Abstract
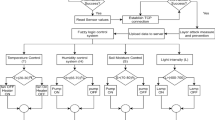
There is an increasing tendency of industrial sensors becoming intelligent devices when they incorporate additional functions to their primary task of measuring. The embedded systems follow the tendency to use computational intelligence tools in an embedded way in machines, sensors, and actuators, making them intelligent. There are several works in the field of embedded systems, sensors, and pure or hybrid intelligent systems; however, few unite these fields into one single project. This work shows a Takagi Hayashi Fuzzy Neural system for embedding in industrial sensors, making them intelligent devices with the function of automatically detecting calibration errors and self-compensating in operation. The system was tested with data from actual sensors, and the results were analyzed with regard to the speed of execution, frequency of data input in the system, and the number of logic elements used. The results obtained showed that embedding the proposed system in industrial sensors is viable for making intelligent devices. The system proposed was able to self-compensate for errors caused by sensor decalibration and to identify the moment to perform a new calibration after the advanced deterioration of the sensor. The software Quartus II\(^\circledR \), from Altera\(^\circledR \), was used to develop the project, perform the simulation, and analyze the results.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellis, S., Razeeb, K., Saha, C., Delaney, K., Mathuna, C., Pounds-Cornish, A., de Souza, G., Colley, M., Hagras, H., Clarke, G., Callaghan, V., Argyropoulos, C., Karistianos, C. & Nikiforidis, G. (2004). FPGA implementation of spiking neural networks—an initial step towards building tangible collaborative autonomous agents. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Field Programmable Technology pp. 449–452.
Chakra, S. A., & Huyart, B. (2004). Auto calibration with training sequences for wireless local loop at 26 GHz. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 14(8), 392–394.
Clemons, T. M, I. I. I., Chang, K. C. C., & George, M. (2012). Sensor calibration using in-situ celestial observations to estimate bias in space-based missile tracking. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 48(2), 1403–1427.
Ding, W., Hayashi, R., Suehiro, J., Zhou, G., Imasaka, K., & Hara, M. (2006). Calibration methods of carbon nanotube gas sensor for partial discharge detection in SF/sub 6/. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 13(2), 353–361.
Goh, C. Z. D., Georgiou, P., Constandinou, T. G., Prodromakis, T., & Toumazou, C. (2011). A CMOS-based ISFET chemical imager with auto-calibration capability. IEEE Sensors Journal, 11(12), 3253–3260.
Gubian, M., Marconato, A., Boni, A., & Petri, D. (2009). A study on uncertainty-complexity tradeoffs for dynamic nonlinear sensor compensation. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 58(1), 26–32.
Guély, F., Siarry, P. (1993). Gradient descent method for optimization various fuzzy rules. In Proceedings of Second IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems pp. 1241–1246.
Hayashi, I., Nomura, H., Yamasaki, H., & Wakami, N. (1992). Contruction of inference rules by NDF and NDFL. International Journing of Approximating Reasoning, 6, 241–266.
Haykin, S. (1999). Neural networks: A comprehensive foundation (2nd ed.). Hamilton: Prentice-Hall.
Hichihashi, H., Miyoshi, T., Nagasaka, K. (1993). Computed tomography by neuro-fuzzy inversion. Proceedings 1993 Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Part 1 (of 3), Nagoya, pp. 709–712.
Holt, J., & Hwang, J. N. (1993). Finite precision error analysis of neural network hardware implementations. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 42(3), 281–290.
Hurdle, J. F. (1997). The synthesis of compact fuzzy neural circuits. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 5(1), 44–55.
Jang, J. S., & Sun, C. T. (1995). Neuro-fuzzy modeling and control. Proceedings of the IEEE, 83(3), 378–406.
Jeronymo, D. C., Borges, Y. C. C., & Coelho, L. S. (2011). A calibration approach based on Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy inference system for digital electronic compasses. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(11), 13688–13693.
Juang, C., & Tsao, Y. (2008). A type-2 self-organizing neural fuzzy system and its FPGA implementation. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 38(6), 1537–1548.
Juang, C. F., Chiu, S. H., & Chang, S. W. (2007). A self-organizing TS-type fuzzy network with support vector learning and its application to classification problems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 15(5), 998–1008.
Krips, M., Lammert, T., Kummert A. (2002). FPGA implementation of a neural network for a real-time hand tracking system. Proceedings of First IEEE International Workshop on Electronic Design Test and Applications, pp. 313–317.
Lee, S. T., Fang, S. J. J., Allstot, D. J., Bellaouar, A. L., Fridi, A. R., & Fontaine, P. A. (2004). A quad-band GSM-GPRS transmitter with digital auto-calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(12), 2200–2214.
Li, H. X., & Liu, Z. (2008). A probabilistic neural-fuzzy learning system for stochastic modeling. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 16(4), 898–908.
