Abstract
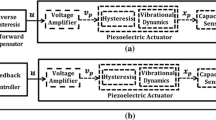
In this manuscript, an adaptive control strategy is presented for piezoactuators with hysteresis and disturbance estimation. The adaptive control scheme learns the piezoelectric actuator’s inverse model with a Lyapunov-based adaptation law. Then, an adaptive estimator is used in a feedback loop to estimate hysteresis and disturbance. Therefore, the controller achieves accurate displacement tracking with hysteresis/disturbance uncertainties. Unlike many controllers, the proposed adaptive control scheme’s stability is guaranteed by Lyapunov direct method. The proposed controller’s performance in coping with hysteresis and disturbance is highlighted in different operating conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang, W., Khosla, P., & Riviere, C. (2007). Feedforward controller with inverse rate-dependent model for piezoelectric actuators in trajectory-tracking applications. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 12(2), 134–142.
Badel, A., Qiu, J., & Nakano, T. (2008). A new simple asymmetric hysteresis operator and its application to inverse control of piezoelectric actuators. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control Society, 55(5), 1086–1094.
Bashash, S., & Jalili, N. (2009). Robust adaptive control of coupled parallel piezo-flexural nanopositioning stages. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 14(1), 11–20.
Chaoui, H., & Sicard, P. (2011). Adaptive displacement tracking control of piezo-actuated manipulation mechanisms with hysteresis and disturbance. In IEEE international workshop on robotic and sensors environments.
Chaoui, H., Sicard, P., & Sawan, M. (2010). High precision ann-based adaptive displacement tracking of piezoelectric actuators for MEMS. In IEEE circuits and systems international conference
Devasia, S., Eleftheriou, E., & Moheimani, S. (2007). A survey of control issues in nanopositioning. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 15(5), 802–823.
Freeman, R. A., & Kokotovic, P. V. (1996). Lyapunov design. The Control Handbook, 77, 932–940.
Gu, G. Y., Zhu, L. M., & Su, C. Y. (2014). Modeling and compensation of asymmetric hysteresis nonlinearity for piezoceramic actuators with a modified prandtlishlinskii model. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 61(3), 1583–1595.
Huang, S., Tan, K. K., & Lee, T. H. (2009). Adaptive sliding-mode control of piezoelectric actuators. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 56(9), 3514–3522.
Kongthon, J., & Devasia, S. (2013). Iterative control of piezoactuator for evaluating biomimetic, cilia-based micromixing. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 18(3), 944–953.
Leang, K., Zou, Q., & Devasia, S. (2009). Feedforward control of piezoactuators in atomic force microscope systems. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 29(1), 70–82.
Liaw, H. C., Shirinzadeh, B., & Smith, J. (2009). Robust neural network motion tracking control of piezoelectric actuation systems for micro/nanomanipulation. IEEE Transaction on Neural Networks, 20(2), 356–367.
Li, Z., Su, C. Y., & Chai, T. (2014). Compensation of hysteresis nonlinearity in magnetostrictive actuators with inverse multiplicative structure for preisach model. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 11(2), 613–619.
Qin, Y., Tian, Y., Zhang, D., Shirinzadeh, B., & Fatikow, S. (2013). A novel direct inverse modeling approach for hysteresis compensation of piezoelectric actuator in feedforward applications. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 18(3), 981–989.
Rakotondrabe, M., Clevy, C., & Lutz, P. (2010). Complete open loop control of hysteretic, creeped, and oscillating piezoelectric cantilevers. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 7(3), 440–450.
Shieh, H. J., & Hsu, C. H. (2008). An adaptive approximator-based backstepping control approach for piezoactuator-driven stages. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 55(4), 1729–1738.
Xu, Q. (2013). Identification and compensation of piezoelectric hysteresis without modeling hysteresis inverse. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(9), 3927–3937.
Yi, J., Chang, S., & Shen, Y. (2009). Disturbance-observer-based hysteresis compensation for piezoelectric actuators. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 14(4), 456–464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaoui, H., Gualous, H. Adaptive Control of Piezoelectric Actuators with Hysteresis and Disturbance Compensation. J Control Autom Electr Syst 27, 579–586 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0270-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0270-2