of Zoology,186(2), 163–173.
Golsorkhi, M., & Lu, D. (2015). A control method for inverter-based islanded microgrids based on V–I droop characteristics. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery,30(3), 1196–1204.
Gu, W., et al. (2014). Modeling, planning and optimal energy management of combined cooling, heating and power microgrid: A review. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,54, 26–37.
Hajizadeh, A., & Golkar, M. (2007). Intelligent power management strategy of hybrid distributed generation system. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,29(10), 783–795.
Hanlon, R. T., & Messenger, J. B. (1996). Cephalopod behaviour. xvi, 232p. Cambridge University Press, 1996. Price £50.00. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom,76(4), 1118.
Hossain, M. A., Pota, H. R., Squartini, S., Zamanand, F., & Muttaqi, K. M. (2019). Energy management of community microgrids considering degradation cost of battery. Journal of Energy Storage,22, 257–269.
Kaundinya, D., Balachandra, P., & Ravindranath, N. (2009). Grid-connected versus stand-alone energy systems for decentralized power—A review of literature. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,13(8), 2041–2050.
Mäthger, L., Denton, E., Marshall, N., & Hanlon, R. (2009). Mechanisms and behavioural functions of structural coloration in cephalopods. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface,6(2), S149–S163.
Moghaddas-Tafreshi, S. M., Mohseni, M., Karami, M. E., & Kelly, S. (2019). Optimal energy management of a grid-connected multiple energy carrier micro-grid. Applied Thermal Engineering,152, 796–806.
Moradi, M., Foroutan, V., & Abedini, M. (2017). Power flow analysis in islanded micro-grids via modeling different operational modes of DGs: A review and a new approach. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,69, 248–262.
Murugaperumal, K., & Raj, P. A. D. V. (2019). Energy storage based MG connected system for optimal management of energy: An ANFMDA technique. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,44(16), 7996–8010.
Najafzadeh, K., & Heydari, H. (2012). New inverter fault current limiting method by considering microgrid control strategy. Advanced Materials Research,463–464, 1647–1653.
Palizban, O., Kauhaniemi, K., & Guerrero, J. (2014). Microgrids in active network management—Part I: Hierarchical control, energy storage, virtual power plants, and market participation. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,36, 428–439.
Pappala, V. S., Wilch, M., Singh, S. N., & Erlich, I. (2007). Reactive power management in offshore wind farms by adaptive PSO. In International conference on intelligent systems applications to power systems, Toki Messe, Niigata, Japan (pp. 1–8).
Pavan Kumar, Y., & Ravikumar, B. (2016). A simple modular multilevel inverter topology for the power quality improvement in renewable energy based green building microgrids. Electric Power Systems Research,140, 147–161.
Pinzon, J. A., Vergara, P. P., Da Silva, L. C., & Rider, M. J. (2017). An MILP model for optimal management of energy consumption and comfort in smart buildings. In IEEE power and energy society innovative smart grid technologies conference, Washington, DC, USA (pp. 1–5).
Prakash, S., & Sinha, S. (2014). Simulation based neuro-fuzzy hybrid intelligent PI control approach in four-area load frequency control of interconnected power system. Applied Soft Computing,23, 152–164.
Praveen Kumar, T., Subrahmanyam, N., & Sydulu, M. (2019). CMBSNN for power flow management of the hybrid renewable energy–storage system-based distribution generation. IETE Technical Review,36(3), 303–314.
Roy, K. (2019). Analysis of power management and cost minimization in MG—A hybrid GOAPSNN technique. International Journal of Numerical Modelling: Electronic Networks, Devices and Fields. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnm.2624.
Roy, K., Mandal, K., & Mandal, A. (2016). Modeling and managing of micro grid connected system using Improved Artificial Bee Colony algorithm. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,75, 50–58.
Roy, K., Mandal, K. K., & Mandal, A. C. (2019). Ant-Lion Optimizer algorithm and recurrent neural network for energy management of micro grid connected system. Energy,167, 402–416.
Sarkar, M. N. I., Meegahapola, L. G., & Datta, M. (2018). Reactive power management in renewable rich power grids: A review of grid-codes, renewable generators, support devices, control strategies and optimization algorithms. IEEE Access,6, 41458–41489.
Sureshkumar, K., & Ponnusamy, V. (2019). Power flow management in micro grid through renewable energy sources using a hybrid modified Dragonfly Algorithm with bat search algorithm. Energy,181, 1166–1178.
Tenfen, D., & Finardi, E. C. (2015). A mixed integer linear programming model for the energy management problem of microgrids. Electric Power Systems Research,122, 19–28.
Thao, N., & Uchida, K. (2016). A control strategy based on fuzzy logic for three-phase grid-connected photovoltaic system with supporting grid-frequency regulation. Journal of Automation and Control Engineering,4(2), 96–103.
The Cephalopod Page. (2019). Octopus, Squid, Cuttlefish, and Nautilus. Thecephalopodpage.org. Retrieved April 28, 2019 from https://www.thecephalopodpage.org/.
Vasquez, J., Guerrero, J., Miret, J., Castilla, M., & Garcia de Vicuna, L. (2010). Hierarchical control of intelligent microgrids. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine,4(4), 23–29.
Yacob, J., Lewis, A. C., Gosling, A., St Hilaire, D. H., Tesar, L., McRae, M., et al. (2011). Principles underlying chromatophore addition during maturation in the European cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Journal of Experimental Biology,214(20), 3423–3432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, N., Mallesham, G. An Efficient Technique-Based Distributed Energy Management for Hybrid MG System: A Hybrid RFCFA Technique. J Control Autom Electr Syst 31, 479–493 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-019-00554-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-019-00554-y