Li, H., Zhang, D., & Foo, S. (2006). A stochastic digital implementation of a neural network controller for small wind turbine systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 21(5), 1502–1507.
Lopez-Garcia J., Moreno-Armendariz M., Riera-Babures J., Balsi M., Vilasis-Cardona X. (2005) Real time vision by FPGA implemented CNNs. Proceedings of the 2005 European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (vol. 1) pp. 281–284.
Misha, J. & Saha, I. (2010). Artificial neural networks in Hardware: A survey of two decades of progress. Neurocomputing, 74, 239–255.
Nomura, H., Hayashi, I., & Wakami, N. (1994). A self-tunning method of fuzzy reasoning by genetic algorithms. In A. Candel & G. Langholz (Eds.), Fuzzy Control Systems (pp. 338–354). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Parkinson, S., Longstaff, A. P., Fletcher, S., Crampton, A., & Gregory, P. (2012). Automatic planning for machine tool calibration: A case study. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(13), 11367–11377.
Patra, J. C., Juhola, M., & Meher, P. K. (2008). Intelligent sensors using computationally efficient Chebyshev neural networks. IET Science Measurement and Technology, 2(2), 68–75.
Pereira, D. R. V., Cagni Júnior, E., Melo, J. D., & Dória Neto, A. D. (2005). The implementation of the self-calibration, self-compensation and self-validation algorithms for foundation Fieldbus sensors are resented using standard function blocks. IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and Applications pp. 220–225.
Pereira, J. M. D., Postolache, O. A., & Girão, P. M. B. S. (2005). Adaptive self-calibration algorithm for smart sensors linearization. Instrumentation and measurement technology conference, 2005. IMTC 2005. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1, 648–652.
Prado, R. N. A., Melo, J. D., Oliveira, J. A. N., Dória Neto, A. D. (2012). FPGA based implementation of a fuzzy neural network modular architecture for embedded systems. WCCI 2012 IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence pp. 610–616.
Ramakrishnan, N., Ertin, E., & Moses, R. L. (2011). Gossip-based algorithm for joint signature estimation and node calibration in sensor networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 5(4), 665–673.
Shin, J., & Shin, H. (2012). A 1.9–3.8 GHz fractional-N PLL frequency synthesizer with fast auto-calibration of loop bandwidth and VCO frequency. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(3), 665–675.
Simões, M. G., & Shaw, I. S. (2007). Controle e Modelagem fuzzy (2nd ed.). Sao Paulo: Editora Blucher, FAPESP.
Terano, T., Asai, K., & Sugeno, M. (1994). Applied fuzzy systems. Boston: Academic Press.
Togai, M., & Watanabe, H. (1986). Expert system on a chip: An engine for real-time approximate reasoning. IEEE Expert, 1(3), 55–62.
Tsoukalas, L. H., & Uhrig, R. E. (1997). Fuzzy and neural approaches in engineering. New York: Wiley Interscience Publications.
Viberg, M., & Swindlehurst, L. L. (1994). A Bayesian approach to auto-calibration for parametric array signal processing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 42(12), 3495–3507.
Wang, D., & Terman, D. (1997). Image segmentation based on oscillatory correlation. Neural Computation, 9(4), 805–836.
Wang, W. Y., & Li, Y. H. (2003). Evolutionary learning of BMF fuzzy-neural networks using a reduced-form genetic algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 33(6), 808–816.
Weeks, M., Freeman, M., Moulds, A., & Austin, J. (2005). Developing hardware-based applications using PRESENCE-2. Perspectives in pervasive computing (pp. 469–474). London: Savoy Place.
Whang, L. X. (1994). Adaptative fuzzy system and control. Englewood Clifs: Prentice Hall.
Wu, A., & Tam, P. K. S. (2000). A fuzzy neural network based on fuzzy hierarchy error approach. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 8(6), 966–976.
Yamakawa, T., & Miki, T. (1986). The current mode fuzzy logic integrated circuits fabricated by the standard CMOS process. IEEE Transactions on Computers, C–35(2), 161–167.
Yang, F., & Paindavoine, M. (2003). Implementation of an RBF neural network on embedded systems: real-time face tracking and identity verification. IEEE Transaction on Neural Networks, 14(5), 1162–1175.
Zavalla, A. H., & Camacho Nieto, O. (2012). Fuzzy hardware: A retrospective and analysis. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 20(4), 623–635.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prado, R.N.A., Oliveira, J.A.N., Melo, J.D. et al. Takagi Hayashi Fuzzy Neural System in Hardware: An Application For Embedding in Industrial Sensors, Making them Intelligent. J Control Autom Electr Syst 25, 585–596 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-014-0131-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-014-0131-9